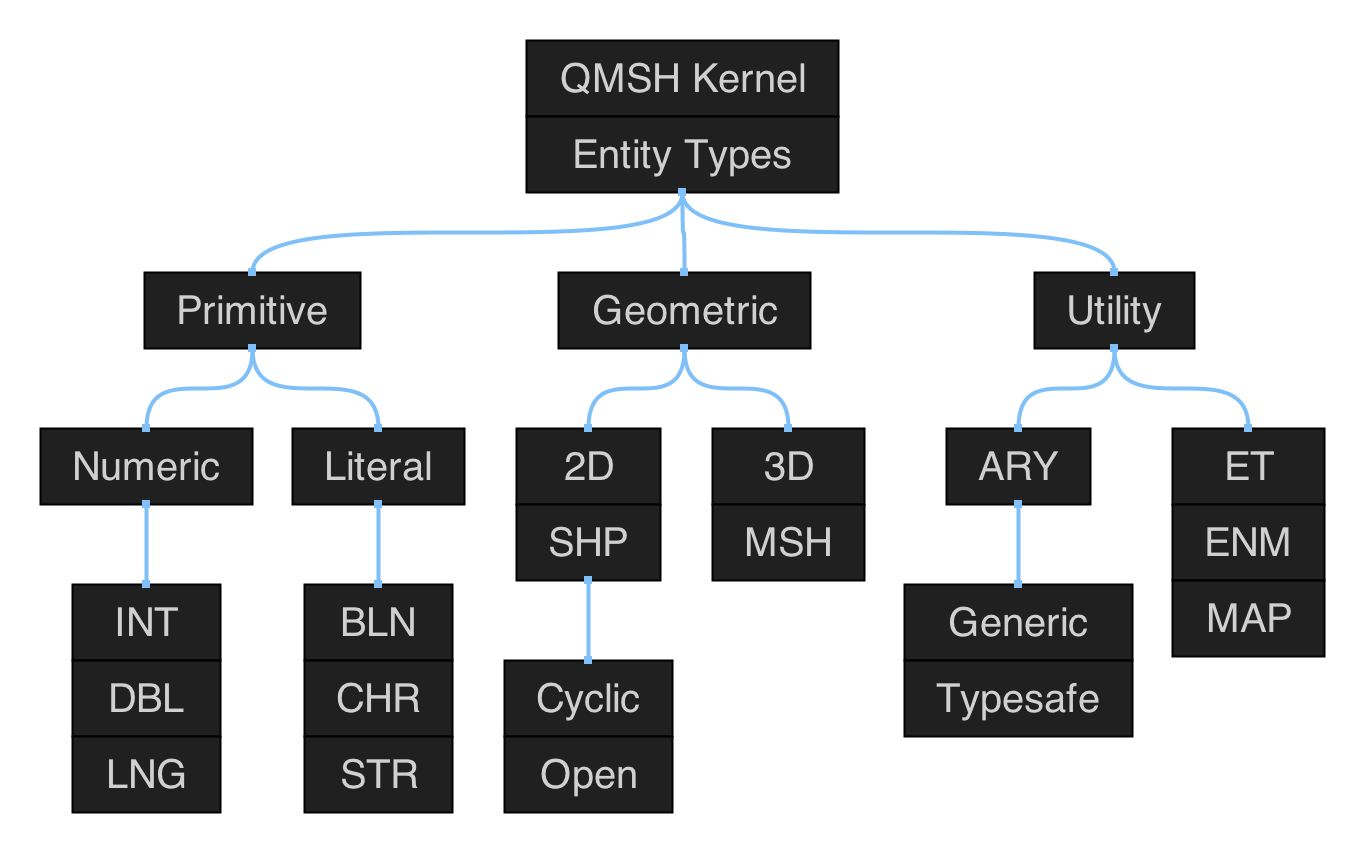
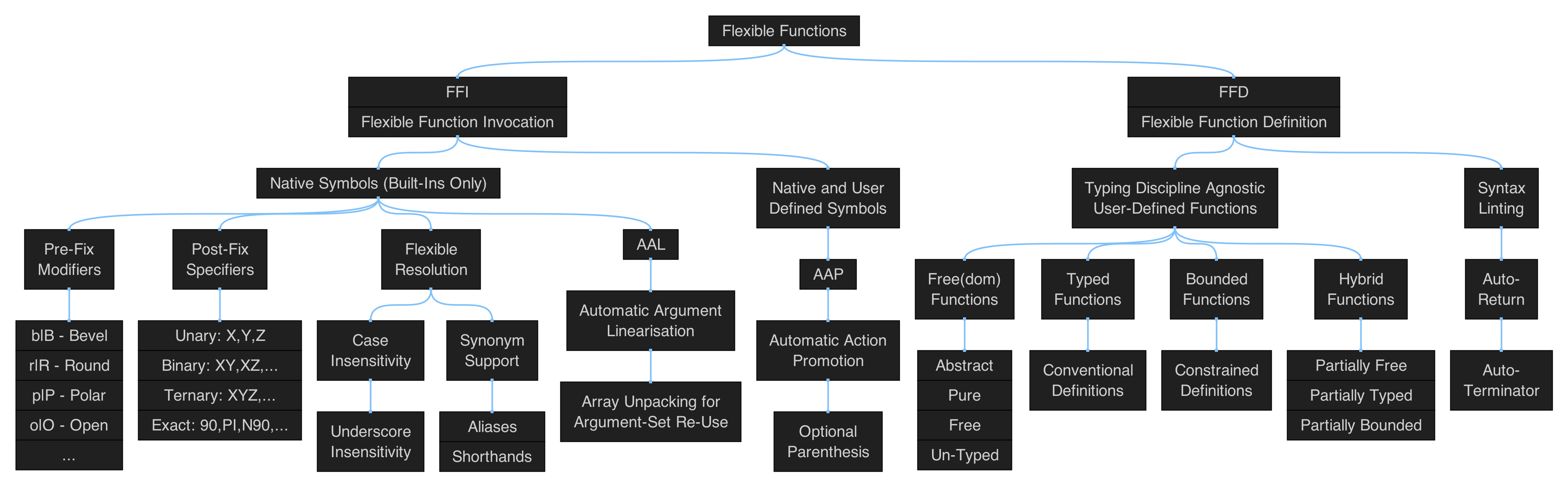
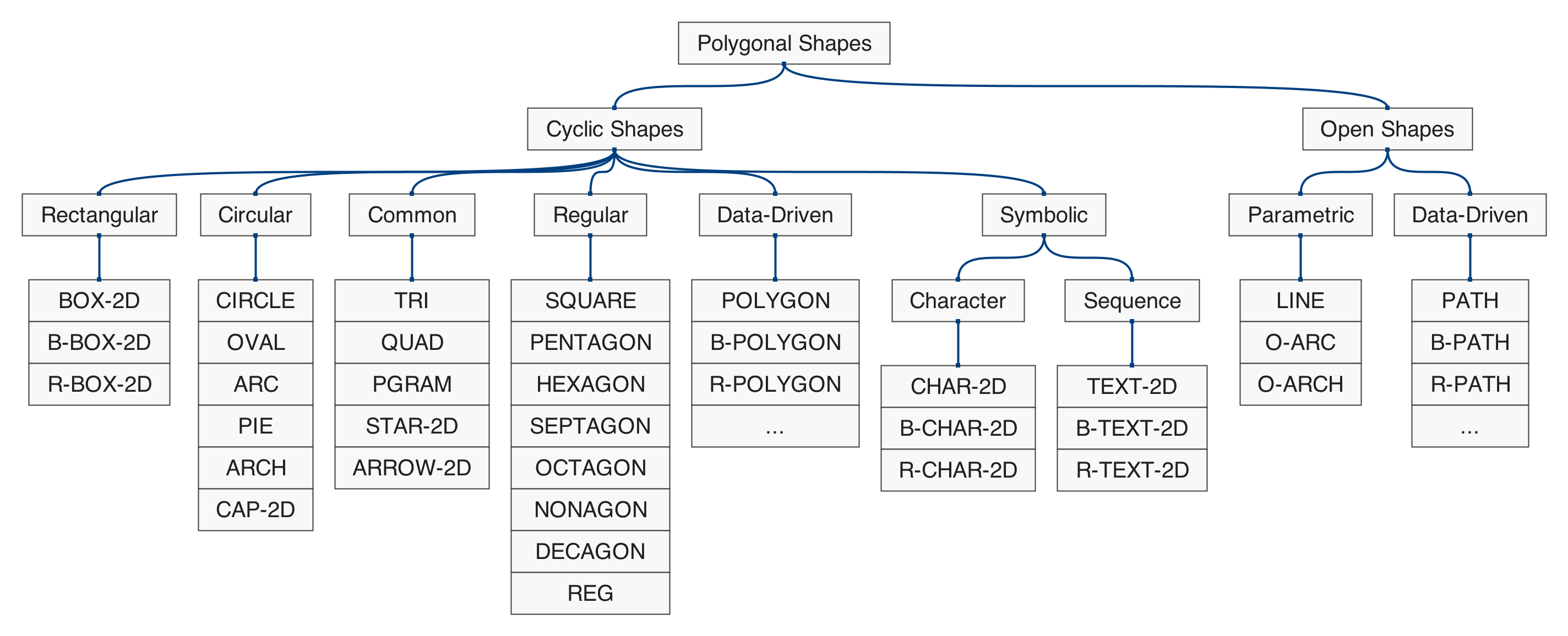
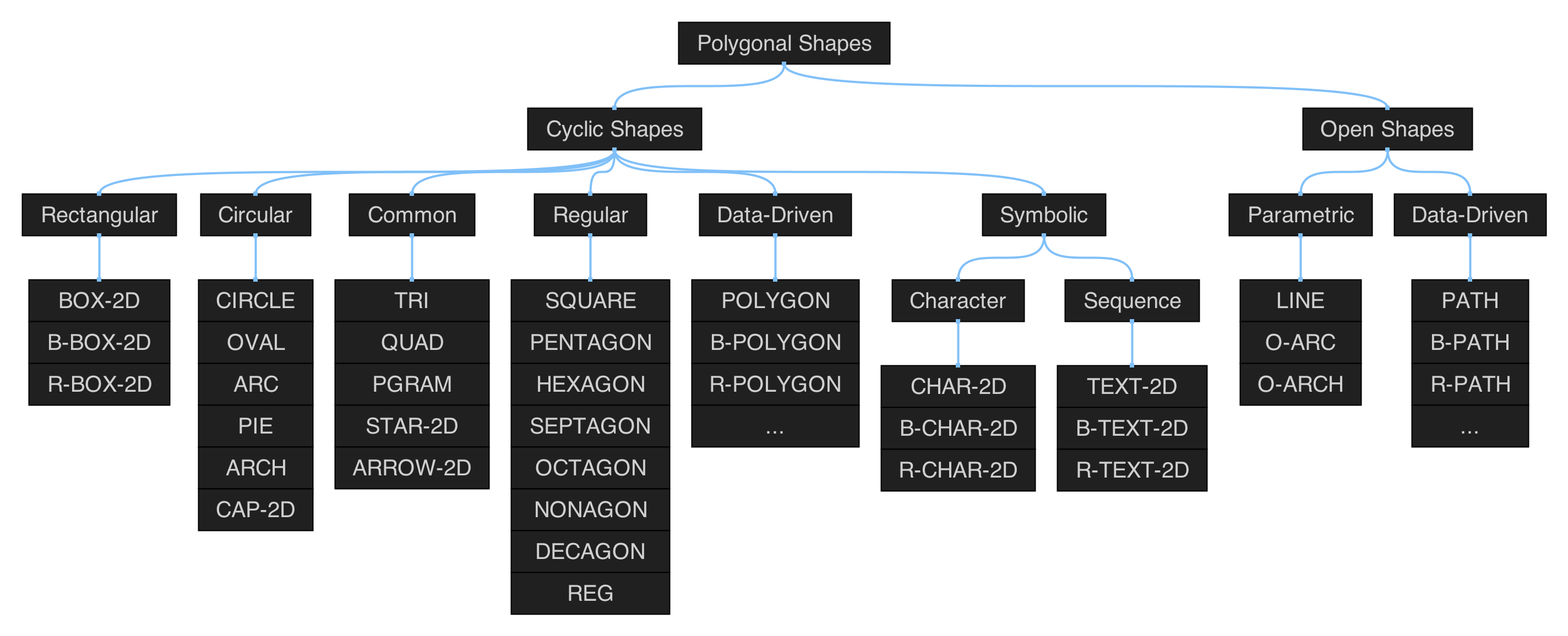
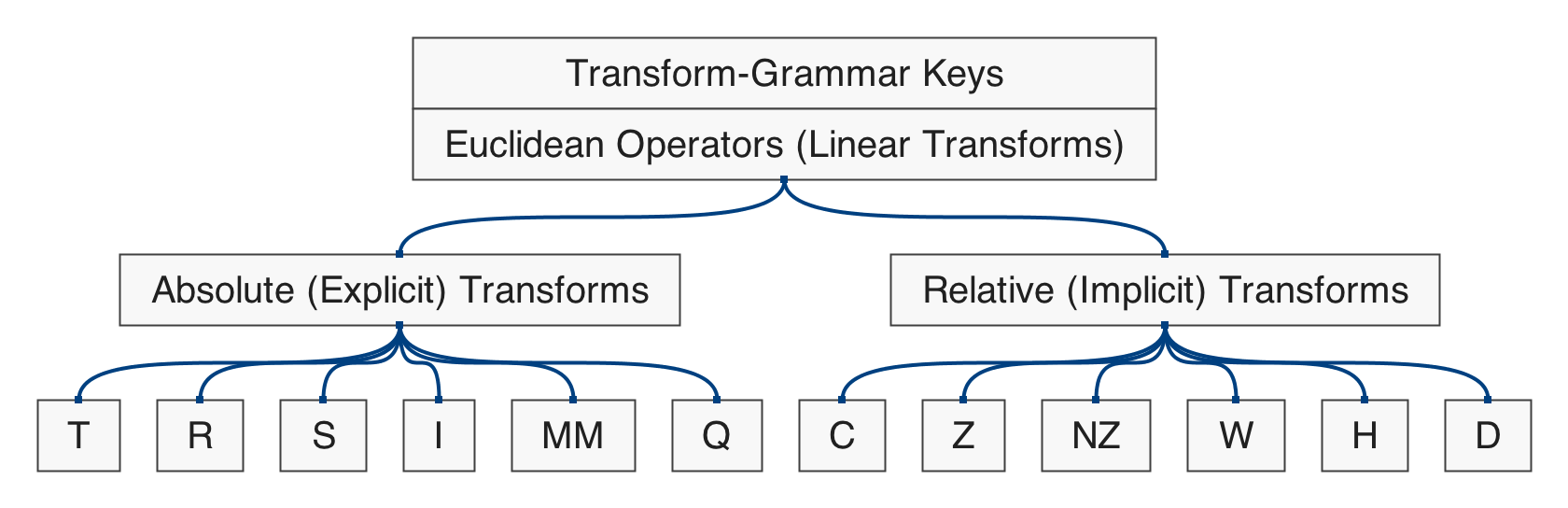
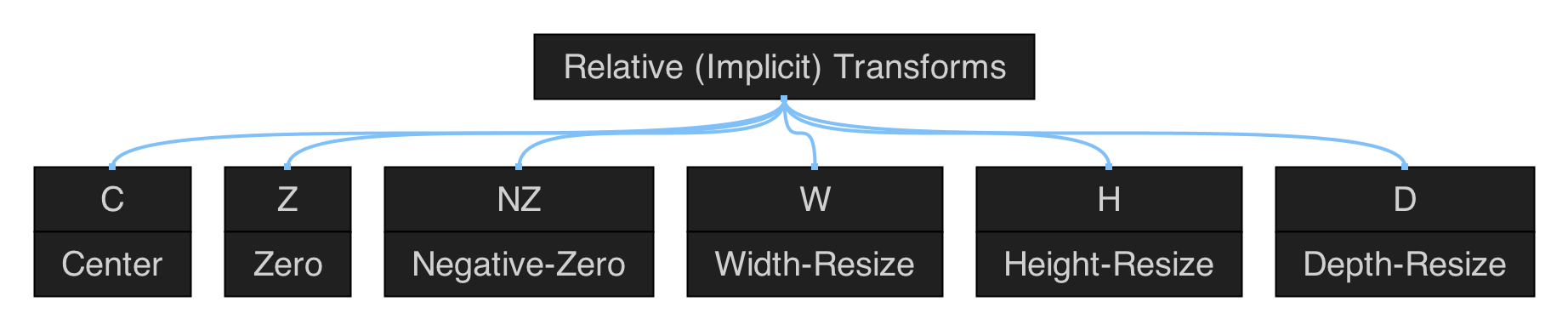
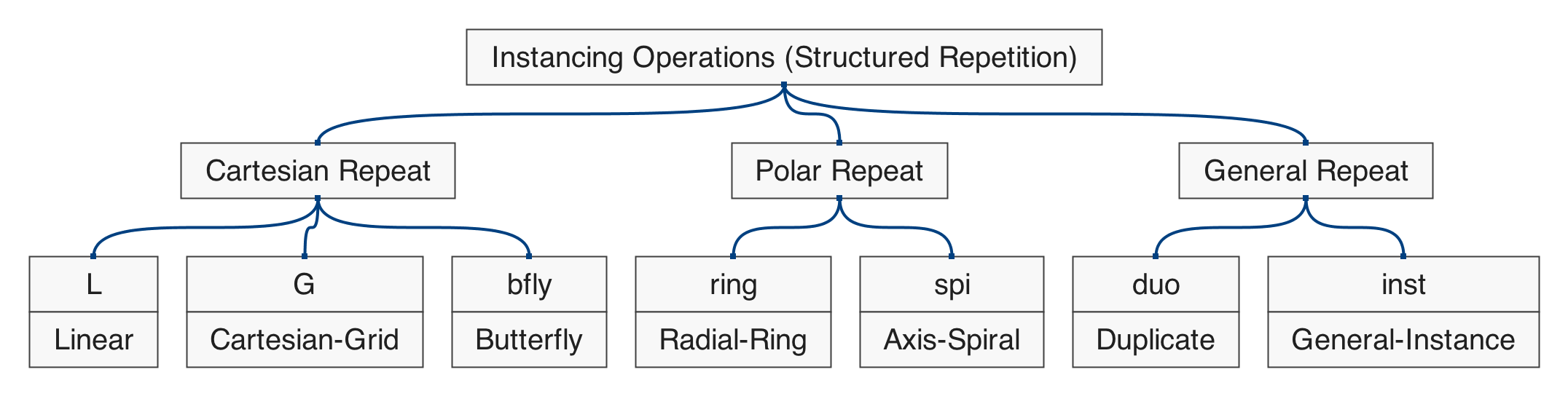
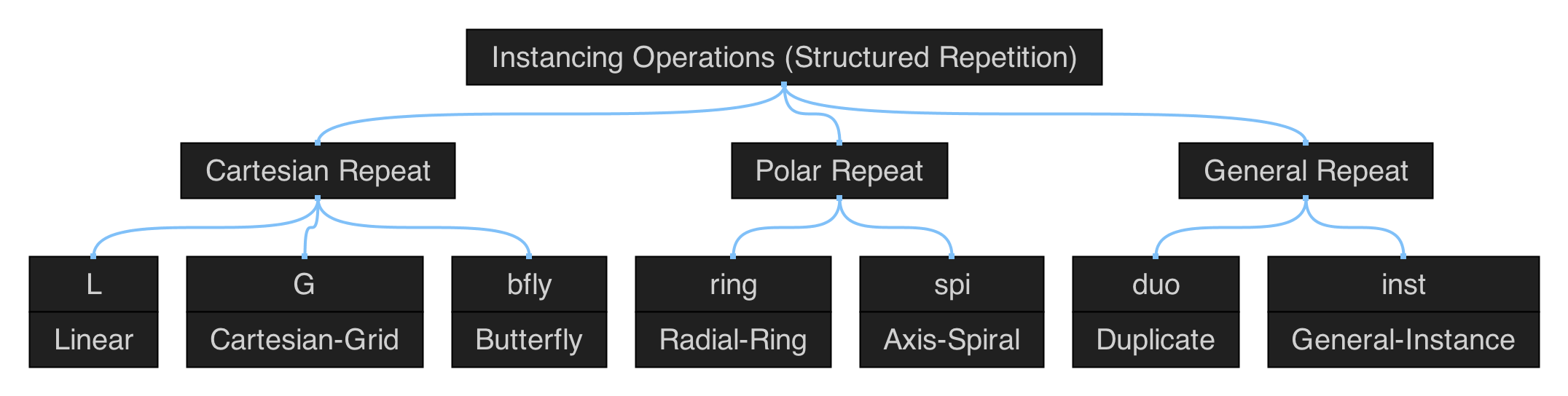
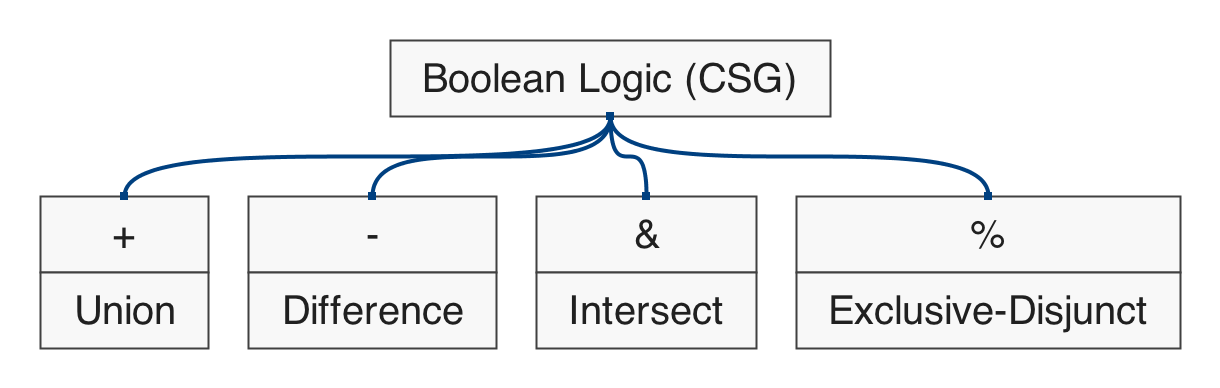
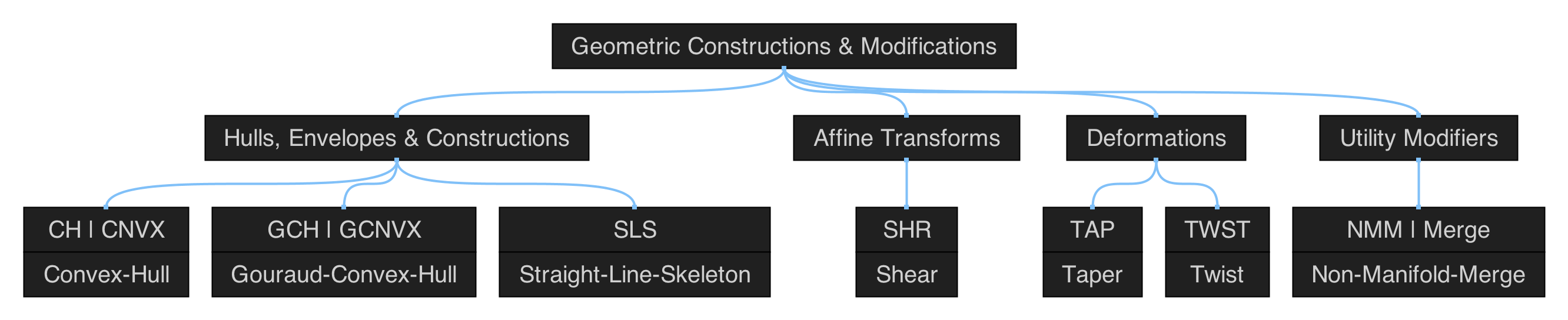
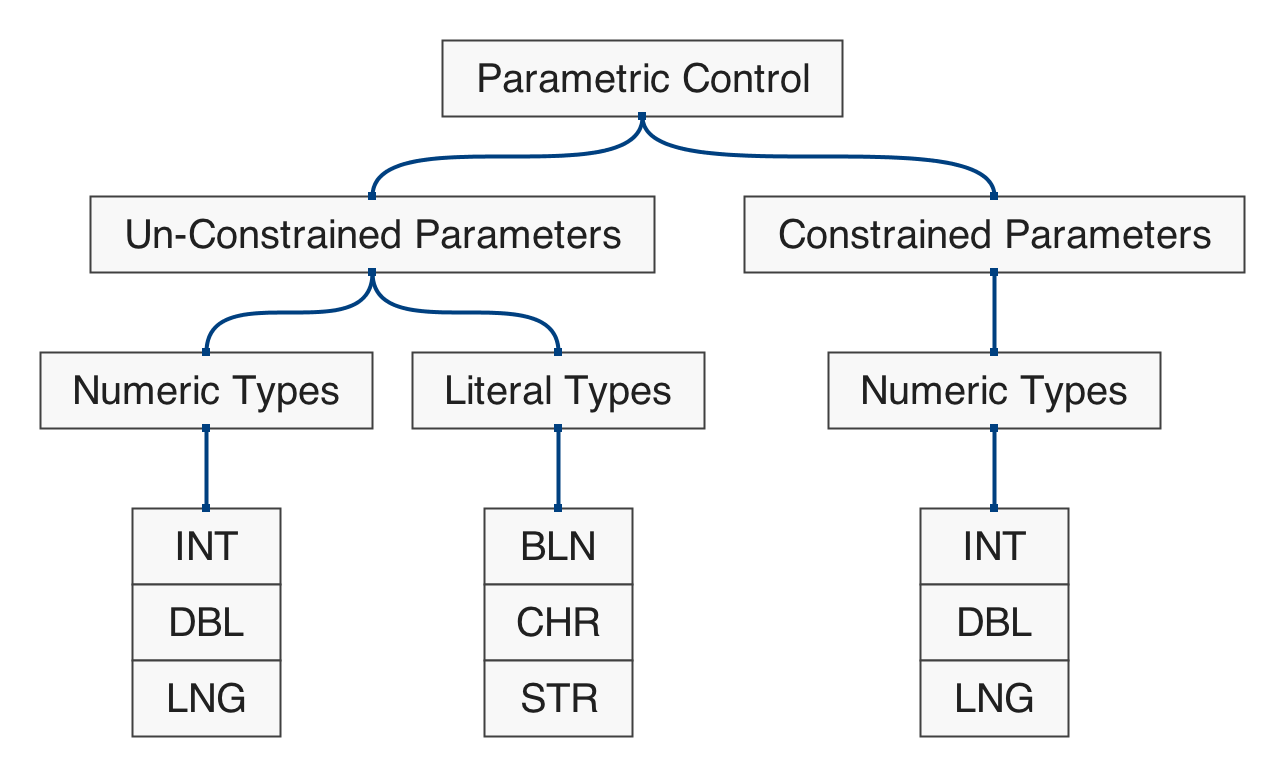
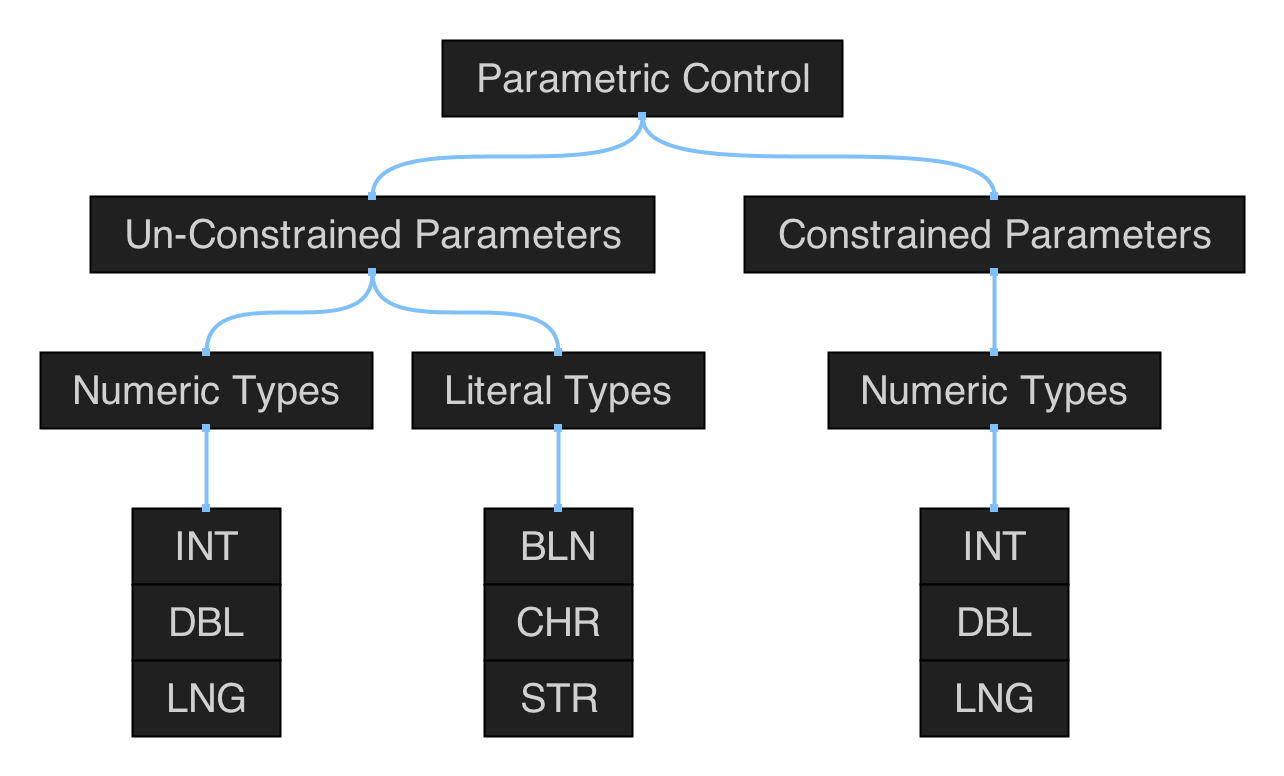
Polygonal Shapes
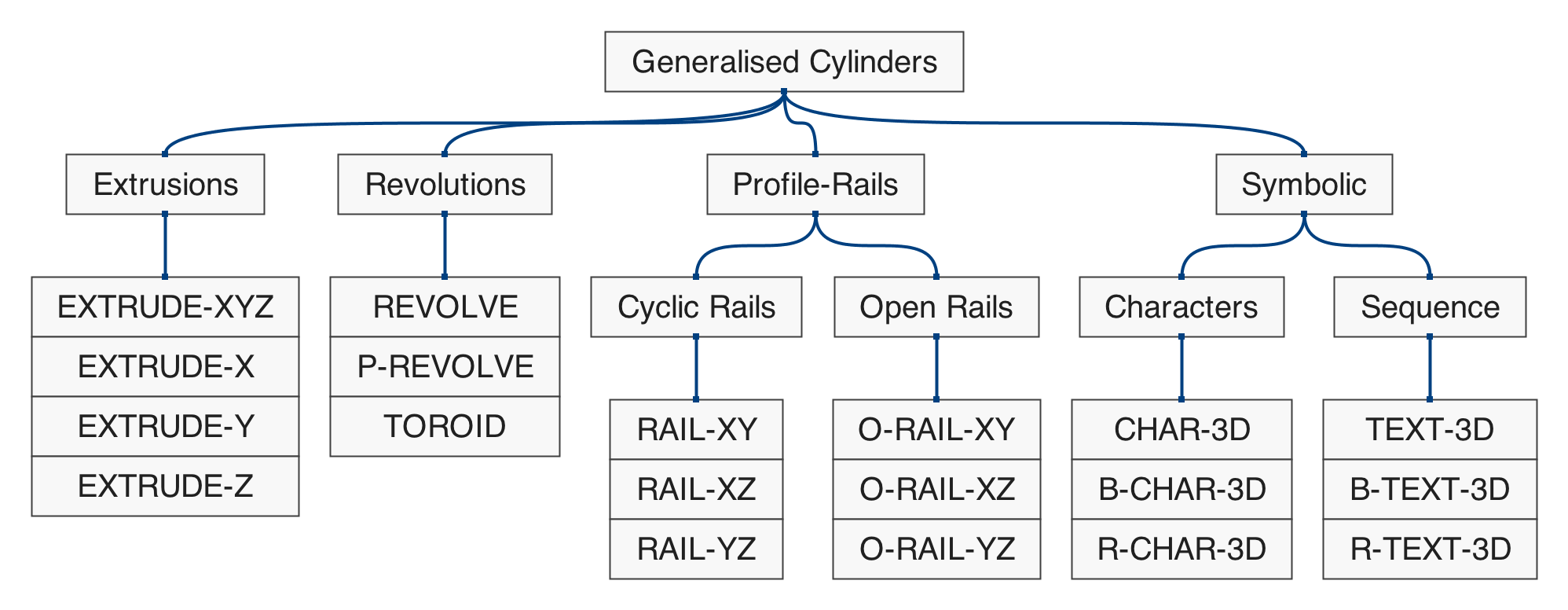
Figure 5.1: hierarchical map of the set of functions in qmsh for creating abstract polygonal shapes.
BOX-2D : Generate 2D Rectangle
→ 'instantiates an axis-aligned 2D rectangular polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, orthogonal, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { box, box_2D, rect, rectangle, rect_2D, rectangle_2D };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 box ( D size )prefix G2 box ( D width, D height )prefix G2 box ( D x, D y, D width, D height )Input Arguments:•
D x :
default = width * -0.5 : the minimum x-axis position of the box - a positive or negative decimal.•
D y :
default = height * -0.5 : the minimum y-axis position of the box - a positive or negative decimal.•
D width :
default = 1.0 : the width of the box - or its extent/span along the x-axis - a positive decimal greater than zero.•
D height :
default = 1.0 : the height of the box - or its extent/span along the y-axis - a positive decimal greater than zero.•
D size :
default = 1.0 : a uniform scale factor used to construct the box - a positive decimal greater than zero.→ [ width, height, size ] > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 4Practical Examples:return box();
// returns the default zero-argument unit box
return box(2);
// returns a uniform box, origin-centered and with a width and height of 2 units
return box(5,1.25);
// returns a non-uniform rectangular box, origin centered - with a width and height of (respectively) 5 and 1.25 units
return box(-1,-1,0.25,0.5);
// returns a non-uniform rectangular box, with minimum position equal to [-1,-1], a width of 0.25 units and a height of 0.5 units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: b-box-2D, r-box-2D B-BOX-2D : Generate 2D Beveled-Rectangle
→ 'instantiates a beveled-corner 2D rectangular polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_box, b_box_2D, b_rect, b_rectangle, b_rect_2D, b_rectangle_2D, bevel_box, bevel_box_2D, bevel_rect, bevel_rectangle, bevel_rect_2D, bevel_rectangle_2D, ... (+24) };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 bbox ( D bevel )prefix G2 bbox ( D size, D bevel )prefix G2 bbox ( D width, D height, D bevel )prefix G2 bbox ( D x, D y, D width, D height, D bevel )prefix G2 bbox ( D width, D height, D bvl_lb, D bvl_lt, D bvl_rt, D bvl_rb )prefix G2 bbox ( D x, D y, D width, D height, D bvl_lb, D bvl_lt, D bvl_rt, D bvl_rb )Input Arguments:•
D x :
default = width * -0.5 : the minimum x-axis position of the bbox - a positive or negative decimal.•
D y :
default = height * -0.5 : the minimum y-axis position of the bbox - a positive or negative decimal.•
D width :
default = 1.0 : the width of the bbox - or its extent/span along the x-axis - a positive decimal greater than zero.•
D height :
default = 1.0 : the height of the box - or its extent/span along the y-axis - a positive decimal greater than zero.•
D bevel :
default = 0.125 : the beveling/chamfering distance/radius to apply to the corners of the bbox - a positive decimal - greater than zero and less than the mimimum of the bbox's width, height or uniform size divided by two.•
D size :
default = 1.0 : the uniform scale factor used to construct the bbox - a positive decimal greater than zero.•
D bvl_lb :
default = 0.125 : the left-base corner bevel/chamfer distance•
D bvl_lt :
default = 0.125 : the left-top corner bevel/chamfer distance•
D bvl_rt :
default = 0.125 : the right-top corner bevel/chamfer distance•
D bvl_rb :
default = 0.125 : the right-base corner bevel/chamfer distance→ [ width, height, size, bevel ] > 0
→ [ width, height, size ] > ( bevel * 2 )
→ [ bvl_lb, bvl_lt, bvl_rt, bvl_rb ] > 0
→ [ bvl_lb, bvl_lt, bvl_rt, bvl_rb ] < [ width, height, size ]
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 8Practical Examples:return bbox();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bbox
return bbox(0.25);
// returns a unit-size bbox with a bevel of 0.25 units applied to its corners
return bbox2D(2,1,0.05);
// returns a rectangular bbox with a width of 2 units, a height of 1 unit and a bevel distance of 0.05 units
return bbox(-1,-1,0.25,0.5,0.0125);
// returns a rectangular bbox with minimum position [-1,-1], a width and height of 0.25 and 5 and a bevel of 0.0125 units applied to each corner
a = { 1,2,3,4 };
return bbox(10,10,a);
// returns a non-uniformly-chamfered (i.e. a varying-bevel) bbox shape using AAL with a generic array to represent the bevel-distances for each corner
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
+
[ box | box_2D | rect | rectangle | rect_2D | rectangle_2D ] R-BOX-2D : Generate 2D Rounded-Rectangle
→ 'instantiates a rounded-corner 2D rectangular polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_box, r_box_2D, r_rect, r_rectangle, r_rect_2D, r_rectangle_2D, rnd_box, rnd_box_2D, rnd_rect, rnd_rectangle, rnd_rect_2D, rnd_rectangle_2D, ... (+12) };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 rbox ( D radius, I steps )prefix G2 rbox ( D size, D radius, I steps )prefix G2 rbox ( D width, D height, D radius, I steps )prefix G2 rbox ( D x, D y, D width, D height, D radius, I steps )prefix G2 rbox ( D width, D height, D rad_lb, D rad_lt, D rad_rt, D rad_rb, I stp_lb, I stp_lt, I stp_rt, I stp_rb )prefix G2 rbox ( D x, D y, D width, D height, D rad_lb, D rad_lt, D rad_rt, D rad_rb, I stp_lb, I stp_lt, I stp_rt, I stp_rb )Input Arguments:•
D x :
default = width * -0.5 : the minimum x-axis position of the rbox - a positive or negative decimal.•
D y :
default = height * -0.5 : the minimum y-axis position of the rbox - a positive or negative decimal.•
D width :
default = 1.0 : the width of the rbox - or its extent/span along the x-axis - a positive or decimal greater than zero.•
D height :
default = 1.0 : the height of the rbox - or its extent/span along the y-axis - a positive or decimal greater than zero.•
D radius :
default = 0.125 : the rounding radius to apply to the corners of the rbox - a positive decimal greater than zero and less than the minimum of the rbox's width, height or uniform size dividded by two.•
I steps :
default = 8 : the nubmer of rounding discretisation steps to apply to the corners of the rbox - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
D size :
default = 1.0 : the uniform scale factor used to construct the rbox - a positive decimal greater than zero.•
D rad_lb :
default = 0.125 : the left-base corner rounding radius•
D rad_lt :
default = 0.125 : the left-top corner rounding radius•
D rad_rt :
default = 0.125 : the right-top corner rounding radius•
D rad_rb :
default = 0.125 : the right-base corner rounding radius•
I stp_lb :
default = 0.125 : the left-base corner round steps•
I stp_lt :
default = 0.125 : the left-top corner round steps•
I stp_rt :
default = 0.125 : the right-top corner round stpes•
I stp_rb :
default = 0.125 : the right-base corner round steps→ [ width, height, size, radius ] > 0
→ steps >= 1
→ [ width, height, size ] > ( radius * 2 )
→ [ rnd_lb, rnd_lt, rnd_rt, rnd_rb ] > 0
→ [ rnd_lb, rnd_lt, rnd_rt, rnd_rb ] < [ width, height, size ]
→ [ stp_lb, stp_lt, stp_rt, stp_rb ] >= 1
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( steps + 1 ) * 4 )Practical Examples:return rbox();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rbox
return rbox(0.25,4);
// returns a unit-size rbox with a rounding radius of 0.25 units applied to its corners - with 4 discretisation steps per corner
return rbox(5,0.25,1);
// returns a uniform rbox with a width and height of 5 units, a round radius of 0.25 units and a single discretisation step applied per corner
return rbox2D(2,1,0.05,16);
// returns a rectangular rbox with a width of 2 units, a height of 1 unit, a round radius of 0.05 units and 16 steps per corner
return rbox(-1,-1,0.25,0.5,0.0125,8);
// returns a rectangular rbox with minimum position [-1,-1], a width and height of 0.25 and 5, a radius of 0.0125 units applied to each corner and 8 steps per corner
a = { 1,2,3,4 };
return rbox(10,10,a,a);
// returns a non-uniformly-rounded (i.e. varying-radii) rbox shape using AAL with a generic array to recycle arguments for both the radius and the discretisation-step components of each corner
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
+
[ box | box_2D | rect | rectangle | rect_2D | rectangle_2D ] CIRCLE : Generate 2D Circle
→ 'instantiates a 2D circular polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { circle };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 circle ( D radius )prefix G2 circle ( D radius, I segments )prefix G2 circle ( D ox, D oy, D radius, I segments )Input Arguments:•
D ox :
default = 0 : the x-axis central position of the circle - the origin x component.•
D oy :
default = 0 : the y-axis central position of the circle - the origin y component.•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the circle - a positive non-zero decimal.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of discretisation steps used to construct the circle - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.→ radius > 0
→ segments >= 3
Vertex Count:→ |V| = segmentsPractical Examples:return circle();
// returns the default zero-argument unit circle
return circle(2);
// returns a circle centered at the origin with a radius of 2 units (i.e. a diameter of 4 units) and the default (32) discretisation steps
return circle(0.5,8);
// returns a circle centered at the origin with a radius of 0.5 units (diameter 1 unit) and 8 discretisation steps
return circle(-1,-1,3,16);
// returns an offset circle (centered at [-1,-1]) with a radius of 3 units (diameter 6 units) and 16 discreisation steps
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: arc, oval, arch, cap-2D OVAL : Generate 2D Oval
→ 'instantiates a 2D elliptic (non-uniformly scaled circle) polygonal shape defined by an axis-aligned box'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { oval, ellipse };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 oval ( D width, D height )prefix G2 oval ( D width, D height, I segments )prefix G2 oval ( D x, D y, D width, D height, I segments )Input Arguments:•
D x :
default = width * -0.5 : the minimum x-axis position of an axis-aligned bounding-box used to define the oval.•
D y :
default = height * -0.5 : the minimum y-axis position of an axis-aligned bounding-box used to the oval.•
D width :
default = 1.0 : the width of the oval - or the extent of its defining axis-aligned bounding-box along the x-axis - a positive non-zero decimal.•
D height :
default = 0.5 : the height of the oval - or the extent of its defining axis-aligned bounding-box along the y-axis - a positive non-zero decimal.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of discreisation steps used to construct the oval - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.→ [ width, height ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
Vertex Count:→ |V| = segmentsPractical Examples:return oval();
// returns the default zero-argument unit oval
return oval(3,1);
// returns an oval centered at the origin with a width of 3 units, height equal to 1 unit and the default (32) circular steps
return oval(5,20,4);
// returns an oval centered at the origin with a width and height of 5 and 20 units and 4 circular steps
return oval(-10,-2,4,2,64);
// returns an offset oval with miminum aabb position equal to [-10,-2], a width and height of 4 and 2 units and 64 circular steps
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: circle, arc ARC : Generate 2D Arc
→ 'instantiates a 2D circular arc polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { arc };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 arc ( I segments, D start_angle, D end_angle )prefix G2 arc ( D radius, I segments, D start_angle, D end_angle )prefix G2 arc ( D ox, D oy, D radius, I segments, D start_angle, D end_angle )Input Arguments:•
D ox :
default = 0 : the origin x-axis position of the arc - its center or pivot - a decimal number.•
D oy :
default = 0 : the origin y-axis position of the arc - its center or pivot a decimal number.•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the arc - a positive non-zero deecimal number.•
I segments :
default = 24 : the number of circular discretisation steps used to construct the arc - a positive integer greater than or equal to 2.•
D start_angle :
default = 0 : the starting angle for the arc's sweep specified in degrees.•
D end_angle :
default = 270 : the ending angle for the arc's sweep specified in degrees.→ radius > 0
→ segments >= 2
→ start_angle != end_angle
→ |( end_angle - start_angle )| < 360
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments + 1 )Practical Examples:return arc();
// returns the default zero-argument unit arc
return arc(8,0,90);
// returns an arc centered at the origin with 8 circular steps ranging from 0 degrees to 90 degrees and the default radius of 0.5 units
return arc(2,4,-90,90);
// returns an arc centered at the origin with a radius of 2 units, 4 circular steps and an angular range from -90 degrees to 90 degrees
return arc(-5,2,3.21,24,0,-270);
// returns an arc centered at coordinate-position [-5,2], with a radius of 3.21 units, 24 circular steps and an angular range from 0 degrees to -270 degrees
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: circle, oval, pie, o-arc PIE : Generate 2D Pie
→ 'instantiates a 2D pie segment polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { pie };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 pie ( I segments, D start_angle, D end_angle )prefix G2 pie ( D radius, I segments, D start_angle, D end_angle )prefix G2 pie ( D ox, D oy, D radius, I segments, D start_angle, D end_angle )Input Arguments:•
D ox :
default = 0 : the origin x-axis position of the pie - its center or pivot - a decimal number.•
D oy :
default = 0 : the origin y-axis position of the pie - its center or pivot - a decimal number.•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the pie - a positive non-zero decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 24 : the number of circular steps used to construct the pie - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
D start_angle :
default = 0 : the starting angle for the pie's sweep specified in degrees.•
D end_angle :
default = 270 : the ending angle for the pie's sweep specified in degrees.→ radius > 0
→ segments >= 1
→ start_angle != end_angle
→ |( end_angle - start_angle )| < 360
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments + 2 )Practical Examples:return pie();
// returns the default zero-argument unit pie
return pie(8,0,90);
// returns a pie centered at the origin with 8 circular steps ranging from 0 degrees to 90 degrees and the default radius of 0.5 units
return pie(2,4,-90,90);
// returns a pie centered at the origin with a radius of 2 units, 4 circular steps and an angular range from -90 degrees to 90 degrees
return pie(-5,2,3.21,24,0,-270);
// returns a pie centered at coordinate-position [-5,2], with a radius of 3.21 units, 24 circular steps and an angular range from 0 degrees to -270 degrees
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: arc ARCH : Generate 2D Archway
→ 'instantiates a 2D circular archway polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { arch, archway };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 arch ( D radius, D length )prefix G2 arch ( D radius, D length, I steps )prefix G2 arch ( D radius, D y, D length, I steps )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the circular portion of the arch - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D y :
default = -0.5|0 : the lowest y-axis position of the arch - or its ground position.•
D length :
default = 0.5 : the length of the upright portion of the arch - i.e. the height of its verticals - a positive non-zero decimal.•
I steps :
default = 32 : the number of semi-circular steps used to construct the arch - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ steps >= 1
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( steps + 1 + 2 )Practical Examples:return arch();
// returns the default zero-argument unit arch
return arch(0.5,2);
// returns an arch with a radius of 0.5 units, a length of 2 units and the default 32 circular steps - resulting in an aabb width and height of respectively 1 and 2.5 units
return arch(3,10,2);
// returns an arch with a radius of 3 units, a length of 10 units and 2 circular steps - which yields a triangular peak with aabb extents equal to 6 units and 13 units
return arch(1,-1,1,2);
// returns an arch with a radius of 1 unit, a minimum y-coordinate of -1, a length of 1 unit and 2 circular steps - resulting in a non-uniform pentagon with aabb width and height of 2 units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: circle, o-arch CAP-2D : Generate 2D Capsule
→ 'instantiates a 2D capsule polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { cap_2D, capsule_2D };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 cap2D ( D radius, D length )prefix G2 cap2D ( D radius, D length, I steps )prefix G2 cap2D ( D radius, D x1, D y1, D x2, D y2, I steps )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius of the semi-circular portions of the capsule - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D length :
default = 0.5 : the length of the straight portion of the capsule - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D x1 :
default = length * -0.5 : the x-axis component of the first vertex in a line defining the spine of the capsule.•
D y1 :
default = 0 : the y-axis component of the first vertex in a line defining the spine of the capsule.•
D x2 :
default = length * 0.5 : the x-axis component of the second vertex in a line defining the spine of the capsule.•
D y2 :
default = 0 : the y-axis component of the second vertex in a line defining the spine of the capsule.•
I steps :
default = 32 : the number of semi-circular steps used to construct the capsule - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ steps >= 1
→ ( x1, y1 ) != ( x2, y2 )
→ |( x2, y2 ) - ( x1, y1 )| > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( steps + 1 ) * 2 )Practical Examples:return cap2D();
// returns the default zero-argument unit cap2D
return cap2D(4,12);
// returns an origin centered 2D capsule shape with a radius of 4 units, a straight-section length of 12 units and the default 32 circular steps for each semi-circle
return cap2D(1,8,2);
// returns an origin centered 2D capsule shape with radius 1 unit, straight-section length of 8 units and 2 circular steps for each semi-circle - yielding a pair of triangle peaks
return cap2D(0.25,-5,-5,5,5,8);
// returns a diagonal data-driven 2D capsule shape constructed using the coordinate positions [-5,-5] and [5,5], with a radius of 0.25 units and 8 circular steps for each semi-circle
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: circle, capsule TRIANGLE : Generate 2D Triangle
→ 'instantiates a 2D triangular polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { tri, triangle };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 tri ( D radius )prefix G2 tri ( D ax, D ay, D bx, D by, D cx, D cy )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the origin centered equilateral triangle - a positive decimal greater than zero.•
D ax :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the triangle.•
D ay :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the triangle.•
D bx :
the x-axis component of the second vertex coordinate position in the triangle.•
D by :
the y-axis-component of the second vertex coordinate position in the triangle.•
D cx :
the x-axis component of the third vertex coordinate position in the triangle.•
D cy :
the y-axis component of the third vertex coordinate position in the triangle.→ radius > 0
→ ( ax, ay ) != ( bx, by ) != ( cx, cy )
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 3Practical Examples:return tri();
// returns the default zero-argument unit tri
return tri(1);
// returns an equilateral triangle centered at the origin with a radius of 1 unit
return tri(-5,-5, -5,5, 5,-5);
// returns a right-angled triangle defined by the vertex coordinates [-5,-5], [-5,5] and [5,-5]
Additional Notes:•
The triangle function provides two complementary overloads. The unary overload returns an origin-centered equilateral triangle - whilst the hexad overload (which accepts vertex-position data) can return any valid 2D triangle be it right-angled, scalene, isosceles and/or obtuse. QUADRILATERAL : Generate 2D Quadrilateral
→ 'instantiates a 2D quadrilateral polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { quad, quadrilateral };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 quad ( D ax, D ay, D bx, D by, D cx, D cy, D dx, D dy )Input Arguments:•
D ax :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the quadrilateral.•
D ay :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the quadrilateral.•
D bx :
the x-axis component of the second vertex coordinate position in the quadrilateral.•
D by :
the y-axis component of the second vertex coordinate position in the quadrilateral.•
D cx :
the x-axis component of the third vertex coordinate position in the quadrilateral.•
D cy :
the y-axis component of the third vertex coordinate position in the quadrilateral.•
D dx :
the x-axis component of the fourth vertex coordinate position in the quadrilateral.•
D dy :
the y-axis component of the fourth vertex coordinate position in the quadrilateral.→ ( ax, ay ) != ( bx, by ) != ( cx, cy ) != ( dx, dy )
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 4Practical Examples:return quad();
// returns the default zero-argument unit quad
return quad(0,-0.5,-0.5,-0.25,0,0.5,0.5,-0.25);
// returns a convex kite-shaped 2D quadrilateral defined by four pairs of vertex coordinates
return quad(-0.5,-0.5,0,0.5,0.5,-0.5,0,0);
// returns a concave pointer-shaped 2D quadrilateral defined by four pairs of vertex coordinates
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: parallelogram, square PARALLELOGRAM : Generate 2D Parallelogram
→ 'instantiates a 2D parallelogram specified by 3 points which define the first two edges'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { pgram, plgram, parallelogram };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 pgram ( D ax, D ay, D bx, D by, D cx, D cy )Input Arguments:•
D ax :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the parallelogram.•
D ay :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the parallelogram.•
D bx :
the x-axis component of the second vertex coordinate position in the parallelogram.•
D by :
the y-axis component of the second vertex coordinate position in the parallelogram.•
D cx :
the x-axis component of the third vertex coordinate position in the parallelogram.•
D cy :
the y-axis component of the third vertex coordinate position in the parallelogram.→ ( ax, ay ) != ( bx, by ) != ( cx, cy )
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 4Practical Examples:return pgram();
// returns the default zero-argument unit pgram
return pgram(0,0,1,1,2,1);
// returns a parallelogram shape defined by the pair of 2D bounded-edges [0,0]->[1,1] and [1,1]->[2,1]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: quadrilateral, square STAR-2D : Generate 2D Star
→ 'instantiates a 2D star polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { star_2D };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 star2D ( I N, D r0, D r1 )Input Arguments:•
I N :
the number of points defining the star - a positive integer greater than or equal to 2.•
D r0 :
the first radius defining the star - a non-zero decimal whose sign matches the sign of the star's second radius.•
D r1 :
the second radius defining the star - a non-zero decimal whose sign matches the sign of the star's first radius.→ N > 1
→ sign( r0 ) == sign( r1 )
Vertex Count:→ |V| = N * 2Practical Examples:return star2D();
// returns the default zero-argument unit star2D
return star2D(4,1,0.5);
// returns an origin-centered four-point star shape with a major-radius of 1 unit and a minor-radius of 0.5 units
return star2D(5,2,0.25);
// returns an origin-centered five-point star shape with a major-radius of 2 units and a minor-radius of 0.25 units
return star2D(16,1,0.875);
// returns an origin-centered sixteen-point star shape with a major-radius of 1 unit and a minor-radius of 0.875 units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: arrow-2D ARROW-2D : Generate 2D Arrow
→ 'instantiates a 2D arrow polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { arrow_2D };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 arrow2D ( D x0, D y0, D x1, D y1, D r0, D r1, D l )Input Arguments:•
D x0 :
the x-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the arrow - the start-x.•
D y0 :
the y-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the arrow - the start-y.•
D x1 :
the x-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the arrow - the end-x.•
D y1 :
the y-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the arrow - the end-y.•
D r0 :
the radius of the arrow's central spine.•
D r1 :
the radius of the arrow's pointed tip.•
D l :
the length of the arrow's pointed tip.→ abs( x1-x0 ) + abs( y1-y0 ) != 0
→ r0 != r1
→ sign( r0 ) == sign( r1 )
→ l != 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 7Practical Examples:return arrow2D();
// returns the default zero-argument unit arrow2D
return arrow2D(0,1,0,0,0.5,0.25,0.25);
// returns a 2D arrow shape starting at [0,1] and ending at [0,0] (i.e. pointing vertically downwards) with a central-spine radius of 0.5 units and a pointed tip radius and length of (respectively) 0.25 and 0.25 units
return arrow2D(0,1,0,0,0.5,0.125,0.75);
// returns a 2D arrow shape starting at [0,1] and ending at [0,0] (i.e. pointing verticallly downwards) with a central-spine radius of 0.5 units and a pointed tip radius and length of (respectively) 0.125 and 0.75 units
return arrow2D(0,0.25,0,0,0.5,0.375,-0.75);
// returns a 2D arrow shape starting at [0,0.25] and ending at [0,0] - with a central-spine radius of 0.5 units and a pointed tip radius and length of (respectively) 0.375 and -0.75 units - note: that the negative tip-length has the effect of inverting the direction of the arrow's point relative to the direction defined by its central spine - in this instance resulting in the pointed-tip appearing to form a cut-out recess within the arrow - rather than protuding beyond the central spine
return arrow2D(0,0,1,0,0.25,0.25,0.25);
// returns a 2D arrow shape starting at [0,0] and ending at [1,0] (i.e. pointing horizontally from left to right) with a central-spine radius of 0.25 units and a pointed tip radius and length of (respectively) 0.25 and 0.25 units
Additional Notes:•
The arrow function typically yields shapes defined by seven (7) vertex. However: if the radius of the central-spine is equal to the radius of the pointed-tip then an exception is made (in order to prevent the introduction of zero-length edges) and the function returns five (5) vertices rather than the typical seven (7). SQUARE : Generate 2D Square
→ 'instantiates a four (4) sided regular 2D polygon centered at the origin (0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { square, reg_4, regular_4, reg_poly_4, regular_polygon_4 };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 square ( D radius )prefix G2 square ( D vx, D vy )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the origin centered square - a positive non-zero decimal.•
D vx :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the square.•
D vy :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the square.→ radius > 0
→ |( vx, vy )| > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 4Practical Examples:return square();
// returns the default zero-argument unit square
return square(1.25);
// returns a regular square with a radius of 1.25 units
return square(3,4);
// returns a regular square with a radius of 5 units - i.e. the square-root of (3*3)+(4*4) - and initial vertex located at coordinate position [3,4] units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: quadrilateral, parallelogram, pentagon, hexagon, septagon, octagon, nonagon, decagon, reg → regular-polygon PENTAGON : Generate 2D Pentagon
→ 'instantiates a five (5) sided regular 2D polygon centered at the origin (0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { pentagon, reg_5, regular_5, reg_poly_5, regular_polygon_5 };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 pentagon ( D radius )prefix G2 pentagon ( D vx, D vy )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the origin centered pentagon - a positive non-zero decimal.•
D vx :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the pentagon.•
D vy :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the pentagon.→ radius > 0
→ |( vx, vy )| > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 5Practical Examples:return pentagon();
// returns the default zero-argument unit pentagon
return pentagon(1.25);
// returns a regular pentagon with a radius of 1.25 units
return pentagon(3,4);
// returns a regular pentagon with a radius of 5 units - i.e. the square-root of (3*3)+(4*4) - and initial vertex located at coordinate position [3,4] units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: square, hexagon, septagon, octagon, nonagon, decagon, reg → regular-polygon HEXAGON : Generate 2D Hexagon
→ 'instantiates a six (6) sided regular 2D polygon centered at the origin (0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { hexagon, reg_6, regular_6, reg_poly_6, regular_polygon_6 };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 hexagon ( D radius )prefix G2 hexagon ( D vx, D vy )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the origin centered hexagon - a positive non-zero decimal.•
D vx :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the hexagon.•
D vy :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the hexagon.→ radius > 0
→ |( vx, vy )| > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 6Practical Examples:return hexagon();
// returns the default zero-argument unit hexagon
return hexagon(1.25);
// returns a regular hexagon with a radius of 1.25 units
return hexagon(3,4);
// returns a regular hexagon with a radius of 5 units - i.e. the square-root of (3*3)+(4*4) - and initial vertex located at coordinate position [3,4] units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: square, pentagon, septagon, octagon, nonagon, decagon, reg → regular-polygon SEPTAGON : Generate 2D Septagon
→ 'instantiates a seven (7) sided regular 2D polygon centered at the origin (0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { septagon, heptagon, reg_7, regular_7, reg_poly_7, regular_polygon_7 };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 septagon ( D radius )prefix G2 septagon ( D vx, D vy )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the origin centered septagon - a positive non-zero decimal.•
D vx :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the septagon.•
D vy :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the septagon.→ radius > 0
→ |( vx, vy )| > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 7Practical Examples:return septagon();
// returns the default zero-argument unit septagon
return septagon(1.25);
// returns a regular septagon with a radius of 1.25 units
return septagon(3,4);
// returns a regular septagon with a radius of 5 units - i.e. the square-root of (3*3)+(4*4) - and initial vertex located at coordinate position [3,4] units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: square, pentagon, hexagon, octagon, nonagon, decagon, reg → regular-polygon OCTAGON : Generate 2D Octagon
→ 'instantiates an eight (8) sided regular 2D polygon centered at the origin (0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { octagon, reg_8, regular_8, reg_poly_8, regular_polygon_8 };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 octagon ( D radius )prefix G2 octagon ( D vx, D vy )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the origin centered octagon - a positive non-zero decimal.•
D vx :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the octagon.•
D vy :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the octagon.→ radius > 0
→ |( vx, vy )| > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 8Practical Examples:return octagon();
// returns the default zero-argument unit octagon
return octagon(1.25);
// returns a regular octagon with a radius of 1.25 units
return octagon(3,4);
// returns a regular octagon with a radius of 5 units - i.e. the square-root of (3*3)+(4*4) - and initial vertex located at coordinate position [3,4] units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: square, pentagon, hexagon, septagon, nonagon, decagon, reg → regular-polygon NONAGON : Generate 2D Nonagon
→ 'instantiates a nine (9) sided regular 2D polygon centered at the origin (0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { nonagon, reg_9, regular_9, reg_poly_9, regular_polygon_9 };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 nonagon ( D radius )prefix G2 nonagon ( D vx, D vy )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the origin centered nonagon - a positive non-zero decimal.•
D vx :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the nonagon.•
D vy :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the nonagon.→ radius > 0
→ |( vx, vy )| > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 9Practical Examples:return nonagon();
// returns the default zero-argument unit nonagon
return nonagon(1.25);
// returns a regular nonagon with a radius of 1.25 units
return nonagon(3,4);
// returns a regular nonagon with a radius of 5 units - i.e. the square-root of (3*3)+(4*4) - and initial vertex located at coordinate position [3,4] units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: square, pentagon, hexagon, septagon, octagon, decagon, reg → regular-polygon DECAGON : Generate 2D Decagon
→ 'instantiates a ten (10) sided regular 2D polygon centered at the origin (0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { decagon, reg_10, regular_10, reg_poly_10, regular_polygon_10 };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 decagon ( D radius )prefix G2 decagon ( D vx, D vy )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the origin centered decagon - a positive non-zero decimal.•
D vx :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the decagon.•
D vy :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the decagon.→ radius > 0
→ |( vx, vy )| > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 10Practical Examples:return decagon();
// returns the default zero-argument unit decagon
return decagon(1.25);
// returns a regular decagon with a radius of 1.25 units
return decagon(3,4);
// returns a regular decagon with a radius of 5 units - i.e. the square-root of (3*3)+(4*4) - and initial vertex located at coordinate position [3,4] units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: square, pentagon, hexagon, septagon, octagon, nonagon, reg → regular-polygon REG → REGULAR-POLYGON : Generate 2D Regular-Polygon
→ 'instantiates an N-sided regular 2D polygon centered at the origin (0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { reg, reg_n, regular, reg_poly, regular_polygon };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 reg ( I sides )prefix G2 reg ( D radius, I sides )prefix G2 reg ( D vx, D vy, I sides )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the origin centered regular polygon - a positive decimal number greater than zero.•
I sides :
default = 16 : the number of sides (or edges) in the regular polygon - a positive integer greater than over equal to 3.•
D vx :
the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the regular polygon.•
D vy :
the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position in the regular polygon.→ radius > 0
→ sides >= 3
→ |( vx, vy )| > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = sidesPractical Examples:return reg();
// returns the default zero-argument unit reg
return reg(11);
// returns an eleven-sided regular-polygon shape centered at the origin - with the default radius of 0.5 units
return reg(0.25,11);
// returns an eleven-sided regular-polygon shape centered at the origin - with a radius of 0.25 units
return reg(3,4,11);
// returns an eleven-sided regular-polygon shape centered at the origin - with a radius of 5 units and with the initial vertex located at [3,4]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: triangle, square, pentagon, hexagon, septagon, octagon, nonagon, decagon POLYGON : Generate 2D Cyclic-Polygon
→ 'instantiates a data-driven 2D polygon defined by a set of positional coordinate values'
Classification:→ { instantiative, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { poly, poly_2D, polygon, polygon_2D };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 poly ( D[] coordinates )prefix G2 poly ( G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
D[] coordinates :
the vertex coordinate position data that defines the polygon - an array containing pairs of (x,y) decimal values.•
G2 source_shape :
the source shape whose vertex data is to be used to derive the vertex coordinate position data of the newly instantiated polygon.→ |coordinates| >= 6
→ ( |coordinates| % 2 ) == 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = |coordinates| / 2Practical Examples:return poly();
// returns the default zero-argument unit poly
return poly(0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1);
// returns a 2D polygon shape defined by four pairs of XY coordinates supplied as direct variadic function arguments
a = { 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1 };
return poly(a);
// returns a 2D polygon shape defined by four pairs of XY coordinates using the array-argument function overload
Additional Notes:•
The polygon function's overloads are equivalent to the path function's overloads. B-POLYGON : Generate 2D Beveled-Cyclic-Polygon
→ 'instantiates a beveled-corner data-driven 2D polygon defined by a bevel distance and a set of positional coordinate values'
Classification:→ { instantiative, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_poly, b_poly_2D, b_polygon, b_polygon_2D, bevel_poly, bevel_poly_2D, bevel_polygon, bevel_polygon_2D, beveled_poly, beveled_poly_2D, beveled_polygon, beveled_polygon_2D, ... (+12) };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 bpoly ( D bevel_distance, D[] coordinates )prefix G2 bpoly ( D bevel_distance, G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the bevel/chamfer distance/radius applied to compatible corners of the bpolygon - a positive decimal greater than zero and less than half of the minimum edge-length of the coordinate data.•
D[] coordinates :
the vertex coordinate position data that defines the base polygon used to construct the bpolygon - an array containing pairs of (x,y) decimal values.•
G2 source_shape :
the source shape whose vertex data is to be used to derive the vertex coordinate position data of the base polygon used to construct the newly instantiated bpolygon.→ bevel > 0
→ |coordinates| >= 6
→ ( |coordinates| % 2 ) == 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( |coordinates| / 2 ) * 2Practical Examples:return bpoly();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bpoly
return bpoly(0.25, 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1);
// returns a beveled-polygon 2D shape defined by a decimal bevel-distance of 0.25 units followed by four pairs of XY coordinates supplied as direct variadic function arguments
a = { 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1 };
return bpoly(0.25,a);
// returns a beveled-polygon 2D shape defined by a decimal bevel-distance of 0.25 units followed by four pairs of XY coordinates using the array-argument function overload
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
+
[ poly | poly_2D | polygon | polygon_2D ]•
The b-poly function's overloads are equivalent to the b-path function's overloads.•
The b-poly function's beveling of corners behaves conditionally based on the Euclidean length of edges adjacent to a vertex being greater than twice the specified bevel-distance. Essentially this function will not bevel corners for vertex associated with edges whose length is insufficient for the specified distance. Hence use of this function requires some care in selecting an appropriate bevel-distance for a given coordinate set. R-POLYGON : Generate 2D Rounded-Cyclic-Polygon
→ 'instantiates a rounded-corner data-driven 2D polygon defined by a round radius, a number of round steps and a set of positional coordinate values'
Classification:→ { instantiative, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_poly, r_poly_2D, r_polygon, r_polygon_2D, rnd_poly, rnd_poly_2D, rnd_polygon, rnd_polygon_2D, round_poly, round_poly_2D, round_polygon, round_polygon_2D, ... (+4) };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 rpoly ( D radius, I steps, D[] coordinates )prefix G2 rpoly ( D radius, I steps, G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.125 : the rounding radius applied to compatible corners of the rpolygon - a positive decimal greater than zero and less than half of the minimum edge-length of the coordinate data.•
I steps :
default = 8 : the number of rounding steps applied to compatible corners of the rpolygon - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
D[] coordinates :
the vertex coordinate position data that defines the base polygon used to construct the rpolygon - an array containing pairs of (x,y) decimal values.•
G2 source_shape :
the source shape whose vertex data is to be used to derive the vertex coordinate position data of the base polygon used to construct the newly instantiated rpolygon.→ radius > 0
→ steps >= 1
→ |coordinates| >= 6
→ ( |coordinates| % 2 ) == 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( |coordinates| / 2 ) * ( steps + 1 )Practical Examples:return rpoly();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rpoly
return rpoly(0.25,4, 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1);
// returns a rounded-polygon 2D shape defined by a decimal rounding-radius of 0.25 units and an integer discretisation value of 4, followed by four pairs of XY coordinates supplied as direct variadic function arguments
a = { 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1 };
return rpoly(0.25,4,a);
// returns a rounded-polygon 2D shape defined by a decimal rounding-radius of 0.25 units and an integer discretisation value of 4, followed by four pairs of XY coordinates using the array-argument function overload
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
+
[ poly | poly_2D | polygon | polygon_2D ]•
The r-poly function's overloads are equivalent to the r-path function's overloads.•
The r-poly function's rounding of corners behaves conditionally based on the Euclidean length of edges adjacent to a vertex being greater than twice the specified rounding-radius. Essentially this function will not round corners for vertex associated with edges whose length is insufficient for the specified radius. Hence use of this function requires some care in selecting an appropriate radius for a given coordinate set. CURVE-2D : Generate 2D Cyclic-Curve
→ 'instatiates a 2D data-driven closed curve polygonal shape defined by a set of control-points'
Classification:→ { instantiative, cyclic };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { curve_2D, curve, round_curve_2D, rounded_curve_2D };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 curve2D ( I steps, D[] control_points )prefix G2 curve2D ( I steps, G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
I steps :
default = 32 : the number of discretisation steps applied to generate the cyclic curve.•
D[] control_points :
the vertex coordinate position data of the control-points that define the cyclic curve as X-Y decimals.•
G2 source_shape :
the source cyclic-shape whose vertex data is to be used to derive the vertex coordinate position data of the control-points that define the cyclic curve.→ steps >= 3
→ |control_points| >= 6
→ ( |control_points| % 2 ) == 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = stepsPractical Examples:return curve2D();
// returns the default zero-argument unit curve2D
cp = { 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1 };
return curve2D(32,cp);
// returns a 2D cyclic-curve shape defined by four pairs of XY coordinates (denoting the control-points) supplied as an array argument
return curve2D(64,arrow2D);
// returns a 2D cyclic-curve shaped defined by XY control-points derived from the default 2D arrow shape's vertices
return curve2D(64,star2D);
// returns a 2D cyclic-curve shape defined by XY control-points derived from the default 2D star shape's vertices
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: o-curve-2D BEZIER-2D :
Generate 2D Cyclic-Bezier-Curve→ 'instantiates a 2D data-driven closed bezier curve polygonal shape defined by a set of control-points' RAIL-2D :
Generate 2D Cyclic-Rail→ 'instantiates a 2D data-driven projected cyclic-rail complex polygonal shape' B-RAIL-2D :
Generate 2D Beveled-Cyclic-Rail→ 'instantiates a 2D data-driven beveled projected cyclic-rail complex polygonal shape' R-RAIL-2D :
Generate 2D Rounded-Cyclic-Rail→ 'instantiates a 2D data-driven rounded projected cyclic-rail complex polygonal shape' O-RAIL-2D : Generate 2D Open-Rail
→ 'instantiates a 2D data-driven projected open-rail polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { o_rail_2D, o_projection_rail_2D, o_projected_rail_2D, open_rail_2D, open_projection_rail_2D, open_projected_rail_2D };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 orail2D ( D pd0, D pd1, D[] source_vertex )prefix G2 orail2D ( D pd0, D pd1, G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
D pd0 :
the first perpandicular projective distance applied to generate the first half of the open-rail shape - a signed decimal.•
D pd1 :
the second perpandicular projective distance applied to generate the second half of the open-rail shape - a signed decimal.•
D[] source_vertex :
the vertex coordinate positional data defining the spine of the open-rail - as X-Y decimals.•
G2 source_shape :
the source open-shape whose vertex data is to be used to define the spine of the open-rail.→ pd0 != pd1
→ |source_vertex| >= 4
→ ( |source_vertex| % 2 ) == 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( |source_vertex| / 2 ) * 2Practical Examples:return orail2D();
// returns the default zero-argument unit orail2D
return orail2D(-0.125,0.125, { 0,0,0,1,1,1 });
// returns a 2D projection-rail polygonal (cyclic) shape defined by projective-distances of -0.125 and 0.125 units and 3 pairs of XY points denoting the source open polyline path - supplied directly as an array argument
return orail2D(-0.125,0.125, path(0,0,0,1,1,1));
// returns a 2D projection-rail polygonal (cyclic) shape defined by projective-distances of -0.125 and 0.125 units and 3 pairs of XY points denoting the source open polyline - wrapped in a invocation to the 2D path generator function to explicitly force faceting between adjacent elements in the return
return orail2D(-0.05,0, oarch);
// returns a 2D projection-rail polygonal (cyclic) shape defined by projective distances of -0.05 and 0 units and using the vertices of the default open-archway 2D polyline path shape as the source
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ o | open ]
+
[ rail_2D | projection_rail_2D | projected_rail_2D ]•
The o-rail-2D function can be rationalised as the two-dimensional analog to the three-dimensional profile-rails.•
Take care not to confuse the o-rail-2D function with the open (non-cyclical) polyline path generator functions. Although this function is prefixed with the O (open) modifier - in this instance it applies to the nature of the input it operates on rather than the output. In other words - the input to the o-rail-2D function is an open-shape - however the output is a closed cyclic-shape - in an analogous fashion to the three-dimensional rails.•
The projective-distances (pd0 and pd1) specified must take into account the minimum-edge-length of the source-shape in order to ensure a coherent return. In plain terms: if the magnitude of (pd1-pd0) is too great (relative to the spatial characteristics of the input) then the projected-rail generated may be malformed. O-B-RAIL-2D : Generate 2D Beveled-Open-Rail
→ 'instantiates a 2D data-driven beveled projected open-rail polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { o_b_rail_2D, o_b_projection_rail_2D, o_b_projected_rail_2D, o_bevel_rail_2D, o_bevel_projection_rail_2D, o_bevel_projected_rail_2D, o_beveled_rail_2D, o_beveled_projection_rail_2D, o_beveled_projected_rail_2D, o_bevelled_rail_2D, o_bevelled_projection_rail_2D, o_bevelled_projected_rail_2D, ... (+24) };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 obrail2D ( D pd0, D pd1, D bevel, D[] source_vertex )prefix G2 obrail2D ( D pd0, D pd1, D bevel, G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
D pd0 :
the first perpandicular projective distance applied to generate the first half of the beveled open-rail shape - a signed decimal.•
D pd1 :
the second perpandicular projective distance applied to generate the second half of the beveled open-rail shape - a signed decimal.•
D bevel :
the bevel/chamfer distance/radius applied to compatible corners of the vertex-set defining the spine of the beveled open-rail - a positive decimal greater than zero.•
D[] source_vertex :
the vertex coordinate positional data defining the spine of the beveled open-rail - as X-Y decimals.•
G2 source_shape :
the source open-shape whose vertex data is to be used to define the spine of the beveled open-rail.→ pd0 != pd1
→ |source_vertex| >= 4
→ ( source_vertex| % 2 ) == 0
→ bevel > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( |source_vertex| / 2 ) - 2 ) * 4 + ( 2 * 2 )Practical Examples:return obrail2D();
// returns the default zero-argument unit obrail2D
return obrail2D(-0.125,0.125, 0.125, { 0,0,0,1,1,1 });
// returns a 2D beveled-projection-rail polygonal (cyclic) shape defined by projective-distances of -0.125 and 0.125 units, a bevel of 0.125 units and 3 pairs of XY points denoting the source open polyline path - supplied directly as an array argument
return obrail2D(-0.025,0.025, 0.05, path);
// returns a 2D beveled-projection-rail polygonal (cyclic) shape defined by projective-distances of -0.025 and 0.025 units, a bevel of 0.05 units and the vertices of the default 2D polyline path shape
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ o | open ]
+
[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]+
[ rail_2D | projection_rail_2D | projected_rail_2D ]•
The o-b-rail-2D function can be considered a convenience for invoking the b-path function followed by the o-rail-2D function. In other words this function is subject to the behavioural considerations applicable to both the b-path and o-rail-2D functions. O-R-RAIL-2D : Generate 2D Rounded-Open-Rail
→ 'instantiates a 2D data-driven rounded projected open-rail polygonal shape'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { o_r_rail_2D, o_r_projection_rail_2D, o_r_projected_rail_2D, o_rnd_rail_2D, o_rnd_projection_rail_2D, o_rnd_projected_rail_2D, o_round_rail_2D, o_round_projection_rail_2D, o_round_projected_rail_2D, o_rounded_rail_2D, o_rounded_projection_rail_2D, o_rounded_projected_rail_2D, ... (+12) };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 orrail2D ( D pd0, D pd1, D radius, I steps, D[] source_vertex )prefix G2 orrail2D ( D pd0, D pd1, D radius, I steps, G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
D pd0 :
the first perpandicular projective distance applied to generate the first half of the rounded open-rail shape - a signed decimal.•
D pd1 :
the second perpandicular projective distance applied to generate the second half of the rounded open-rail shape - a signed decimal.•
D radius :
the rounding radius applied to compatible corners of the vertex-set defining the spine of the rounded open-rail - a positive decimal greater than zero.•
I steps :
the number of rounding steps applied to compatible corners of the vertex-set defining the spine of the rounded open-rail - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
D[] source_vertex :
the vertex coordinate positional data defining the spine of the rounded open-rail - as X-Y decimals.•
G2 source_shape :
the source open-shape whose vertex data is to be used to define the spine of the rounded open-rail.→ pd0 != pd1
→ |source_vertex| >= 4
→ ( source_vertex| % 2 ) == 0
→ radius > 0
→ steps >= 1
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( |source_vertex| / 2 ) - 2 ) * ( steps + 1 ) + ( 2 * 2 )Practical Examples:return orrail2D();
// returns the default zero-argument unit orrail2D
return orrail2D(-0.125,0.125, 0.25,4, { 0,0,0,1,1,1 });
// returns a 2D rounded-projection-rail polygonal (cyclic) shape defined by projective-distances of -0.125 and 0.125 units, a rounding-radius of 0.25 units, 4 rounding-steps per-corner and 3 pairs of XY points denoting the source open polyline path - supplied directly as an array argument
return orrail2D(-0.025,0.025, 0.05,1, path);
// returns a 2D rounded-projection-rail polygonal (cyclic) shape defined by projective-distances of -0.025 and 0.025 units, a rounding-radius of 0.05 units, a single rounding-step per-corner and the vertices of the default 2D polyline path shape - which has the effect of matching the geometry of the related obrail2D return whilst preserving smoothing-groups along the rail for use in 3D (such as when extruded)
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ o | open ]
+
[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]+
[ rail_2D | projection_rail_2D | projected_rail_2D ]•
The o-r-rail-2D function can be considered a convenience for invoking the r-path function followed by the o-rail-2D function. In other words this function is subject to the behavioural considerations applicable to both the r-path and o-rail-2D functions. CHARACTER-2D :
Generate 2D Character-Symbol→ 'instantiates a 2D symbolic (alpha-numeric) character polygonal shape' B-CHARACTER-2D :
Generate 2D Beveled-Character-Symbol→ 'instantiates a beveled-corner 2D symbolic (alpha-numeric) character polygonal shape' R-CHARACTER-2D :
Generate 2D Rounded-Character-Symbol→ 'instantiates a rounded-corner 2D symbolic (alpha-numeric) character polygonal shape' TEXT-2D :
Generate 2D Character-Sequence→ 'instantiates a 2D symbolic (alpha-numeric) character sequence compound polygonal shape' B-TEXT-2D :
Generate 2D Beveled-Character-Sequence→ 'instantiates a beveled-corner 2D symbolic (alpha-numeric) character sequence compound polygonal shape' R-TEXT-2D :
Generate 2D Rounded-Character-Sequence→ 'instantiates a rounded-corner 2D symbolic (alpha-numeric) character sequence compound polygonal shape' LINE : Generate 2D Line
→ 'instantiates a 2D line-segment defined by a start and end position'
Classification:→ { instantiative, open };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { line, line_2D };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 line ( D x1, D y1, D x2, D y2 )Input Arguments:•
D x1 :
default = -0.5 : the x-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position of the line - its start/initial x-value.•
D y1 :
default = -0.5 : the y-axis component of the first vertex coordinate position of the line - its starting/initial y-value.•
D x2 :
default = 0.5 : the x-axis component of the second vertex coordinate position of the line - its end/finish x-value.•
D y2 :
default = 0.5 : the y-axis component of the second vertex coordinate position of the line - its end/finish y-value.→ ( x1, y1 ) != ( x2, y2 )
→ |( x2, y2 ) - ( x1, y1 )| > 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = 2Practical Examples:return line();
// returns the default zero-argument unit line
return line(-5,-5,5,5);
// returns a diagonal line segment passing through the origin with start coordinate [-5,-5] and end coordinate [5,5]
Additional Notes: O-ARC : Generate 2D Open-Arc
→ 'instantiates a 2D open circular arc polyline path'
Classification:→ { instantiative, open };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { o_arc, open_arc };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 oarc ( I segments, D start_angle, D end_angle )prefix G2 oarc ( D radius, I segments, D start_angle, D end_angle )prefix G2 oarc ( D ox, D oy, D radius, I segments, D start_angle, D end_angle )Input Arguments:•
D ox :
default = 0 : the origin x-axis position of the oarc - its center or pivot - a decimal number.•
D oy :
default = 0 : the origin y-axis position of the oarc - its center or pivot a decimal number.•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the oarc - a positive non-zero deecimal number.•
I segments :
default = 24 : the number of circular discretisation steps used to construct the oarc - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
D start_angle :
default = 0 : the starting angle for the oarc's sweep specified in degrees.•
D end_angle :
default = 270 : the ending angle for the oarc's sweep specified in degrees.→ radius > 0
→ segments >= 1
→ start_angle != end_angle
→ |( end_angle - start_angle )| < 360
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments + 1 )Practical Examples:return oarc();
// returns the default zero-argument unit oarc
return oarc(8,0,90);
// returns an oarc centered at the origin with 8 circular steps ranging from 0 degrees to 90 degrees and the default radius of 0.5 units
return oarc(2,4,-90,90);
// returns an oarc centered at the origin with a radius of 2 units, 4 circular steps and an angular range from -90 degrees to 90 degrees
return oarc(-5,2,3.21,24,0,-270);
// returns an oarc centered at coordinate-position [-5,2], with a radius of 3.21 units, 24 circular steps and an angular range from 0 degrees to -270 degrees
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ o | open ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: arc O-ARCH : Generate 2D Open-Archway
→ 'instantiates a 2D open circular archway polyline path'
Classification:→ { instantiative, open };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { o_arch, o_archway, open_arch, open_archway };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 oarch ( D radius, D length )prefix G2 oarch ( D radius, D length, I steps )prefix G2 oarch ( D radius, D y, D length, I steps )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the circular portion of the oarch - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D y :
default = -0.5|0 : the lowest y-axis position of the oarch - or its ground position.•
D length :
default = 0.5 : the length of the upright portion of the oarch - i.e. the height of its verticals - a positive non-zero decimal.•
I steps :
default = 32 : the number of semi-circular steps used to construct the oarch - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ steps >= 1
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments + 1 + 2 )Practical Examples:return oarch();
// returns the default zero-argument unit oarch
return oarch(0.5,2);
// returns an oarch with a radius of 0.5 units, a length of 2 units and the default 32 circular steps - resulting in an aabb width and height of respectively 1 and 2.5 units
return oarch(3,10,2);
// returns an oarch with a radius of 3 units, a length of 10 units and 2 circular steps - which yields a triangular peak with aabb extents equal to 6 units and 13 units
return oarch(1,-1,1,2);
// returns an oarch with a radius of 1 unit, a minimum y-coordinate of -1, a length of 1 unit and 2 circular steps - resulting in a non-uniform pentagon with aabb width and height of 2 units
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ o | open ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: arch PATH : Generate 2D Open-Polyline
→ 'instantiates a data-driven 2D polyline path defined by a set of positional coordinate values'
Classification:→ { instantiative, open };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { path, polyline, polyline_path };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 path ( D[] coordinates )prefix G2 path ( G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
D[] coordinates :
the vertex coordinate position data that defines the path - an array containing pairs of (x,y) decimal values.•
G2 source_shape :
the source shape whose vertex data is to be used to derive the vertex coordinate position data of the newly instantiated path.→ |coordinates| >= 4
→ ( |coordinates| % 2 ) == 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = |coordinates| / 2Practical Examples:return path();
// returns the default zero-argument unit path
return path(0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1);
// returns an open path 2D shape defined by four pairs of XY coordinates supplied as direct variadic function arguments
a = { 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1 };
return path(a);
// returns an open path 2D shape defined by four pairs of XY coordinates using the array-argument function overload
Additional Notes:•
The path function's overloads are equivalent to the polygon function's overloads. B-PATH : Generate 2D Beveled-Open-Polyline
→ 'instantiates a beveled-corner data-driven 2D polyline path defined by a bevel distance and a set of positional coordinate values'
Classification:→ { instantiative, open };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_path, b_polyline, b_polyline_path, bevel_path, bevel_polyline, bevel_polyline_path, beveled_path, beveled_polyline, beveled_polyline_path, bevelled_path, bevelled_polyline, bevelled_polyline_path, ... (+6) };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 bpath ( D bevel_distance, D[] coordinates )prefix G2 bpath ( D bevel_distance, G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.05 : the bevel/chamfer distance/radius applied to compatible corners of the bpath - a positive decimal greater than zero and less than half of the minimum edge-length of the coordinate data.•
D[] coordinates :
the vertex coordinate position data that defines the base path used to construct the bpath - an array containing pairs of (x,y) decimal values.•
G2 source_shape :
the source shape whose vertex data is to be used to derive the vertex coordinate position data of the base path used to construct the newly instantiated bpath.→ bevel_distance > 0
→ |coordinates| >= 6
→ ( |coordinates| % 2 ) == 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( |coordinates| / 2 ) * 2 - 2Practical Examples:return bpath();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bpath
return bpath(0.25, 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1);
// returns an open beveled-path 2D shape defined by a decimal bevel-distance of 0.25 units followed by four pairs of XY coordinates supplied as direct variadic function arguments
a = { 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1 };
return bpath(0.25,a);
// returns an open beveled-path 2D shape defined by a decimal bevel-distance of 0.25 units followed by four pairs of XY coordinates using the array-argument function overload
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
+
[ path | polyline | polyline_path ]•
The b-path function's overloads are equivalent to the b-poly function's overloads.•
The b-path function's beveling of corners behaves conditionally based on the Euclidean length of edges adjacent to a vertex being greater than twice the specified bevel-distance. Essentially this function will not bevel corners for vertex associated with edges whose length is insufficient for the specified distance. Hence use of this function requires some care in selecting an appropriate bevel-distance for a given coordinate set. R-PATH : Generate 2D Rounded-Open-Polyline
→ 'instantiates a rounded-corner data-driven 2D polyline path defined by a round radius, a number of round steps and a set of positional coordinate values'
Classification:→ { instantiative, open };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_path, r_polyline, r_polyline_path, rnd_path, rnd_polyline, rnd_polyline_path, round_path, round_polyline, round_polyline_path, rounded_path, rounded_polyline, rounded_polyline_path };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 rpath ( D radius, I steps, D[] coordinates )prefix G2 rpath ( D radius, I steps, G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.05 : the rounding radius applied to compatible corners of the rpath - a positive decimal greater than zero and less than half of the minimum edge-length of the coordinate data.•
I steps :
default = 8 : the number of rounding steps applied to compatible corners of the rpath - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
D[] coordinates :
the vertex coordinate position data that defines the base path used to construct the rpath - an array containing pairs of (x,y) decimal values.•
G2 source_shape :
the source shape whose vertex data is to be used to derive the vertex coordinate position data of the base polygon used to construct the newly instantiated rpath.→ radius > 0
→ steps >= 1
→ |coordinates| >= 6
→ ( |coordinates| % 2 ) == 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( |coordinates| / 2 ) * ( steps + 1 ) - ( steps * 2 )Practical Examples:return rpath();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rpath
return rpath(0.25,4, 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1);
// returns an open rounded-path 2D shape defined by a decimal rounding-radius of 0.25 units and an integer discretisation value of 4, followed by four pairs of XY coordinates supplied as direct variadic function arguments
a = { 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1 };
return rpath(0.25,4,a);
// returns an open rounded-path 2D shape defined by a decimal rounding-radius of 0.25 units and an integer discretisation value of 4, followed by four pairs of XY coordinates using the array-argument function overload
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
+
[ path | polyline | polyline_path ]•
The r-path function's overloads are equivalent to the r-poly function's overloads.•
The r-path function's rounding of corners behaves conditionally based on the Euclidean length of edges adjacent to a vertex being greater than twice the specified rounding-radius. Essentially this function will not round corners for vertex associated with edges whose length is insufficient for the specified radius. Hence use of this function requires some care in selecting an appropriate radius for a given coordinate set. O-CURVE-2D : Generate 2D Open-Curve
→ 'instatiates a 2D data-driven open curve polyline path shape defined by a set of control-points'
Classification:→ { instantiative, open };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { o_curve_2D, o_curve, o_round_curve_2D, o_rounded_curve_2D, open_curve_2D, open_curve, open_round_curve_2D, open_rounded_curve_2D };
Invocation Options:prefix G2 ocurve2D ( I steps, D[] control_points )prefix G2 ocurve2D ( I steps, G2 source_shape )Input Arguments:•
I steps :
default = 32 : the number of discretisation steps applied to generate the open curve.•
D[] control_points :
the vertex coordinate position data of the control-points that define the open curve as X-Y decimals.•
G2 source_shape :
the source open-shape whose vertex data is to be used to derive the vertex coordinate position data of the control-points that define the open curve.→ steps >= 3
→ |control_points| >= 6
→ ( |control_points| % 2 ) == 0
Vertex Count:→ |V| = steps + 1Practical Examples:return ocurve2D();
// returns the default zero-argument unit ocurve2D
cp = { 0,0,-1,1,0,2,1,1 };
return ocurve2D(32,cp);
// returns a 2D open-curve shape defined by four pairs of XY coordinates (denoting the control-points) supplied as an array argument
return ocurve2D(64, path(0,0,1,1,2,0,3,0));
// returns a 2D open-curve shape defined by control-points derived from the vertices of a source open-path shape
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ o | open ]
+
[ curve_2D | curve | round_curve_2D | rounded_curve_2D ] O-BEZIER-2D :
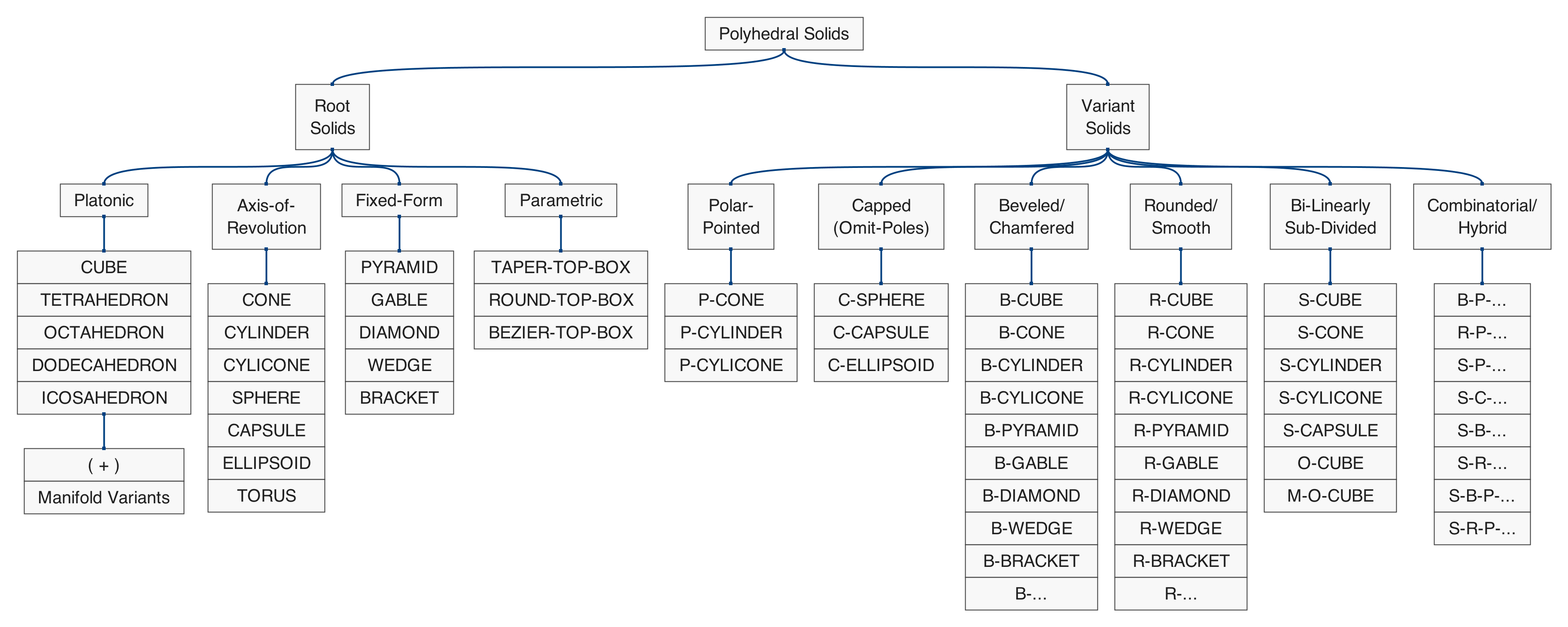
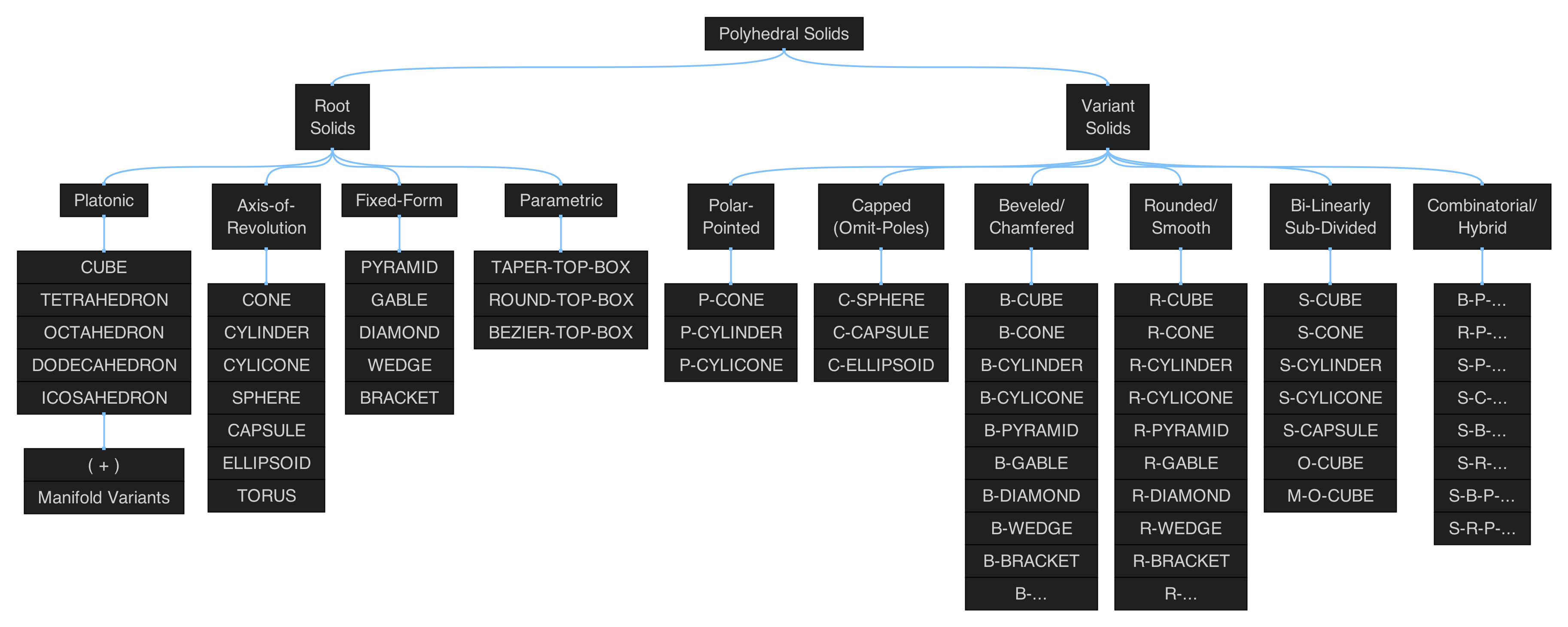
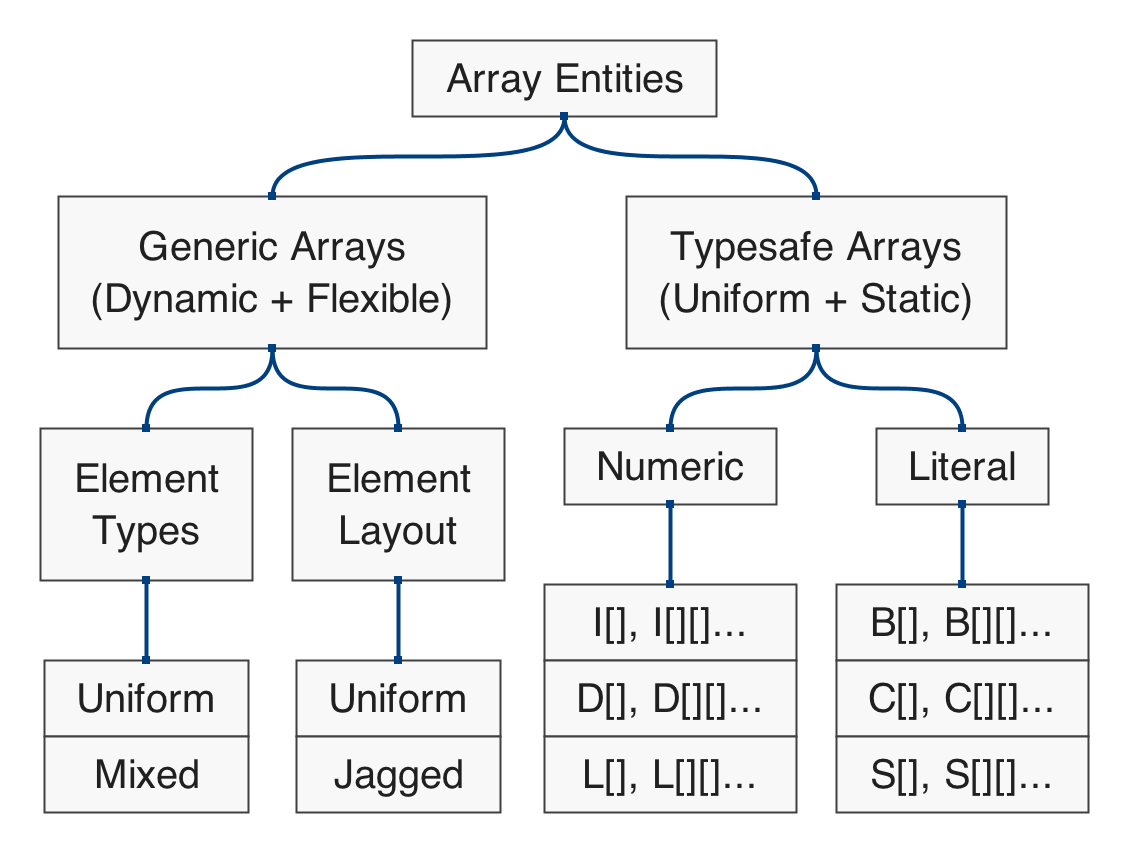
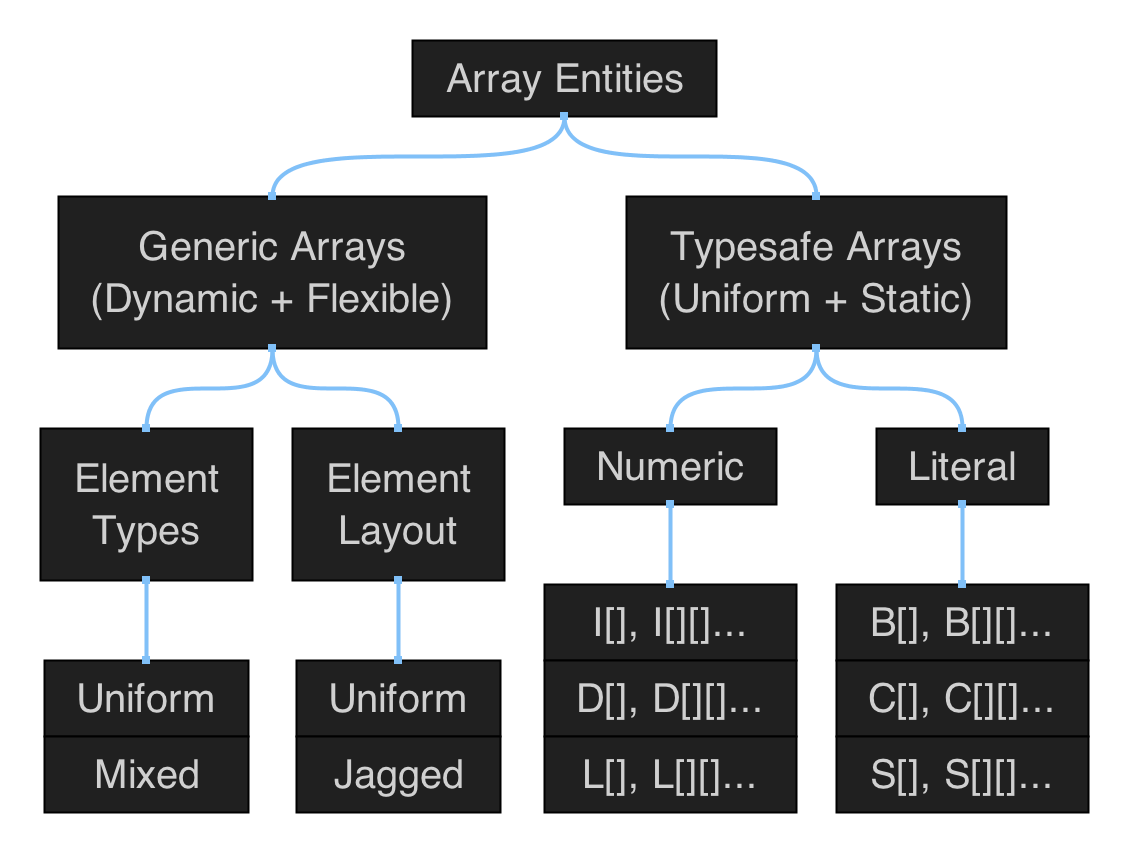
Generate 2D Open-Bezier-Curve→ 'instantiates a 2D data-driven open bezier curve polyline path shape defined by a set of control-points' Polyhedral Solids
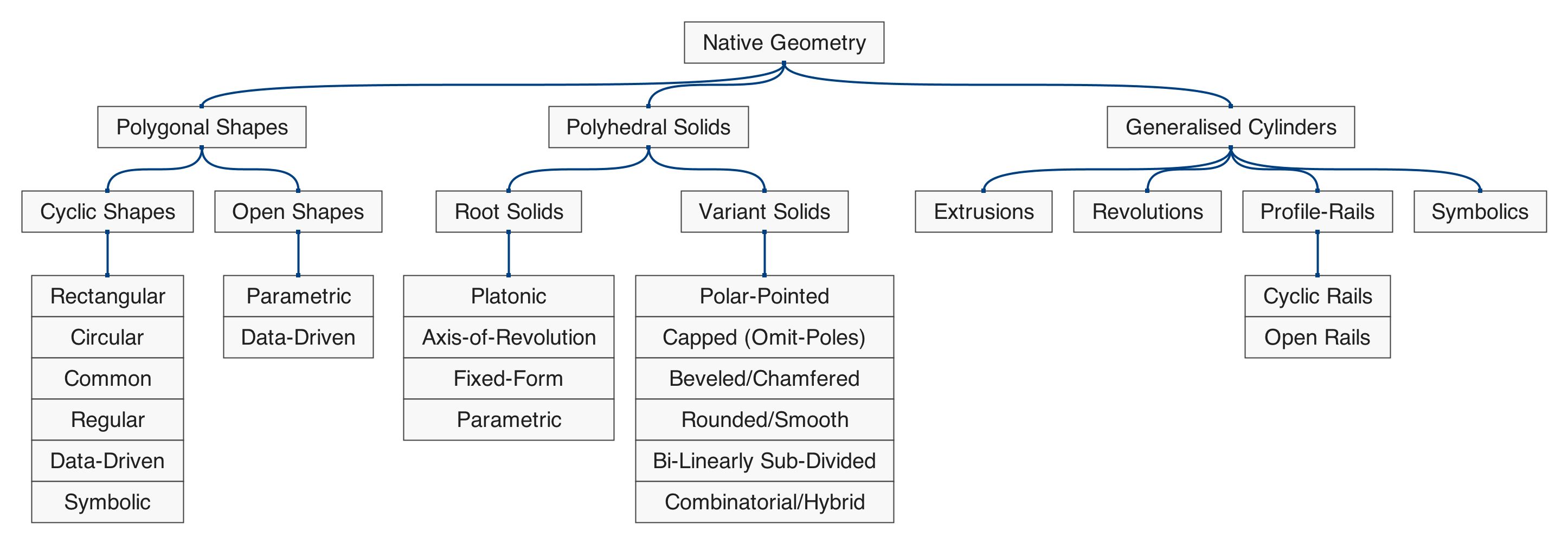
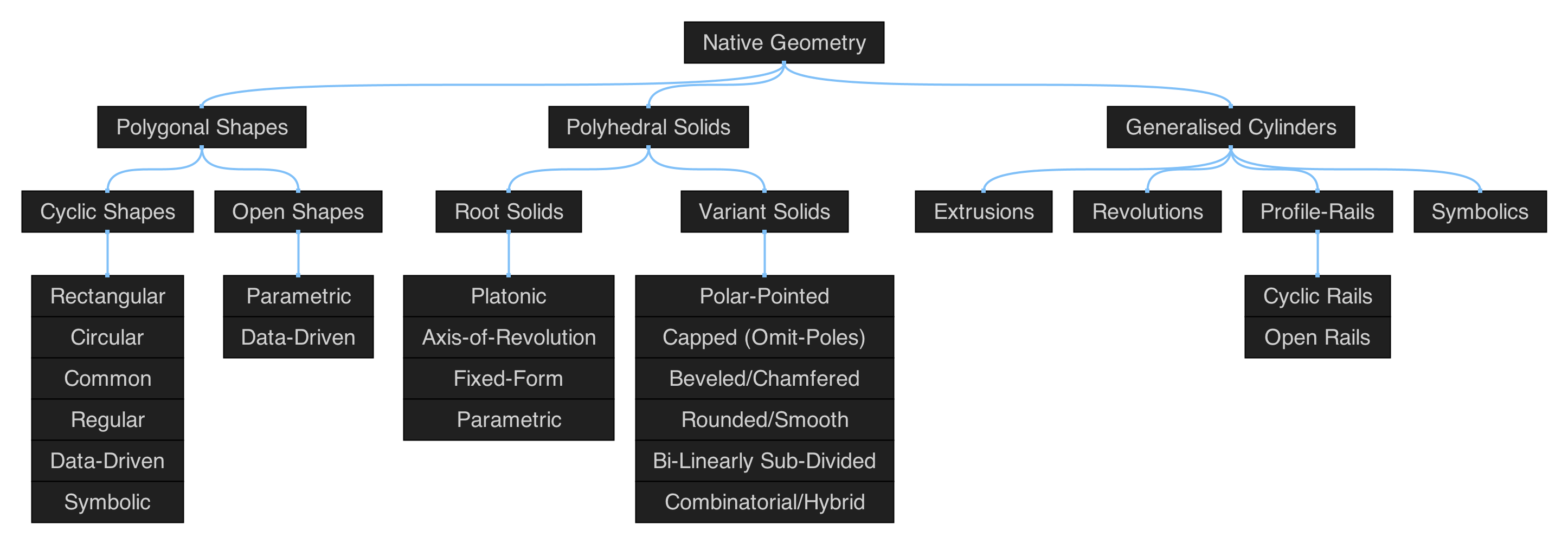
Figure 5.2: hierarchical map of the set of functions in qmsh that create solid (volumetric) polyhedra.
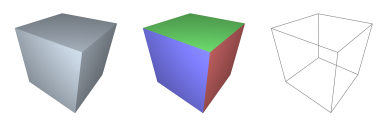
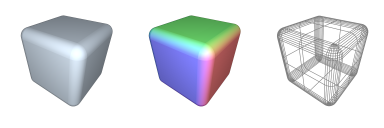
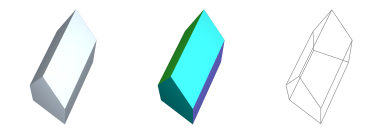
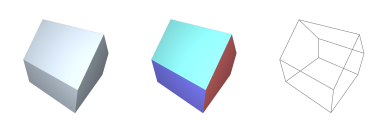
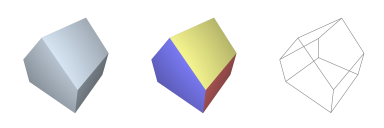
CUBE : Generate 3D Platonic-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates a 3D axis-aligned cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex, orthogonal };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { cube, box_3D, cuboid };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 cube ( D size )prefix G3 cube ( D width, D height, D depth )prefix G3 cube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the cube - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum x-coordinate value of the cube - a decimal number.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum y-coordinate value of the cube - a decimal number.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum z-coordinate value of the cube - a decimal number.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the cube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum x-coordinate value is equal to (x + width).•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the cube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum y-coordinate value is equal to (y + height).•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the cube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum z-coordinate value is equal to (z + depth).→ [ size, width, height, depth ] > 0
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 24Polygon Count:→ |P| = 6Practical Examples:return cube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit cube
return cube(6);
// returns a uniform cube with width, height and depth equal to 6 units
return cuboid(1,2,3);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled cube centered about the origin - with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units
return box3D(0,-5,2,8,10,4);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled, offset cube with minimum aabb position equal to [0,-5,2] and a width, height and depth equal to [8,10,4] units
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: m-cube, b-cube, r-cube, s-cube, hexahedron, o-cube, m-o-cube, b-o-cube, r-o-cube, s-b-cube, s-r-cube TETRAHEDRON : Generate 3D Platonic-Tetrahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D tetrahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { tetrahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 tetrahedron ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the tetrahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 12Polygon Count:→ |P| = 4Practical Examples:return tetrahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit tetrahedron
return tetrahedron(3.21);
// returns a tetrahedron with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: m-tetrahedron, b-tetrahedron, r-tetrahedron OCTAHEDRON : Generate 3D Platonic-Octahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D octahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { octahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 octahedron ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the octahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 24Polygon Count:→ |P| = 8Practical Examples:return octahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit octahedron
return octahedron(3.21);
// returns an octahedron with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: m-octahedron, b-octahedron, r-octahedron DODECAHEDRON : Generate 3D Platonic-Docedahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D dodecahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { dodecahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 dodecahedron ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the dodecahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ pentagons ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 60Polygon Count:→ |P| = 12Practical Examples:return dodecahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit dodecahedron
return dodecahedron(3.21);
// returns a dodecahedron with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: m-dodecahedron, b-dodecahedron, r-dodecahedron ICOSAHEDRON : Generate 3D Platonic-Icosahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D icosahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { icosahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 icosahedron ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the icosahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 60Polygon Count:→ |P| = 20Practical Examples:return icosahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit icosahedron
return icosahedron(3.21);
// returns an icosahedron with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: m-icosahedron, b-icosahedron, r-icosahedron HEXAHEDRON : Generate 3D Platonic-Hexahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D hexahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex, orthogonal };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { hexahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 hexahedron ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the hexahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 24Polygon Count:→ |P| = 6Practical Examples:return hexahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit hexahedron
return hexahedron(3.21);
// returns a hexahedron with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: m-hexahedron, b-hexahedron, r-hexahedron, cube M-CUBE : Generate 3D Manifold-Platonic-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates an axis-aligned 3D manifold cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex, orthogonal };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { m_cube, m_box_3D, m_cuboid, manifold_cube, manifold_box_3D, manifold_cuboid };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 mcube ( D size )prefix G3 mcube ( D width, D height, D depth )prefix G3 mcube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the mcube - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum x-coordinate value of the mcube - a decimal number.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum y-coordinate value of the mcube - a decimal number.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum z-coordinate value of the mcube - a decimal number.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the mcube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum x-coordinate value is equal to (x + width).•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the mcube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum y-coordinate value is equal to (y + height).•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the mcube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum z-coordinate value is equal to (z + depth).→ [ size, width, height, depth ] > 0
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 8Polygon Count:→ |P| = 6Practical Examples:return mcube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit mcube
return mcube(6);
// returns a uniform mcube with width, height and depth equal to 6 units
return mcuboid(1,2,3);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled mcube centered about the origin - with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units
return mbox3D(0,-5,2,8,10,4);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled, offset mcube with minimum aabb position equal to [0,-5,2] and a width, height and depth equal to [8,10,4] units
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ m | manifold ]
+
[ cube | box_3D | cuboid ] M-TETRAHEDRON : Generate 3D Manifold-Platonic-Tetrahedron
→ 'instantiates a manifold 3D tetrahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { m_tetrahedron, manifold_tetrahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 mtetrahedron ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the mtetrahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 4Polygon Count:→ |P| = 4Practical Examples:return mtetrahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit mtetrahedron
return mtetrahedron(3.21);
// returns a mtetrahedron with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ m | manifold ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: tetrahedron, b-tetrahedron, r-tetrahedron M-OCTAHEDRON : Generate 3D Manifold-Platonic-Octahedron
→ 'instantiates a manifold 3D octahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { m_octahedron, manifold_octahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 moctahedron ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the moctahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 6Polygon Count:→ |P| = 8Practical Examples:return moctahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit moctahedron
return moctahedron(3.21);
// returns an moctahedron with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ m | manifold ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: octahedron, b-octahedron, r-octahedron M-DODECAHEDRON : Generate 3D Manifold-Platonic-Dodecahedron
→ 'instantiates a manifold 3D dodecahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { m_dodecahedron, manifold_dodecahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 mdodecahedron ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the mdodecahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ pentagons ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 20Polygon Count:→ |P| = 12Practical Examples:return mdodecahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit mdodecahedron
return mdodecahedron(3.21);
// returns a mdodecahedron with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ m | manifold ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: dodecahedron, b-dodecahedron, r-dodecahedron M-ICOSAHEDRON : Generate 3D Manifold-Platonic-Icosahedron
→ 'instantiates a manifold 3D icosahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { m_icosahedron, manifold_icosahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 micosahedron ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the micosahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 12Polygon Count:→ |P| = 20Practical Examples:return micosahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit micosahedron
return micosahedron(3.21);
// returns an micosahedron with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ m | manifold ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: icosahedron, b-icosahedron, r-icosahedron M-HEXAHEDRON : Generate 3D Manifold-Platonic-Hexahedron
→ 'instantiates a manifold 3D hexahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, platonic, convex, orthogonal };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { m_hexahedron, manifold_hexahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 mhexahedron ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the mhexahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 8Polygon Count:→ |P| = 6Practical Examples:return mhexahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit mhexahedron
return mhexahedron(3.21);
// returns a mhexahedron with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ m | manifold ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: hexahedron, b-hexahedron, r-hexahedron, r-cube Axis-of-Revolution Solids
CONE : Generate 3D Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, developable, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { cone };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 cone ( I segments )prefix G3 cone ( D radius, D length )prefix G3 cone ( D radius, D length, I segments )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the cone (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1.0 : the length of the cone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * 2 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments + 1 )Practical Examples:return cone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit cone
return cone(16);
// returns a unit cone with the default radius and height (0.5 and 1.0 units) and 16 circular segments
return cone(2,5.5);
// returns a cone with a base diameter of 4 units, a height of 5.5 units and the default 32 circular segments
return cone(1,5,64);
// returns a cone with a base diameter of 2 units, a height of 5 units and 64 segments
Additional Notes:•
The cone function's overloads are equivalent to the cylinder function's overloads. CYLINDER : Generate 3D Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, developable, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { cylinder };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 cylinder ( I segments )prefix G3 cylinder ( D radius, D length )prefix G3 cylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the cylinder (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1.0 : the length of the cylinder (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * 4 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments + 2 )Practical Examples:return cylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit cylinder
return cylinder(16);
// returns a unit cylinder with the default radius and height (0.5 and 1.0 units) and 16 circular segments
return cylinder(2,5.5);
// returns a cylinder with a base diameter of 4 units, a height of 5.5 units and the default 32 circular segments
return cylinder(1,5,64);
// returns a cylinder with a diameter of 2 units, a height of 5 units and 64 segments
Additional Notes:•
The cylinder function's overloads are equivalent to the cone function's overloads. CYLICONE : Generate 3D Cyclicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D parametric conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, developable, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { cylicone };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 cylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius )prefix G3 cylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, I segments )prefix G3 cylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the cylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius at the top of the cylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1.0 : the length of the cylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or it vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.→ radius > 0
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] >= 0
→ segments >= 3
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( lower_radius == 0 || upper_radius == 0 ) ? ( segments * 2 + 2 ) : ( segments * 4 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( lower_radius == 0 || upper_radius == 0 ) ? ( segments + 1 ) : ( segments + 2 )Practical Examples:return cylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit cylicone
return cylicone(1,2);
// returns a cylicone with a lower-radius of 1 unit, an upper-radius of 2 units, and the default length (1) and segments (32)
return cylicone(0.5,1,16);
// returns a cylicone with a lower-radius of 0.5 units, an upper-radius of 1 unit, the default length (1 unit) and 16 circular segments
return cylicone(1,0.5,4,64);
// returns a cylicone with a lower-radius of 1, an upper-radius of 0.5, a length of 4 and 64 segments
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: p-cylicone, b-cylicone, r-cylicone, s-cylicone, b-p-cylicone, r-p-cylicone, s-b-cylicone, s-r-cylicone, s-b-p-cylicone, s-r-p-cylicone SPHERE : Generate 3D Sphere
→ 'instantiates a 3D polar-sphere solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { sphere };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 sphere ( D diameter )prefix G3 sphere ( I slices, I stacks )prefix G3 sphere ( D diameter, I slices, I stacks )Input Arguments:•
D diameter :
default = 1.0 : the diameter of the sphere - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I slices :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps about the Y-axis) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I stacks :
default = 16 : the number of latitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of half-circle steps from the sphere's north pole to its south pole) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 2.→ diameter > 0
→ slices >= 3
→ stacks >= 2
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( slices * ( stacks - 1 ) + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( slices * stacks )Practical Examples:return sphere();
// returns the default zero-argument unit sphere
return sphere(2.4);
// returns a sphere with a diameter of 2.4 units and the default slices (32) and stacks (16)
return sphere(16,8);
// returns a sphere with the default diameter (1 unit) and respectively 16 and 8 slices and stacks
return sphere(4,64,32);
// returns a sphere with diameter of 4 units, 64 circular slices and 32 semi-circular stacks
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: c-sphere, icosphere, octasphere, tetrasphere, geosphere CAPSULE : Generate 3D Capsule
→ 'instantiates a 3D polar-capsule solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { capsule, cap_3D, capsule_3D };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 capsule ( D radius, D length )prefix G3 capsule ( D radius, D length, I slices, I stacks )prefix G3 capsule ( D radius, D x1, D y1, D z1, D x2, D y2, D z2 )prefix G3 capsule ( D radius, D x1, D y1, D z1, D x2, D y2, D z2, I slices, I stacks )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius of the capsule's hemispheres - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 0.5 : the length of the capsule's straight-edge section (i.e. its cylindrical portion's height along the Y-axis between its north and south hemispheres) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I slices :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps about the Y-axis) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I stacks :
default = 16 : the number of latitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of quarter-circle steps from each of the capsule's hemisphere's poles, to their equators) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
D x1 :
default = 0 : the x-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the capsule's central spine.•
D y1 :
default = -0.25 : the y-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the capsule's central spine.•
D z1 :
default = 0 : the z-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the capsule's central spine.•
D x2 :
default = 0 : the x-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the capsule's central spine.•
D y2 :
default = 0.25 : the y-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the capsule's central spine.•
D z2 :
default = 0 : the z-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the capsule's central spine.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ slices >= 3
→ stacks >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( slices * stacks * 2 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( slices + slices * stacks * 2 )Practical Examples:return capsule();
// returns the default zero-argument unit capsule
return capsule(1,10);
// returns a capsule with a radius of 1 unit, a length of 10-units and the default 32 and 16 longitudinal slices and latitudinal stacks
return capsule(5,20,4,8);
// returns a capsule with a radius of 5 units, a cylindrical-length of 20 units, 4 longitudinal steps and 8 latitudinal steps for each hemisphere
return capsule(0.25,-5,-5,-5,5,5,5);
// returns a capsule with a radius of 0.25 units and start and end positions of respectively [-5,-5,-5] and [5,5,5] - corresponding to a dialogonal line with length sqrt(300) (approximately: 17.35 units) - using the default 32 slices and 16 stacks
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: c-capsule, s-capsule, cap-2D ELLIPSOID : Generate 3D Ellipsoid
→ 'instantiates a 3D polar-ellipsoid solid (a non-uniformly scaled sphere) centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { ellipsoid };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 ellipsoid ( D size_x, D size_y, D size_z )prefix G3 ellipsoid ( D size_x, D size_y, D size_z, I slices, I stacks )Input Arguments:•
D size_x :
default = 0.5 : the width of the ellipsoid (i.e. its extent along the x-axis) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D size_y :
default = 1 : the height of the ellipsoid (i.e. its extent along the y-axis) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D size_z :
default = 0.25 : the depth of the ellipsoid (i.e. its extent along the z-axis) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I slices :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments in the base sphere used to construct the ellipsoid (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps about the Y-axis) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I stacks :
default = 16 : the number of latitudinal segments in the base sphere used to construct the ellipsoid (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of half-circle steps from the base sphere's north pole to its south pole) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 2.→ [ size_x, size_y, size_z ] > 0
→ slices >= 3
→ stacks >= 2
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( slices * ( stacks - 2 ) + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( slices * stacks )Practical Examples:return ellipsoid();
// returns the default zero-argument unit ellipsoid
return ellipsoid(1,2,3);
// returns an ellipsoid with a width, height and depth (of respectively) 1, 2, and 3 units and the default slices (32) and stacks (16)
return ellipsoid(2,1,2,64,4);
// returns an ellipsoid with a width, height and depth (of respectively) 2, 1 and 2 units, and with 64 longitudinal steps and 4 latitudinal steps
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: c-ellipsoid TORUS : Generate 3D Torus
→ 'instantiates a 3D toroidal solid defined by a major and a minor circle and centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, complex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { torus };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 torus ( D major_radius, D minor_radius )prefix G3 torus ( D major_radius, D minor_radius, I major_steps, I minor_steps )Input Arguments:•
D major_radius :
default = 0.35 : the radius of the major circle used to construct the torus - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D minor_radius :
default = 0.15 : the radius of the minor circle used to construct the torus - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I major_steps :
default = 32 : the number of segments in the major circle - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3 - such that higher values equate to a more accurate approximation of a circle.•
I minor_steps :
default = 16 : the number of segments in the minor circle - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3 - such that higher values equate to a more accurate approximation of a circle.→ [ major_radius, minor_radius ] > 0
→ [ major_steps, minor_steps ] >= 3
→ minor_radius < ( major_radius * 0.5 )
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( major_steps * minor_steps )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( major_steps * minor_steps )Practical Examples:return torus();
// returns the default zero-argument unit torus
return torus(8,1);
// returns a torus with a major radius of 8 units, a minor radius of 1 unit and the default major and minor steps (32 and 16)
return torus(5,0.5,64,4);
// returns a torus with a major radius of 5 units, a minor radius of 0.5 units, 64 major steps and 4 minor steps
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: toroid PYRAMID : Generate 3D Pyramid
→ 'instantiates a 3D fixed-form pyramid solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { pyramid };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 pyramid ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the pyramid - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 16Polygon Count:→ |P| = 5Practical Examples:return pyramid();
// returns the default zero-argument unit pyramid
return pyramid(3.21);
// returns a pyramid with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: b-pyramid, r-pyramid GABLE : Generate 3D Gable
→ 'instantiates a 3D fixed-form gable solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { gable };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 gable ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the gable - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 18Polygon Count:→ |P| = 5Practical Examples:return gable();
// returns the default zero-argument unit gable
return gable(3.21);
// returns a gable with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: b-gable, r-gable DIAMOND : Generate 3D Diamond
→ 'instantiates a 3D fixed-form diamond solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { diamond };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 diamond ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the diamond - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 24Polygon Count:→ |P| = 8Practical Examples:return diamond();
// returns the default zero-argument unit diamond
return diamond(3.21);
// returns a diamond with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: b-diamond, r-diamond WEDGE : Generate 3D Wedge
→ 'instantiates a 3D fixed-form wedge solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { wedge };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 wedge ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the wedge - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 18Polygon Count:→ |P| = 5Practical Examples:return wedge();
// returns the default zero-argument unit wedge
return wedge(3.21);
// returns a wedge with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: b-wedge, r-wedge BRACKET : Generate 3D Bracket
→ 'instantiates a 3D fixed-form right-angled bracket solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, concave, orthogonal };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { bracket };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bracket ( D size )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bracket - a non-zero positive decimal number.→ size > 0
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 44Polygon Count:→ |P| = 14Practical Examples:return bracket();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bracket
return bracket(3.21);
// returns a bracket with a maximum AABB extent of 3.21
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: b-bracket, r-bracket TAPER-TOP-BOX : Generate 3D Taper-Top-Box
→ 'instantiates a parametric 3D taper-top parallax building-block solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { t_box, t_t_box, taper_box, taper_top_box, tapered_box, tapered_top_box };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 tbox ( D size_x, D size_z, D ground_y, D mass_y, D roof_y, D scale_x, D scale_z, D offset_x, D offset_z )Input Arguments:•
D size_x :
default = 1 : the extent of the taper-box mass along the x-axis - equivalent to its width - a positive decimal number greater than zero.•
D size_z :
default = 1 : the extent of the taper-box mass along the z-axis - equivalent to its depth - a positive decimal number greater than zero.•
D ground_y :
default = -0.5 : the smallest (lowest) y-axis position of the taper-box mass - i.e. the ground position - a positive or negative decimal.•
D mass_y :
default = 0 : the middle (intermediary) y-axis position for the taper-box mass - a positive or negative decimal greater than the ground_y value.•
D roof_y :
default = 0.5 : the upper (highest) y-axis position for the taper-box mass - i.e. its roof peak position - a positive or negative decimal.•
D scale_x :
default = 1 : the tapering scale factor applied to the roof of the mass along the x-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [0:1] inclusive.•
D scale_z :
default = 0 : the tapering scale factor applied to the roof of the mass along the z-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [0:1] inclusive.•
D offset_x :
default = 0 : the shearing offset (translational shift) factor applied to the roof of the mass along the x-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [-0.5:0.5] inclusive.•
D offset_z :
default = 0 : the shearing offset (translational shift) factor applied to the roof of the mass along the z-axis - epxressed in unit normalised form - in the range [-0.5:0.5] inclusive.→ [ size_x, size_z, scale_x, scale_z ] > 0
→ [ mass_y, roof_y ] > ground_y
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 40Polygon Count:→ |P| = 10 - ( ( scale_x * scale_z ) == 0 ? 1 : 0 )Practical Examples:return tbox();
// returns the default zero-argument unit tbox
return tbox(5,2,0,3,4,0.6,0,0,0.5);
// returns a taper-top-box mass with a width and depth of 5 units and 2 units, ground, mass and roof positions of 0, 3 and 4 units, a roof-peak tapering scale factor of 0.6 along the width and 0.0 along the depth and normalised roof-peak offsets of 0.0 along the x-axis and 0.5 along the z-axis
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: round-top-box, bezier-top-box ROUND-TOP-BOX : Generate 3D Rounded-Taper-Top-Box
→ 'instantiates a parametric 3D rounded-taper-top parallax building-block solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_t_box, r_t_t_box, round_taper_box, round_top_box, round_taper_top_box };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rtbox ( D size_x, D size_z, D ground_y, D mass_y, D roof_y, D scale_x, D scale_z, D offset_x, D offset_z, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size_x :
default = 1 : the extent of the round-taper-box mass along the x-axis - equivalent to its width - a positive decimal number greater than zero.•
D size_z :
default = 1 : the extent of the round-taper-box mass along the z-axis - equivalent to its depth - positive decimal number greater than zero.•
D ground_y :
default = -0.5 : the smallest (lowest) y-axis position of the round-taper-box mass - i.e. the ground position - a positive or negative decimal.•
D mass_y :
default = 0 : the middle (intermediary) y-axis position for the round-taper-box mass - a positive or negative decimal greater than the ground_y value.•
D roof_y :
default = 0.5 : the upper (highest) y-axis position for the taper-box mass - i.e. its roof peak position - a positive or negative decimal.•
D scale_x :
default = 1 : the tapering scale factor applied to the roof of the mass along the x-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [0:1] inclusive.•
D scale_z :
default = 0 : the tapering scale factor applied to the roof of the mass along the z-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [0:1] inclusive.•
D offset_x :
default = 0 : the shearing offset (translational shift) factor applied to the roof of the mass along the x-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [-0.5:0.5] inclusive.•
D offset_z :
default = 0 : the shearing offset (translational shift) factor applied to the roof of the mass along the z-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [-0.5:0.5] inclusive.•
I round_steps :
default = 16 : the number of circular discretisation steps to apply to the mass - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size_x, size_z, scale_x, scale_z ] > 0
→ [ mass_y, roof_y ] > ground_y
→ round_steps >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 24 + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * 2 * 4 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = 6 + ( round_steps * 4 ) - ( ( scale_x * scale_z ) == 0 ? 1 : 0 )Practical Examples:return rtbox();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rtbox
return rtbox(5,2,0,3,4,0.6,0,0,0.5,16);
// returns a round-taper-top-box mass with a width and depth of 5 units and 2 units, ground, mass and roof positions of 0, 3 and 4 units, a roof-peak tapering scale factor of 0.6 along the width and 0.0 along the depth and normalised roof-peak offsets of 0.0 along the x-axis and 0.5 along the z-axis - with 16 circular discretisation steps
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: taper-top-box, bezier-top-box BEZIER-TOP-BOX : Generate 3D Bezier-Taper-Top-Box
→ 'instantiates a parametric 3D bezier-taper-top parallax building-block solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_t_box, b_t_t_box, bezier_taper_box, bezier_top_box, bezier_taper_top_box };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 btbox ( D size_x, D size_z, D ground_y, D mass_y, D roof_y, D scale_x, D scale_z, D offset_x, D offset_z, I bezier_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size_x :
default = 1 : the extent of the bezier-taper-box mass along the x-axis - equivalent to its width - a positive decimal number greater than zero.•
D size_z :
default = 1 : the extent of the bezier-taper-box mass along the z-axis - equivalent to its depth - a positive decimal number greater than zero.•
D ground_y :
default = -0.5 : the smallest (lowest) y-axis position of the bezier-taper-box mass - i.e. the ground position - a positive or negative decimal.•
D mass_y :
default = 0 : the middle (intermediary) y-axis position for the bezier-taper-box mass - a positive or negative decimal greater than the ground_y value.•
D roof_y :
default = 0.5 : the upper (highest) y-axis position for the bezier-taper-box mass - i.e. its roof peak position - a positive or negative decimal.•
D scale_x :
default = 1 : the tapering scale factor applied to the roof of the mass along the x-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [0:1] inclusive.•
D scale_z :
default = 0 : the tapering scale factor applied to the roof of the mass along the z-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [0:1] inclusive.•
D offset_x :
default = 0 : the shearing offset (translational shift) factor applied to the roof of the mass along the x-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [-0.5:0.5] inclusive.•
D offset_z :
default = 0 : the shearing offset (translational shift) factor applied to the roof of the mass along the z-axis - expressed in unit normalised form - in the range [-0.5:0.5] inclusive.•
I bezier_steps :
default = 16 : the number of bezier discretisation steps to apply to the mass - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size_x, size_z, scale_x, scale_z ] > 0
→ [ mass_y, roof_y ] > ground_y
→ bezier_steps >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 24 + ( ( bezier_steps + 1 ) * 2 * 4 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = 6 + ( bezier_steps * 4 ) - ( ( scale_x * scale_z ) == 0 ? 1 : 0 )Practical Examples:return btbox();
// returns the default zero-argument unit btbox
return btbox(5,2,0,3,4,0.6,0,0,0.5,16);
// returns a bezier-taper-top-box mass with a width and depth of 5 units and 2 units, ground, mass and roof positions of 0, 3 and 4 units, a roof-peak tapering scale factor of 0.6 along the width and 0.0 along the depth and normalised roof-peak offsets of 0.0 along the x-axis and 0.5 along the z-axis - with 16 bezier curve sampling steps
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: taper-top-box, round-top-box P-CONE : Generate 3D Polar-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D polar conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { p_cone, polar_cone, pole_cone, polar_point_cone };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 pcone ( I segments )prefix G3 pcone ( D radius, D length )prefix G3 pcone ( D radius, D length, I segments )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the pcone (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1.0 : the length of the pcone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * 2 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments * 2 )Practical Examples:return pcone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit pcone
return pcone(16);
// returns a unit pcone with the default radius and height (0.5 and 1.0 units) and 16 circular segments
return pcone(2,5.5);
// returns a pcone with a base diameter of 4 units, a height of 5.5 units and the default 32 circular segments
return pcone(1,5,64);
// returns a pcone with a base diameter of 2 units, a height of 5 units and 64 segments
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ]
Additional Notes:•
The polar-cone function's overloads are equivalent to the polar-cylinder function's overloads. P-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Polar-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D polar cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { p_cylinder, polar_cylinder, pole_cylinder, polar_point_cylinder };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 pcylinder ( I segments )prefix G3 pcylinder ( D radius, D length )prefix G3 pcylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the pcylinder (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1.0 : the length of the pcylinder (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * 4 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments * 3 )Practical Examples:return pcylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit pcylinder
return pcylinder(16);
// returns a unit pcylinder with the default radius and height (0.5 and 1.0 units) and 16 circular segments
return pcylinder(2,5.5);
// returns a pcylinder with a base diameter of 4 units, a height of 5.5 units and the default 32 circular segments
return pcylinder(1,5,64);
// returns a pcylinder with a diameter of 2 units, a height of 5 units and 64 segments
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ]
Additional Notes:•
The polar-cylinder function's overloads are equivalent to the polar-cone function's overloads. P-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Polar-Cylicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D polar parametric conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { p_cylicone, polar_cylicone, pole_cylicone, polar_point_cylicone };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 pcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius )prefix G3 pcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, I segments )prefix G3 pcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the pcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius at the top of the pcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1.0 : the length of the pcylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or it vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] >= 0
→ segments >= 3
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( lower_radius == 0 || upper_radius == 0 ) ? ( segments * 2 + 2 ) : ( segments * 4 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( lower_radius == 0 || upper_radius == 0 ) ? ( segments * 2 ) : ( segments * 3 )Practical Examples:return pcylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit pcylicone
return pcylicone(1,2);
// returns a pcylicone with a lower-radius of 1 unit, an upper-radius of 2 units, and the default length (1) and segments (32)
return pcylicone(0.5,1,16);
// returns a pcylicone with a lower-radius of 0.5 units, an upper-radius of 1 unit, the default length (1 unit) and 16 circular segments
return pcylicone(1,0.5,4,64);
// returns a pcylicone with a lower-radius of 1, an upper-radius of 0.5, a length of 4 and 64 segments
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: cylicone, b-cylicone, r-cylicone, s-cylicone C-SPHERE : Generate 3D Capped-Sphere
→ 'instantiates a 3D flat-topped (capped) spherical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { c_sphere, cap_sphere, capped_sphere };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 csphere ( D diameter )prefix G3 csphere ( I slices, I stacks )prefix G3 csphere ( D diameter, I slices, I stacks )Input Arguments:•
D diameter :
default = 1.0 : the diameter of the csphere - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I slices :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps about the Y-axis) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I stacks :
default = 16 : the number of latitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of half-circle steps from the csphere's north pole to its south pole) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.→ diameter > 0
→ slices >= 3
→ stacks >= 3
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = slices ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( slices * ( stacks - 1 ) + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( slices * ( stacks - 2 ) + 2 )Practical Examples:return csphere();
// returns the default zero-argument unit csphere
return csphere(2.4);
// returns a csphere with a diameter of 2.4 units and the default slices (32) and stacks (16)
return csphere(16,8);
// returns a csphere with the default diameter (1 unit) and respectively 16 and 8 slices and stacks
return csphere(4,64,32);
// returns a csphere with diameter of 4 units, 64 circular slices and 32 semi-circular stacks
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ c | cap | capped ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: sphere, icosphere, octasphere, tetrasphere, geosphere C-CAPSULE : Generate 3D Capped-Capsule
→ 'instantiates a 3D flat-topped (capped) capsule solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { c_capsule, c_cap_3D, c_capsule_3D, cap_capsule, cap_cap_3D, cap_capsule_3D, capped_capsule, capped_cap_3D, capped_capsule_3D };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 ccapsule ( D radius, D length )prefix G3 ccapsule ( D radius, D length, I slices, I stacks )prefix G3 ccapsule ( D radius, D x1, D y1, D z1, D x2, D y2, D z2 )prefix G3 ccapsule ( D radius, D x1, D y1, D z1, D x2, D y2, D z2, I slices, I stacks )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius of the ccapsule's hemispheres - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 0.5 : the length of the ccapsule's straight-edge section (i.e. its cylindrical portion's height along the Y-axis between its north and south hemispheres) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I slices :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps about the Y-axis) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I stacks :
default = 16 : the number of latitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of quarter-circle steps from each of the ccapsule's hemisphere's poles, to their equators) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 2.•
D x1 :
default = 0 : the x-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the ccapsule's central spine.•
D y1 :
default = -0.25 : the y-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the ccapsule's central spine.•
D z1 :
default = 0 : the z-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the ccapsule's central spine.•
D x2 :
default = 0 : the x-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the ccapsule's central spine.•
D y2 :
default = 0.25 : the y-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the ccapsule's central spine.•
D z2 :
default = 0 : the z-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the ccapsule's central spine.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ slices >= 3
→ stacks >= 2
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = slices ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( slices * stacks * 2 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( slices + 2 + slices * ( stacks - 1 ) * 2 )Practical Examples:return ccapsule();
// returns the default zero-argument unit ccapsule
return ccapsule(1,10);
// returns a ccapsule with a radius of 1 unit, a length of 10-units and the default 32 and 16 longitudinal slices and latitudinal stacks
return ccapsule(5,20,4,8);
// returns a ccapsule with a radius of 5 units, a cylindrical-length of 20 units, 4 longitudinal steps and 8 latitudinal steps for each hemisphere
return ccapsule(0.25,-5,-5,-5,5,5,5);
// returns a ccapsule with a radius of 0.25 units and start and end positions of respectively [-5,-5,-5] and [5,5,5] - corresponding to a dialogonal line with length sqrt(300) (approximately: 17.35 units) - using the default 32 slices and 16 stacks
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ c | cap | capped ]
+
[ capsule | cap_3D | capsule_3D ] C-ELLIPSOID : Generate 3D Capped-Ellipsoid
→ 'instantiates a 3D flat-topped (capped) ellipsoidal solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { c_ellipsoid, cap_ellipsoid, capped_ellipsoid };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 cellipsoid ( D size_x, D size_y, D size_z )prefix G3 cellipsoid ( D size_x, D size_y, D size_z, I slices, I stacks )Input Arguments:•
D size_x :
default = 0.5 : the width of the cellipsoid (i.e. its extent along the x-axis) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D size_y :
default = 1 : the height of the cellipsoid (i.e. its extent along the y-axis) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D size_z :
default = 0.25 : the depth of the cellipsoid (i.e. its extent along the z-axis) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I slices :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments in the base sphere used to construct the cellipsoid (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps about the Y-axis) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I stacks :
default = 16 : the number of latitudinal segments in the base sphere used to construct the cellipsoid (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of half-circle steps from the base sphere's north pole to its south pole) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.→ [ size_x, size_y, size_z ] > 0
→ slices >= 3
→ stacks >= 3
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = slices ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( slices * ( stacks - 2 ) + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( slices * ( stacks - 2 ) + 2 )Practical Examples:return cellipsoid();
// returns the default zero-argument unit cellipsoid
return cellipsoid(1,2,3);
// returns a cellipsoid with a width, height and depth (of respectively) 1, 2, and 3 units and the default slices (32) and stacks (16)
return cellipsoid(2,1,2,64,4);
// returns a cellipsoid with a width, height and depth (of respectively) 2, 1 and 2 units, and with 64 longitudinal steps and 4 latitudinal steps
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ c | cap | capped ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: ellipsoid B-CUBE : Generate 3D Beveled-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_cube, b_box_3D, b_cuboid, bevel_cube, bevel_box_3D, bevel_cuboid, beveled_cube, beveled_box_3D, beveled_cuboid, bevelled_cube, bevelled_box_3D, bevelled_cuboid, ... (+6) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bcube ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcube ( D size, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcube ( D width, D height, D depth, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bcube - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum x-coordinate value of the bcube - a decimal number.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum y-coordinate value of the bcube - a decimal number.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum z-coordinate value of the bcube - a decimal number.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the bcube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum x-coordinate value is equal to (x + width).•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the bcube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum y-coordinate value is equal to (y + height).•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the bcube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum z-coordinate value is equal to (z + depth).•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bcube - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than half of the minimum of the bcubes's width, height, depth or uniform size factor.→ [ size, width, height, depth, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ [ size, width, height, depth ] > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 96Polygon Count:→ |P| = 26Practical Examples:return bcube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bcube
return bcube(0.25);
// returns a beveled-cuboid with a uniform size of 1 unit and bevel-distance of 0.25 units
return bevel_cuboid(1,2,3,0.125);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled beveled-cuboid with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units and a bevel-distance of 0.125 units
return bbox3D(0,-5,2,8,10,4,0.5);
// returns a non-uniform scaled, offset beveled-cuboid with minimum aabb position equal to [0,-5,2] units, width, height and depth equal to [8,10,4] units and a bevel-distance of 0.5 units
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
+
[ cube | box_3D | cuboid ] B-CONE : Generate 3D Beveled-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_cone, bevel_cone, beveled_cone, bevelled_cone, chamfer_cone, chamfered_cone };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bcone ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcone ( I segments, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcone ( D radius, D length, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcone ( D radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the bcone (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the bcone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bcone - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than the bcone's radius and less than the bcones's length.→ [ radius, length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ radius, length ] > bevel_distance
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * 4 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments * 2 + 1 )Practical Examples:return bcone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bcone
return bcone(0.05);
// returns a unit bcone with a bevel-distance of 0.05 units and the default 32 segments
return bcone(4,0.125);
// returns a unit bcone with 4 segments and a bevel-distance of 0.125 units
return bcone(0.25,4.5,0.05);
// returns a bcone with a radius of 0.25 units, a length of 4.5 units and a bevel-distance of 0.05 units
return bcone(2,10,16,1);
// returns a bcone with a radius of 2 units, a length of 10 units, 16 segments and a bevel-distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: cone, r-cone, s-cone, b-p-cone, s-b-cone, s-b-p-cone B-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Beveled-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_cylinder, bevel_cylinder, beveled_cylinder, bevelled_cylinder, chamfer_cylinder, chamfered_cylinder };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bcylinder ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcylinder ( I segments, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcylinder ( D radius, D length, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the bcylinder (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the bcylinder (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than the bcylinder's radius and less than half of the bcylinder's length.→ [ radius, length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ radius > bevel_distance
→ length > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * 8 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments * 3 + 2 )Practical Examples:return bcylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bcylinder
return bcylinder(0.05);
// returns a unit bcylinder with a bevel-distance of 0.05 units and the default 32 segments
return bcylinder(4,0.125);
// returns a unit bcylinder with 4 segments and a bevel-distance of 0.125 units
return bcylinder(0.25,4.5,0.05);
// returns a bcylinder with a radius of 0.25 units, a length of 4.5 units and a bevel-distance of 0.05 units
return bcylinder(2,10,16,1);
// returns a bcylinder with a radius of 2 units, a length of 10 units, 16 segments and a bevel-distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: cylinder, r-cylinder, s-cylinder, b-p-cylinder, s-b-cylinder, s-b-p-cylinder B-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Beveled-Cylicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_cylicone, bevel_cylicone, beveled_cylicone, bevelled_cylicone, chamfer_cylicone, chamfered_cylicone };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bcylicone ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, I segments, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the bcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius at the top of the bcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the bcylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bcylicone (both its lower and upper circular edges) - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than the bcylicone's lower and upper radii and less than half of the bcylicone's length.→ [ length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] > bevel_distance
→ length > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * 8 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments * 3 + 2 )Practical Examples:return bcylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bcylicone
return bcylicone(0.05);
// returns a unit bcylicone with a bevel-distance of 0.05 units and the default 32 segments
return bcylicone(0.25,0.5,0.125);
// returns a unit bcylicone with a lower-radius of 0.25 units an upper-radius of 0.5 units, the default 32 segments and a bevel-distance of 0.125 units
return bcylicone(0.75,0.25,4.5,0.05);
// returns a bcylicone with a lower-radius of 0.75 units, an upper-radius of 0.25 units, a length of 4.5 units and a bevel-distance of 0.05 units
return bcylicone(4,2,10,16,1);
// returns a bcylicone with a lower-radius of 4 units, an upper-radius of 2 units, a length of 10 units, 16 segments and a bevel-distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: cylicone, r-cylicone, s-cylicone, b-p-cylicone, s-b-cylicone, s-b-p-cylicone B-PYRAMID : Generate 3D Beveled-Pyramid
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) fixed-form pyramid solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_pyramid, bevel_pyramid, beveled_pyramid, bevelled_pyramid, chamfer_pyramid, chamfered_pyramid };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bpyramid ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bpyramid ( D size, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bpyramid - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 * size : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bpyramid - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than half of the uniform scale factor size of the bpyramid.→ [ size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ size > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 32Polygon Count:→ |P| = 9Practical Examples:return bpyramid();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bpyramid
return bpyramid(0.05);
// returns a bpyramid with a bevel distance of 0.05 units and the default scale factor size of 1 unit
return bpyramid(8,1);
// returns a bpyramid with a uniform size of 8 units and a bevel distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: pyramid, r-pyramid B-GABLE : Generate 3D Beveled-Gable
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) fixed-form gable solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_gable, bevel_gable, beveled_gable, bevelled_gable, chamfer_gable, chamfered_gable };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bgable ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bgable ( D size, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bgable - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 * size : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bgable - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than approximately three tenths of the uniform scale factor size of the bgable.→ [ size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ bevel_distance < ( size * 0.309 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 72Polygon Count:→ |P| = 20Practical Examples:return bgable();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bgable
return bgable(0.05);
// returns a bgable with a bevel distance of 0.05 units and the default scale factor size of 1 unit
return bgable(8,1);
// returns a bgable with a uniform size of 8 units and a bevel distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: gable, r-gable B-WEDGE : Generate 3D Beveled-Wedge
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) fixed-form wedge solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_wedge, bevel_wedge, beveled_wedge, bevelled_wedge, chamfer_wedge, chamfered_wedge };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bwedge ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bwedge ( D size, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bwedge - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 * size : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bwedge - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than approximately (just under) three tenths of the uniform scale factor size of the bwedge.→ [ size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ bevel_distance < ( size * 0.292 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 72Polygon Count:→ |P| = 20Practical Examples:return bwedge();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bwedge
return bwedge(0.05);
// returns a bwedge with a bevel distance of 0.05 units and the default scale factor size of 1 unit
return bwedge(8,1);
// returns a bwedge with a uniform size of 8 units and a bevel distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: wedge, r-wedge B-DIAMOND : Generate 3D Beveled-Diamond
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) fixed-form diamond solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_diamond, bevel_diamond, beveled_diamond, bevelled_diamond, chamfer_diamond, chamfered_diamond };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bdiamond ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bdiamond ( D size, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bdiamond - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 * size : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bdiamond - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than root two multiplied by half of the uniform scale factor size of the bdiamond.→ [ size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ bevel_distance < ( size * 0.707 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 40Polygon Count:→ |P| = 12Practical Examples:return bdiamond();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bdiamond
return bdiamond(0.05);
// returns a bdiamond with a bevel distance of 0.05 units and the default scale factor size of 1 unit
return bdiamond(8,1);
// returns a bdiamond with a uniform size of 8 units and a bevel distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: diamond, r-diamond B-BRACKET : Generate 3D Beveled-Bracket
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) fixed-form right-angled bracket solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_bracket, bevel_bracket, beveled_bracket, bevelled_bracket, chamfer_bracket, chamfered_bracket };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bbracket ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bbracket ( D size, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bbracket - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 * size : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bbracket - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than a quarter of the uniform scale factor size of the bbracket.→ [ size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ size > ( bevel_distance * 4 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 144Polygon Count:→ |P| = 44Practical Examples:return bbracket();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bbracket
return bbracket(0.05);
// returns a bbracket with a bevel distance of 0.05 units and the default scale factor size of 1 unit
return bbracket(8,1);
// returns a bbracket with a uniform size of 8 units and a bevel distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: bracket, r-bracket B-TETRAHEDRON : Generate 3D Beveled-Tetrahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) tetrahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_tetrahedron, bevel_tetrahedron, beveled_tetrahedron, bevelled_tetrahedron, chamfer_tetrahedron, chamfered_tetrahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 btetrahedron ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 btetrahedron ( D size, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the btetrahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 * size : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the btetrahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than approximately two fifths of the uniform scale factor size of the btetrahedron.→ [ size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ bevel_distance < ( size * 0.408 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 48Polygon Count:→ |P| = 14Practical Examples:return btetrahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit btetrahedron
return btetrahedron(0.05);
// returns a btetrahedron with a bevel distance of 0.05 units and the default scale factor size of 1 unit
return btetrahedron(8,1);
// returns a btetrahedron with a uniform size of 8 units and a bevel distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: tetrahedron, m-tetrahedron, r-tetrahedron B-OCTAHEDRON : Generate 3D Beveled-Octahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) octahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_octahedron, bevel_octahedron, beveled_octahedron, bevelled_octahedron, chamfer_octahedron, chamfered_octahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 boctahedron ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 boctahedron ( D size, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the boctahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 * size : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the boctahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than approximately one fifth of the uniform scale factor size of the boctahedron.→ [ size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ bevel_distance < ( size * 0.204 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 96Polygon Count:→ |P| = 26Practical Examples:return boctahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit boctahedron
return boctahedron(0.05);
// returns a boctahedron with a bevel distance of 0.05 units and the default scale factor size of 1 unit
return boctahedron(8,1);
// returns a boctahedron with a uniform size of 8 units and a bevel distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: octahedron, m-octahedron, r-octahedron B-DODECAHEDRON : Generate 3D Beveled-Dodecahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) dodecahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_dodecahedron, bevel_dodecahedron, beveled_dodecahedron, bevelled_dodecahedron, chamfer_dodecahedron, chamfered_dodecahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bdodecahedron ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bdodecahedron ( D size, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bdodecahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 * size : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bdodecahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than approximately a quarter of the uniform scale factor size of the bdodecahedron.→ [ size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ bevel_distance < ( size * 0.262 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 240Polygon Count:→ |P| = 62Practical Examples:return bdodecahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bdodecahedron
return bdodecahedron(0.05);
// returns a bdodecahedron with a bevel distance of 0.05 units and the default scale factor size of 1 unit
return bdodecahedron(8,1);
// returns a bdodecahedron with a uniform size of 8 units and a bevel distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: dodecahedron, m-dodecahedron, r-dodecahedron B-ICOSAHEDRON : Generate 3D Beveled-Icosahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) icosahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0) '
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_icosahedron, bevel_icosahedron, beveled_icosahedron, bevelled_icosahedron, chamfer_icosahedron, chamfered_icosahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bicosahedron ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bicosahedron ( D size, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bicosahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 * size : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bicosahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than approximately nine fiftieths of the uniform scale factor size of the bicosahedron.→ [ size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ bevel_distance < ( size * 0.178 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 240Polygon Count:→ |P| = 62Practical Examples:return bicosahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bicosahedron
return bicosahedron(0.05);
// returns a bicosahedron with a bevel distance of 0.05 units and the default scale factor size of 1 unit
return bicosahedron(8,1);
// returns a bicosahedron with a uniform size of 8 units and a bevel distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: icosahedron, m-icosahedron, r-icosahedron B-HEXAHEDRON : Generate 3D Beveled-Hexahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) hexahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0) '
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_hexahedron, bevel_hexahedron, beveled_hexahedron, bevelled_hexahedron, chamfer_hexahedron, chamfered_hexahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bhexahedron ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bhexahedron ( D size, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bhexahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 * size : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bhexahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than half of the uniform scale factor size of the bhexahedron.→ [ size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ size > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 96Polygon Count:→ |P| = 26Practical Examples:return bhexahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bhexahedron
return bhexahedron(0.05);
// returns a bhexahedron with a bevel distance of 0.05 units and the default scale factor size of 1 unit
return bhexahedron(8,1);
// returns a bhexahedron with a uniform size of 8 units and a bevel distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: hexahedron, m-hexahedron, r-hexahedron, b-cube R-CUBE : Generate 3D Rounded-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_cube, r_box_3D, r_cuboid, rnd_cube, rnd_box_3D, rnd_cuboid, round_cube, round_box_3D, round_cuboid, rounded_cube, rounded_box_3D, rounded_cuboid };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rcube ( D size )prefix G3 rcube ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcube ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcube ( D width, D height, D depth, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the rcube - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum x-coordinate value of the rcube - a decimal number.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum y-coordinate value of the rcube - a decimal number.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum z-coordinate value of the rcube - a decimal number.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the rcube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum x-coordinate value is equal to (x + width).•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the rcube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum y-coordinate value is equal to (y + height).•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the rcube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum z-coordinate value is equal to (z + depth).•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the rcube - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than half of the minimum of the rcube's width, height, depth or uniform size factor.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the rcube - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, width, height, depth, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ [ size, width, height, depth ] > ( round_radius * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * round_steps ) + 1 ) * 8Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( round_steps * round_steps ) * 8 ) + 6 + ( round_steps * 4 * 3 )Practical Examples:return rcube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rcube
return rcube(2);
// returns a rounded-cuboid with a uniform size of 2 units and rounding-radius of 0.25 units - with the default 8 rounding-steps per-axis-corner
return RCUBE(0.125,1);
// returns a uniformly-sized rounded-cuboid with a rounding-radius of 0.125 units and a single rounding-step per-axis-corner - which has the effect of matching the geometric form of a beveled-cuboid whilst retaining smooth-shading across the surface
return round_cuboid(1,2,3,0.125,8);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled rounded-cuboid with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units and a rounding-radius of 0.125 units - with 8 rounding-steps per-axis-corner
return rbox3D(0,-5,2,8,10,4,0.5,4);
// returns a non-uniform scaled, offset rounded-cuboid with minimum aabb position equal to [0,-5,2] units, width, height and depth equal to [8,10,4] units and a rounding-radius of 0.5 units - with 4 rounding-steps per-axis-corner
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
+
[ cube | box_3D | cuboid ] R-CONE : Generate 3D Rounded-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_cone, rnd_cone, round_cone, rounded_cone };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rcone ( I segments )prefix G3 rcone ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcone ( I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcone ( D radius, D length, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcone ( D radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the rcone (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the rcone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the circular edge of the rcone - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than the radius of the rcone and less than the length of the rcone.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the circular edge of the rcone (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, round_radius ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ radius, length ] > round_radius
→ round_steps >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * segments ) + 1Practical Examples:return rcone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rcone
return rcone(8);
// returns a unit rcone with 8 segments and default main-radius, length, round-radius and round-steps of (respectively) 0.5 units, 1 unit, 0.125 units and 8
return rcone(0.125,1);
// returns a unit rcone with a round-radius of 0.125 units and 1 round-step - with defaults for all other arguments - which results in mirroring the geometry of the default unit bcone whilst preserving smooth-shading across the surface
return rcone(16,0.25,4);
// returns a unit rcone with 16 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.25 units and 4 rounding-steps
return rcone(2,5,1,2);
// returns a rcone with a main-radius of 2 units, a length of 5 units, a rounding-radius of 1 unit and 2 rounding-steps
return rcone(1.23,4.56,78,0.123,4);
// returns a rcone with main-radius of 1.23 units, a length of 4.56 units, 78 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.123 units and 4 rounding-steps
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: cone, b-cone, s-cone, r-p-cone, s-r-cone, s-r-p-cone R-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Rounded-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_cylinder, rnd_cylinder, round_cylinder, rounded_cylinder };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rcylinder ( I segments )prefix G3 rcylinder ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcylinder ( I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcylinder ( D radius, D length, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the rcylinder (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the rcylinder (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the circular edges of the rcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than the radius of the rcylinder and less than half the length of the rcylinder.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the circular edges of the rcylinder (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, round_radius ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ radius > round_radius
→ length > ( round_radius * 2 )
→ round_steps >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * 2 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( round_steps * 2 + 1 ) * segments + 2Practical Examples:return rcylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rcylinder
return rcylinder(8);
// returns a unit rcylinder with 8 segments and default main-radius, length, round-radius and round-steps of (respectively) 0.5 units, 1 unit, 0.125 units and 8
return rcylinder(0.125,1);
// returns a unit rcylinder with a round-radius of 0.125 units and 1 round-step - with defaults for all other arguments - which results in mirroring the geometry of the default unit bcylinder whilst preserving smooth-shading across the surface
return rcylinder(16,0.25,4);
// returns a unit rcylinder with 16 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.25 units and 4 rounding-steps
return rcylinder(2,5,1,2);
// returns a rcylinder with a main-radius of 2 units, a length of 5 units, a rounding-radius of 1 unit and 2 rounding-steps
return rcylinder(1.23,4.56,78,0.123,4);
// returns a rcylinder with main-radius of 1.23 units, a length of 4.56 units, 78 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.123 units and 4 rounding-steps
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: cylinder, r-cylinder, s-cylinder, r-p-cylinder, s-r-cylinder, s-r-p-cylinder R-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Rounded-Cylicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_cylicone, rnd_cylicone, round_cylicone, rounded_cylicone };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rcylicone ( I segments )prefix G3 rcylicone ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the rcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius at the top of the rcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the rcylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the lower and upper circular edges of the rcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than both the lower and upper radii of the rcylicone and less than half the length of the rcylicone.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the lower and upper circular edges of the rcylicone (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ length, round_radius ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] > round_radius
→ length > ( round_radius * 2 )
→ round_steps >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * 2 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( round_steps * 2 + 1 ) * segments + 2Practical Examples:return rcylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rcylicone
return rcylicone(8);
// returns a unit rcylicone with 8 segments and default lower-radius, upper-radius, length, round-radius and round-steps of (respectively) 0.5 units, 0.25 units, 1 unit, 0.125 units and 8
return rcylicone(0.125,1);
// returns a unit rcylicone with a round-radius of 0.125 units and 1 round-step - with defaults for all other arguments - which results in mirroring the geometry of the default unit bcylicone whilst preserving smooth-shading across the surface
return rcylicone(0.25,0.5,0.05,4);
// returns a unit rcylicone with a lower-radius of 0.25 units, an upper-radius of 0.5 units, the default 32 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.05 units and 4 rounding-steps
return rcylicone(4,2,64,1,2);
// returns a rcylicone with a lower-radius of 4 units, an upper-radius of 2 units, 64 segments, a rounding-radius of 1 unit and 2 rounding-steps
return rcylicone(1.23,4.56,78,9,0.123,4);
// returns a rcylicone with a lower-radius of 1.23 units, an upper-radius of 4.56 units, a length of 78 units, 9 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.123 units and 4 rounding-steps
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: cylicone, r-cylicone, s-cylicone, r-p-cylicone, s-r-cylicone, s-r-p-cylicone R-PYRAMID : Generate 3D Rounded-Pyramid
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) fixed-form pyramid solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_pyramid, rnd_pyramid, round_pyramid, rounded_pyramid };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rpyramid ( D size )prefix G3 rpyramid ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rpyramid ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the rpyramid - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 * size : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the rpyramid - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than half of the scale factor size of the rpyramid.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the rpyramid (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ size > ( round_radius * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( round_steps + 1 + 2 ) * 2 - 2 ) * 4Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * 4 ) + 1Practical Examples:return rpyramid();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rpyramid
return rpyramid(5.5);
// returns a rpyramid with a uniform scale factor size of 5.5 and the default round radius (0.125*size = 0.125*5.5 = 0.6875) and round steps (8)
return rpyramid(0.1,4);
// returns a rpyramid with a round radius of 0.1, 4 round steps and the default scale factor size of 1
return rpyramid(10,2,1);
// returns a rpyramid with a uniform scale factor size of 10, a round radius of 2 and a single round step for each edge - this has the effect of constructing the underlying geometry of a beveled variant whilst maintaining the interpolatability of attributes across the rpyramid
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: pyramid, b-pyramid R-GABLE : Generate 3D Rounded-Gable
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) fixed-form gable solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_gable, rnd_gable, round_gable, rounded_gable };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rgable ( D size )prefix G3 rgable ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rgable ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the rgable - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 * size : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the rgable - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than approximately three tenths of the scale factor size of the rgable.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the rgable (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ round_radius < ( size * 0.309 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( 3 * ( round_steps + 1 ) * round_steps * 2 ) + ( 3 * 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( round_steps + 1 ) * 3 * ( round_steps - 1 ) * 2 + ( round_steps * 3 * 2 ) + ( 3 * 2 ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * 3 ) + 2Practical Examples:return rgable();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rgable
return rgable(5.5);
// returns a rgable with a uniform scale factor size of 5.5 and the default round radius (0.125*size = 0.125*5.5 = 0.6875) and round steps (8)
return rgable(0.1,4);
// returns a rgable with a round radius of 0.1, 4 round steps and the default scale factor size of 1
return rgable(10,2,1);
// returns a rgable with a uniform scale factor size of 10, a round radius of 2 and a single round step for each edge - this has the effect of constructing the underlying geometry of a beveled variant whilst maintaining the interpolatability of attributes across the rgable
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: gable, b-gable R-WEDGE : Generate 3D Rounded-Wedge
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) fixed-form wedge solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_wedge, rnd_wedge, round_wedge, rounded_wedge };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rwedge ( D size )prefix G3 rwedge ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rwedge ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the rwedge - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 * size : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the rwedge - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than approximately (just under) three tenths of the scale factor size of the rwedge.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the rwedge (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ round_radius < ( size * 0.292 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( 3 * ( round_steps + 1 ) * round_steps * 2 ) + ( 3 * 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( round_steps + 1 ) * 3 * ( round_steps - 1 ) * 2 + ( round_steps * 3 * 2 ) + ( 3 * 2 ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * 3 ) + 2Practical Examples:return rwedge();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rwedge
return rwedge(5.5);
// returns a rwedge with a uniform scale factor size of 5.5 and the default round radius (0.125*size = 0.125*5.5 = 0.6875) and round steps (8)
return rwedge(0.1,4);
// returns a rwedge with a round radius of 0.1, 4 round steps and the default scale factor size of 1
return rwedge(10,2,1);
// returns a rwedge with a uniform scale factor size of 10, a round radius of 2 and a single round step for each edge - this has the effect of constructing the underlying geometry of a beveled variant whilst maintaining the interpolatability of attributes across the rwedge
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: wedge, b-wedge R-DIAMOND : Generate 3D Rounded-Diamond
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) fixed-form diamond solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_diamond, rnd_diamond, round_diamond, rounded_diamond };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rdiamond ( D size )prefix G3 rdiamond ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rdiamond ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the rdiamond - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 * size : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the rdiamond - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than root two multiplied by half of the scale factor size of the rdiamond.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the rdiamond (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ round_radius < ( size * 0.707 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( round_steps + 1 + 2 ) * 2 - 2 ) * 4Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( round_steps + 2 ) * 4 )Practical Examples:return rdiamond();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rdiamond
return rdiamond(5.5);
// returns a rdiamond with a uniform scale factor size of 5.5 and the default round radius (0.125*size = 0.125*5.5 = 0.6875) and round steps (8)
return rdiamond(0.1,4);
// returns a rdiamond with a round radius of 0.1, 4 round steps and the default scale factor size of 1
return rdiamond(10,2,1);
// returns a rdiamond with a uniform scale factor size of 10, a round radius of 2 and a single round step for each edge - this has the effect of constructing the underlying geometry of a beveled variant whilst maintaining the interpolatability of attributes across the rdiamond
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: diamond, b-diamond R-BRACKET : Generate 3D Rounded-Bracket
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) fixed-form right-angled bracket solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_bracket, rnd_bracket, round_bracket, rounded_bracket };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rbracket ( D size )prefix G3 rbracket ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rbracket ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the rbracket - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 * size : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the rbracket - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than a quarter of the scale factor size of the rbracket.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the rbracket (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ size > ( round_radius * 4 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( 6 * ( round_steps + 1 ) * round_steps * 2 ) + ( 6 * 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( round_steps + 1 ) * 6 * ( round_steps - 1 ) * 2 + ( round_steps * 6 * 2 ) + ( 6 * 2 ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * 6 ) + ( ( 6 - 2 ) * 2 )Practical Examples:return rbracket();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rbracket
return rbracket(5.5);
// returns a rbracket with a uniform scale factor size of 5.5 and the default round radius (0.125*size = 0.125*5.5 = 0.6875) and round steps (8)
return rbracket(0.1,4);
// returns a rbracket with a round radius of 0.1, 4 round steps and the default scale factor size of 1
return rbracket(10,2,1);
// returns a rbracket with a uniform scale factor size of 10, a round radius of 2 and a single round step for each edge - this has the effect of constructing the underlying geometry of a beveled variant whilst maintaining the interpolatability of attributes across the rbracket
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: bracket, b-bracket R-TETRAHEDRON : Generate 3D Rounded-Tetrahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) tetrahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_tetrahedron, rnd_tetrahedron, round_tetrahedron, rounded_tetrahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rtetrahedron ( D size )prefix G3 rtetrahedron ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rtetrahedron ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the rtetrahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 * size : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the rtetrahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than approximately two fifths of the scale factor size of the rtetrahedron.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the rtetrahedron (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ round_radius < ( size * 0.408 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 12 + ( 6 * ( round_steps - 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( ( round_steps - 1 ) / 2 ) * ( ( round_steps - 1 ) / 2 + ( 1 - ( round_steps % 2 ) ) ) * ( 3 * 4 ) ) + ( ( 1 - ( round_steps % 2 ) ) * 4 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = 4 + ( round_steps * 6 ) + ( ( ( round_steps / 2 ) * ( ( round_steps / 2 ) + ( round_steps % 2 ) ) ) * ( 3 * 4 ) ) + ( ( round_steps % 2 ) * 4 )Practical Examples:return rtetrahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rtetrahedron
return rtetrahedron(5.5);
// returns a rtetrahedron with a uniform scale factor size of 5.5 and the default round radius (0.125*size = 0.125*5.5 = 0.6875) and round steps (8)
return rtetrahedron(0.1,4);
// returns a rtetrahedron with a round radius of 0.1, 4 round steps and the default scale factor size of 1
return rtetrahedron(10,2,1);
// returns a rtetrahedron with a uniform scale factor size of 10, a round radius of 2 and a single round step for each edge - this has the effect of constructing the underlying geometry of a beveled variant whilst maintaining the interpolatability of attributes across the rtetrahedron
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: tetrahedron, m-tetrahedron, b-tetrahedron R-OCTAHEDRON : Generate 3D Rounded-Octahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) octahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_octahedron, rnd_octahedron, round_octahedron, rounded_octahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 roctahedron ( D size )prefix G3 roctahedron ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 roctahedron ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the roctahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 * size : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the roctahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than approximately one fifth of the scale factor size of the roctahedron.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the roctahedron (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ round_radius < ( size * 0.204 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 24 + ( 12 * ( round_steps - 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( ( round_steps - 1 ) / 2 ) * ( ( round_steps - 1 ) / 2 + ( 1 - ( round_steps % 2 ) ) ) * ( 4 * 6 ) ) + ( ( 1 - ( round_steps % 2 ) ) * 6 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = 8 + ( round_steps * 12 ) + ( ( ( round_steps / 2 ) * ( ( round_steps / 2 ) + ( round_steps % 2 ) ) ) * ( 4 * 6 ) ) + ( ( round_steps % 2 ) * 6 )Practical Examples:return roctahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit roctahedron
return roctahedron(5.5);
// returns a roctahedron with a uniform scale factor size of 5.5 and the default round radius (0.125*size = 0.125*5.5 = 0.6875) and round steps (8)
return roctahedron(0.1,4);
// returns a roctahedron with a round radius of 0.1, 4 round steps and the default scale factor size of 1
return roctahedron(10,2,1);
// returns a roctahedron with a uniform scale factor size of 10, a round radius of 2 and a single round step for each edge - this has the effect of constructing the underlying geometry of a beveled variant whilst maintaining the interpolatability of attributes across the roctahedron
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: octahedron, m-octahedron, b-octahedron R-DODECAHEDRON : Generate 3D Rounded-Dodecahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) dodecahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_dodecahedron, rnd_dodecahedron, round_dodecahedron, rounded_dodecahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rdodecahedron ( D size )prefix G3 rdodecahedron ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rdodecahedron ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the rdodecahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 * size : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the rdodecahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than approximately a quarter of the scale factor size of the rdodecahedron.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the rdodecahedron (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ round_radius < ( size * 0.262 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 60 + ( 30 * ( round_steps - 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( ( round_steps - 1 ) / 2 ) * ( ( round_steps - 1 ) / 2 + ( 1 - ( round_steps % 2 ) ) ) * ( 3 * 20 ) ) + ( ( 1 - ( round_steps % 2 ) ) * 20 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = 12 + ( round_steps * 30 ) + ( ( ( round_steps / 2 ) * ( ( round_steps / 2 ) + ( round_steps % 2 ) ) ) * ( 3 * 20 ) ) + ( ( round_steps % 2 ) * 20 )Practical Examples:return rdodecahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rdodecahedron
return rdodecahedron(5.5);
// returns a rdodecahedron with a uniform scale factor size of 5.5 and the default round radius (0.125*size = 0.125*5.5 = 0.6875) and round steps (8)
return rdodecahedron(0.1,4);
// returns a rdodecahedron with a round radius of 0.1, 4 round steps and the default scale factor size of 1
return rdodecahedron(10,2,1);
// returns a rdodecahedron with a uniform scale factor size of 10, a round radius of 2 and a single round step for each edge - this has the effect of constructing the underlying geometry of a beveled variant whilst maintaining the interpolatability of attributes across the rdodecahedron
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: dodecahedron, m-dodecahedron, b-dodecahedron R-ICOSAHEDRON : Generate 3D Rounded-Icosahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) icosahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_icosahedron, rnd_icosahedron, round_icosahedron, rounded_icosahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 ricosahedron ( D size )prefix G3 ricosahedron ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 ricosahedron ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the ricosahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 * size : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the ricosahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than approximately nine fiftieths of the scale factor size of the ricosahedron.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the ricosahedron (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ round_radius < ( size * 0.178 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 60 + ( 30 * ( round_steps - 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( ( round_steps - 1 ) / 2 ) * ( ( round_steps - 1 ) / 2 + ( 1 - ( round_steps % 2 ) ) ) * ( 5 * 12 ) ) + ( ( 1 - ( round_steps % 2 ) ) * 12 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = 20 + ( round_steps * 30 ) + ( ( ( round_steps / 2 ) * ( ( round_steps / 2 ) + ( round_steps % 2 ) ) ) * ( 5 * 12 ) ) + ( ( round_steps % 2 ) * 12 )Practical Examples:return ricosahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit ricosahedron
return ricosahedron(5.5);
// returns a ricosahedron with a uniform scale factor size of 5.5 and the default round radius (0.125*size = 0.125*5.5 = 0.6875) and round steps (8)
return ricosahedron(0.1,4);
// returns a ricosahedron with a round radius of 0.1, 4 round steps and the default scale factor size of 1
return ricosahedron(10,2,1);
// returns a ricosahedron with a uniform scale factor size of 10, a round radius of 2 and a single round step for each edge - this has the effect of constructing the underlying geometry of a beveled variant whilst maintaining the interpolatability of attributes across the ricosahedron
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: icosahedron, m-icosahedron, b-icosahedron R-HEXAHEDRON : Generate 3D Rounded-Hexahedron
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) hexahedral solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_hexahedron, rnd_hexahedron, round_hexahedron, rounded_hexahedron };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rhexahedron ( D size )prefix G3 rhexahedron ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rhexahedron ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the rhexahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 * size : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the rhexahedron - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than half of the scale factor size of the rhexahedron.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the rhexahedron (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ size > ( round_radius * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 24 + ( 12 * ( round_steps - 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( ( round_steps - 1 ) / 2 ) * ( ( round_steps - 1 ) / 2 + ( 1 - ( round_steps % 2 ) ) ) * ( 3 * 8 ) ) + ( ( 1 - ( round_steps % 2 ) ) * 8 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = 6 + ( round_steps * 12 ) + ( ( ( round_steps / 2 ) * ( ( round_steps / 2 ) + ( round_steps % 2 ) ) ) * ( 3 * 8 ) ) + ( ( round_steps % 2 ) * 8 )Practical Examples:return rhexahedron();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rhexahedron
return rhexahedron(5.5);
// returns a rhexahedron with a uniform scale factor size of 5.5 and the default round radius (0.125*size = 0.125*5.5 = 0.6875) and round steps (8)
return rhexahedron(0.1,4);
// returns a rhexahedron with a round radius of 0.1, 4 round steps and the default scale factor size of 1
return rhexahedron(10,2,1);
// returns a rhexahedron with a uniform scale factor size of 10, a round radius of 2 and a single round step for each edge - this has the effect of constructing the underlying geometry of a beveled variant whilst maintaining the interpolatability of attributes across the rhexahedron
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: hexahedron, m-hexahedron, b-hexahedron, r-cube Sub-Divided-Variant Solids
S-CUBE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates a 3D axis-aligned bi-linearly sub-divided cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_cube, s_box_3D, s_cuboid, sd_cube, sd_box_3D, sd_cuboid, subd_cube, subd_box_3D, subd_cuboid, sub_divide_cube, sub_divide_box_3D, sub_divide_cuboid, ... (+3) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 scube ( I ncount )prefix G3 scube ( D size, I ncount )prefix G3 scube ( I xcount, I ycount, I zcount )prefix G3 scube ( D width, D height, D depth, I ncount )prefix G3 scube ( D width, D height, D depth, I xcount, I ycount, I zcount )prefix G3 scube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth, I xcount, I ycount, I zcount )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the scube - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum x-coordinate value of the scube - a decimal number.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum y-coordinate value of the scube - a decimal number.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum z-coordinate value of the scube - a decimal number.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the scube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum x-coordinate value is equal to (x + width).•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the scube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum y-coordinate value is equal to (y + height).•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the scube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum z-coordinate value is equal to (z + depth).•
I ncount :
default = 4 : the uniform number of sub-division partitions applied to the scube along the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scube along the x-axis (i.e. along the scube's width) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scube along the y-axis (i.e. along the scube's height) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I zcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scube along the z-axis (i.e. along the scube's depth) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, width, height, depth ] > 0
→ [ ncount, xcount, ycount, zcount ] >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( xcount + 1 ) * ( ycount + 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( xcount + 1 ) * ( zcount + 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) + ( zcount + 1 ) * 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( xcount * ycount * 2 ) + ( xcount * zcount * 2 ) + ( ycount * zcount * 2 )Practical Examples:return scube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit scube
return scube(4);
// returns a unit scube - uniformly sub-divided at each face into 4x4 grid-cells
return scube(2,8);
// returns a uniformly scaled scube with size equal to 2 units and each face uniformly sub-divided into 8x8 grid-cells
return scube(1,2,3);
// returns a unit scube - non-uniformly sub-divided once along the x-axis (i.e. no-sub-division), twice along the y-axis and thrice along the z-axis - resulting in grid-cells of varying size
return scube(1,2,3,2);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled scube with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units and each face sub-divided into 2x2 grid-cells
return scube(1,2,3,1,2,3);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled scube with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units, and sub-divided once along the x-axis, (i.e. no-sub-dividsion), twice along the y-axis and thrice along the z-axis - which (when coupled with the matching size components) yields a 1x2x3 unit block for which each face is composed of uniform (unit-length-edged) cells
return scube(0,0,0,1,2,3,2,4,6);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled scube with minimum position at the origin [0,0,0], and with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units, and sub-divided twice along the x-axis, 4 times along the y-axis and 6-times along the z-axis
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ cube | box_3D | cuboid ] S-CONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_cone, sd_cone, subd_cone, sub_divide_cone, sub_divided_cone };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 scone ( I segments )prefix G3 scone ( I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 scone ( I segments, I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 scone ( D radius, D length, I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 scone ( D radius, D length, I segments, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the scone (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the scone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scone along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ xcount, ycount ] >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments ) + ( ycount * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( ( xcount - 1 ) + ycount ) * segments ) + 1Practical Examples:return scone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit scone
return scone(16);
// returns a unit scone with 16 segments and default values for all other arguments
return scone(2,4);
// returns a unit scone with 2 sub-divide steps along the scone's base and 4 sub-divide steps along the scone's length
return scone(8,1,2);
// returns a unit scone with 8 segments, a single step along the base and 2 sub-divide steps along the length
return scone(1.75,3.25,4,8);
// returns a scone with radius 1.75 units, a length of 3.25 units, the default 32 segments, 4 sub-divide steps along the base and 8 sub-divide steps along the length
return scone(1.23,4.56,78,9,10);
// returns a scone with radius 1.23 units, a length of 4.56 units, 78 segments, 9 sub-divide steps along the base and 10 sub-divide steps along the length
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: cone, s-p-cone, s-b-cone, s-r-cone, s-b-p-cone, s-r-p-cone S-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_cylinder, sd_cylinder, subd_cylinder, sub_divide_cylinder, sub_divided_cylinder };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 scylinder ( I segments )prefix G3 scylinder ( I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 scylinder ( I segments, I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 scylinder ( D radius, D length, I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 scylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the scylinder (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the scylinder (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scylinder along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base and top) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scylinder along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ xcount, ycount ] >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments * 2 ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( ( xcount - 1 ) * 2 + ycount ) * segments ) + 2Practical Examples:return scylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit scylinder
return scylinder(16);
// returns a unit scylinder with 16 segments and default values for all other arguments
return scylinder(2,4);
// returns a unit scylinder with 2 sub-divide steps along the x-axis and 4 sub-divide steps along the y-axis
return scylinder(8,1,2);
// returns a unit scylinder with 8 segments, a single step along the x-axis and 2 sub-divide steps along the y-axis
return scylinder(1.75,3.25,4,8);
// returns a scylinder with radius 1.75 units, a length of 3.25 units, the default 32 segments, 4 sub-divide steps along the x-axis and 8 sub-divide steps along the y-axis
return scylinder(1.23,4.56,78,9,10);
// returns a scylinder with radius 1.23 units, a length of 4.56 units, 78 segments, 9 sub-divide steps along the x-axis and 10 sub-divide steps along the y-axis
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: cylinder, s-p-cylinder, s-b-cylinder, s-r-cylinder, s-b-p-cylinder, s-r-p-cylinder S-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Cylicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_cylicone, sd_cylicone, subd_cylicone, sub_divide_cylicone, sub_divided_cylicone };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 scylicone ( I segments )prefix G3 scylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius )prefix G3 scylicone ( I lower_xcount, I upper_xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 scylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, I lower_xcount, I upper_xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 scylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments, I lower_xcount, I upper_xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the scylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius at the top of the scylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the scylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I lower_xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scylicone along the x-axis at its lower circular edge - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I upper_xcount :
default = 2 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scylicone along the x-axis at its upper circular edge - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scylicone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] >= 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ lower_xcount, upper_xcount, ycount ] >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( lower_xcount * segments ) + ( upper_xcount * segments ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( lower_xcount + upper_xcount + ycount - 2 ) * segments ) + 2Practical Examples:return scylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit scylicone
return scylicone(4);
// returns a unit scylicone with 4 segments and defaults for all other arguments
return scylicone(0.25,0.375);
// returns a scylicone with a lower-radius of 0.25 units and an upper-radius of 0.375 units and default values for all other arguments
return scylicone(4,2,8);
// returns a unit scylicone sub-divided 4 times along the x-axis at its base, twice at its top and 8 times along the y-axis (along its length)
return scylicone(2,1,4,2,4);
// returns a scylicone with a lower-radius of 2 units, an upper-radius of 1 unit, and sub-divided 4 times and twice along the x-axis (at base and top) and 4 times along the y-axis
return scylicone(5,2,10,64,10,4,20);
// returns a scylicone with a lower-radius of 5 units, an upper-radius of 2 units, a length of 10 units, 64 segments and sub-divided 10 times along the x-axis at its base, 4 times at its top, and 20 times along the y-axis
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
Additional Notes:Related Symbols:See Also: cylicone, s-p-cylicone, s-b-cylicone, s-r-cylicone, s-b-p-cylicone, s-r-p-cylicone S-CAPSULE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Capsule
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided capsule solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_capsule, s_cap_3D, s_capsule_3D, sd_capsule, sd_cap_3D, sd_capsule_3D, subd_capsule, subd_cap_3D, subd_capsule_3D, sub_divide_capsule, sub_divide_cap_3D, sub_divide_capsule_3D, ... (+3) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 scapsule ( I sub_divide_count )prefix G3 scapsule ( D radius, D length, I sub_divide_count )prefix G3 scapsule ( D radius, D length, I segments, I steps, I sub_divide_count )prefix G3 scapsule ( D radius, D x1, D y1, D z1, D x2, D y2, D z2, I sub_divide_count )prefix G3 scapsule ( D radius, D x1, D y1, D z1, D x2, D y2, D z2, I segments, I steps, I sub_divide_count )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius of the scapsule's hemispheres - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 0.5 : the length of the scapsule's straight-edge section (i.e. its cylindrical portion's height along the y-axis between its north and south hemispheres) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal slices (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps about the y-axis) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I steps :
default = 16 : the number of latitudinal stacks (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of quarter-circle steps from each of the scapsule's hemisphere's poles, to their equators) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I sub_divide_count :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the scapsule's straight-edge section along the y-axis - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
D x1 :
default = 0 : the x-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the scapsule's central spine.•
D y1 :
default = -0.25 : the y-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the scapsule's central spine.•
D z1 :
default = 0 : the z-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the scapsule's central spine.•
D x2 :
default = 0 : the x-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the scapsule's central spine.•
D y2 :
default = 0.25 : the y-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the scapsule's central spine.•
D z2 :
default = 0 : the z-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the scapsule's central spine.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ steps, sub_divide_count ] >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * steps * 2 ) + 2 + ( ( sub_divide_count - 1 ) * segments )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments * ( steps - 1 ) * 2 ) + 2 + ( sub_divide_count * segments )Practical Examples:return scapsule();
// returns the default zero-argument unit scapsule
return scapsule(2);
// returns a scapsule sub-divided twice along y-axis - with defaults for all other arguments
return scapsule(1,8,8);
// returns a scapsule with a radius of 1 unit, a length of 8 units and 8 sub-divide steps along its length
return scapsule(1,8,16,8,4);
// returns a scapsule with radius equal to 1 unit, a length of 8 units, 16 segments, 8 semi-spherical-steps and 4 sub-divide steps along its length
return scapsule(0.25,-5,-5,-5,5,5,5,24);
// returns a scapsule with a radius of 0.25 units and start and end positions of respectively [-5,-5,-5] and [5,5,5] - corresponding to a dialogonal line with length sqrt(300) (approximately: 17.35 units) - using the default 32 slices and 16 stacks - with 24 sub-divide steps along its length
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ capsule | cap_3D | capsule_3D ] O-CUBE : Generate 3D Octant-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates a 3D axis-aligned octant-split cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { o_cube, o_box_3D, o_cuboid, oct_cube, oct_box_3D, oct_cuboid, octa_cube, octa_box_3D, octa_cuboid, octo_cube, octo_box_3D, octo_cuboid, ... (+6) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 ocube ( D size )prefix G3 ocube ( D width, D height, D depth )prefix G3 ocube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the ocube - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum x-coordinate value of the ocube - a decimal number.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum y-coordinate value of the ocube - a decimal number.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum z-coordinate value of the ocube - a decimal number.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the ocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum x-coordinate value is equal to (x + width).•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the ocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum y-coordinate value is equal to (y + height).•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the ocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum z-coordinate value is equal to (z + depth).→ [ width, height, depth, size ] > 0
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 54Polygon Count:→ |P| = 24Practical Examples:return ocube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit ocube
return ocube(6);
// returns a uniform ocube with width, height and depth equal to 6 units
return cuboid(1,2,3);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled ocube centered about the origin - with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units
return obox3D(0,-5,2,8,10,4);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled, offset ocube with minimum aabb position equal to [0,-5,2] and a width, height and depth equal to [8,10,4] units
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ o | oct | octa | octo | octant | octant_split ]
+
[ cube | box_3D | cuboid ] M-O-CUBE : Generate 3D Manifold-Octant-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates a 3D axis-aligned manifold octant-split cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { m_o_cube, m_o_box_3D, m_o_cuboid, m_oct_cube, m_oct_box_3D, m_oct_cuboid, m_octa_cube, m_octa_box_3D, m_octa_cuboid, m_octo_cube, m_octo_box_3D, m_octo_cuboid, ... (+24) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 mocube ( D size )prefix G3 mocube ( D width, D height, D depth )prefix G3 mocube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the mocube - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum x-coordinate value of the mocube - a decimal number.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum y-coordinate value of the mocube - a decimal number.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum z-coordinate value of the mocube - a decimal number.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the mocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum x-coordinate value is equal to (x + width).•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the mocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum y-coordinate value is equal to (y + height).•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the mocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum z-coordinate value is equal to (z + depth).→ [ width, height, depth, size ] > 0
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 26Polygon Count:→ |P| = 24Practical Examples:return mocube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit mocube
return mocube(6);
// returns a uniform mocube with width, height and depth equal to 6 units
return cuboid(1,2,3);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled mocube centered about the origin - with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units
return mobox3D(0,-5,2,8,10,4);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled, offset mocube with minimum aabb position equal to [0,-5,2] and a width, height and depth equal to [8,10,4] units
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ m | manifold ]
+
[ o | oct | octa | octo | octant | octant_split ]+
[ cube | box_3D | cuboid ] Hybrid-Combinatorial-Variant Solids
B-O-CUBE : Generate 3D Beveled-Octant-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) octant-split cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_o_cube, b_o_box_3D, b_o_cuboid, b_oct_cube, b_oct_box_3D, b_oct_cuboid, b_octa_cube, b_octa_box_3D, b_octa_cuboid, b_octo_cube, b_octo_box_3D, b_octo_cuboid, ... (+96) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bocube ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bocube ( D size, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bocube ( D width, D height, D depth, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bocube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the bocube - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum x-coordinate value of the bocube - a decimal number.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum y-coordinate value of the bocube - a decimal number.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum z-coordinate value of the bocube - a decimal number.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the bocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum x-coordinate value is equal to (x + width).•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the bocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum y-coordinate value is equal to (y + height).•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the bocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum z-coordinate value is equal to (z + depth).•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than half of the minimum of the bocubes's width, height, depth or uniform size factor.→ [ size, width, height, depth, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ [ size, width, height, depth ] > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 150Polygon Count:→ |P| = 56Practical Examples:return bocube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bocube
return bocube(0.25);
// returns a beveled-octant-cuboid with a uniform size of 1 unit and bevel-distance of 0.25 units
return bevel_octo_cuboid(1,2,3,0.125);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled beveled-octant-cuboid with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units and a bevel-distance of 0.125 units
return bobox3D(0,-5,2,8,10,4,0.5);
// returns a non-uniform scaled, offset beveled-octant-cuboid with minimum aabb position equal to [0,-5,2] units, width, height and depth equal to [8,10,4] units and a bevel-distance of 0.5 units
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
+
[ o | oct | octa | octo | octant | octant_split ]+
[ cube | box_3D | cuboid ] R-O-CUBE : Generate 3D Rounded-Octant-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded (smooth-edged) octant-split cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_o_cube, r_o_box_3D, r_o_cuboid, r_oct_cube, r_oct_box_3D, r_oct_cuboid, r_octa_cube, r_octa_box_3D, r_octa_cuboid, r_octo_cube, r_octo_box_3D, r_octo_cuboid, ... (+60) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rocube ( D size )prefix G3 rocube ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rocube ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rocube ( D width, D height, D depth, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rocube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the rocube - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum x-coordinate value of the rocube - a decimal number.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum y-coordinate value of the rocube - a decimal number.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum z-coordinate value of the rocube - a decimal number.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the rocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum x-coordinate value is equal to (x + width).•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the rocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum y-coordinate value is equal to (y + height).•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the rocube - a non-zero positive decimal number - the maximum z-coordinate value is equal to (z + depth).•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the rocube - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than half of the minimum of the rocube's width, height, depth or uniform size factor.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the corners and edges of the rocube - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ size, width, height, depth, round_radius ] > 0
→ round_steps >= 1
→ [ size, width, height, depth ] > ( round_radius * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( 3 * 3 * 6 ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * ( 3 + 3 + 3 ) * 4 ) + ( ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * round_steps + 1 ) * 8 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( 2 * 2 * 2 * 3 ) + ( round_steps * ( 2 + 2 + 2 ) * 4 ) + ( round_steps * round_steps * 8 )Practical Examples:return rocube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rocube
return rocube(2);
// returns a rounded-octant-cuboid with a uniform size of 2 units and rounding-radius of 0.25 units - with the default 8 rounding-steps per-axis-corner
return ROCUBE(0.125,1);
// returns a uniformly-sized rounded-octant-cuboid with a rounding-radius of 0.125 units and a single rounding-step per-axis-corner - which has the effect of matching the geometric form of a beveled-octant-cuboid whilst retaining smooth-shading across the surface
return round_octo_cuboid(1,2,3,0.125,8);
// returns a non-uniformly scaled rounded-octant-cuboid with width, height and depth equal to [1,2,3] units and a rounding-radius of 0.125 units - with 8 rounding-steps per-axis-corner
return robox3D(0,-5,2,8,10,4,0.5,4);
// returns a non-uniform scaled, offset rounded-octant-cuboid with minimum aabb position equal to [0,-5,2] units, width, height and depth equal to [8,10,4] units and a rounding-radius of 0.5 units - with 4 rounding-steps per-axis-corner
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
+
[ o | oct | octa | octo | octant | octant_split ]+
[ cube | box_3D | cuboid ] B-P-CONE : Generate 3D Beveled-Polar-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) polar conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_p_cone, b_polar_cone, b_pole_cone, b_polar_point_cone, bevel_p_cone, bevel_polar_cone, bevel_pole_cone, bevel_polar_point_cone, beveled_p_cone, beveled_polar_cone, beveled_pole_cone, beveled_polar_point_cone, ... (+12) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bpcone ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bpcone ( I segments, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bpcone ( D radius, D length, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bpcone ( D radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the bpcone (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the bpcone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bpcone - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than the bpcone's radius and less than the bpcones's length.→ [ radius, length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ radius, length ] > bevel_distance
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * 4 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments * 3 )Practical Examples:return bpcone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bpcone
return bpcone(0.05);
// returns a unit bpcone with a bevel-distance of 0.05 units and the default 32 segments
return bpcone(4,0.125);
// returns a unit bpcone with 4 segments and a bevel-distance of 0.125 units
return bpcone(0.25,4.5,0.05);
// returns a bpcone with a radius of 0.25 units, a length of 4.5 units and a bevel-distance of 0.05 units
return bpcone(2,10,16,1);
// returns a bpcone with a radius of 2 units, a length of 10 units, 16 segments and a bevel-distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] B-P-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Beveled-Polar-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) polar cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_p_cylinder, b_polar_cylinder, b_pole_cylinder, b_polar_point_cylinder, bevel_p_cylinder, bevel_polar_cylinder, bevel_pole_cylinder, bevel_polar_point_cylinder, beveled_p_cylinder, beveled_polar_cylinder, beveled_pole_cylinder, beveled_polar_point_cylinder, ... (+12) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bpcylinder ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bpcylinder ( I segments, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bpcylinder ( D radius, D length, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bpcylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the bpcylinder (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the bpcylinder (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bpcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than the bpcylinder's radius and less than half of the bpcylinder's length.→ [ radius, length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ radius > bevel_distance
→ length > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * 8 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments * 5 )Practical Examples:return bpcylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bpcylinder
return bpcylinder(0.05);
// returns a unit bpcylinder with a bevel-distance of 0.05 units and the default 32 segments
return bpcylinder(4,0.125);
// returns a unit bpcylinder with 4 segments and a bevel-distance of 0.125 units
return bpcylinder(0.25,4.5,0.05);
// returns a bpcylinder with a radius of 0.25 units, a length of 4.5 units and a bevel-distance of 0.05 units
return bpcylinder(2,10,16,1);
// returns a bpcylinder with a radius of 2 units, a length of 10 units, 16 segments and a bevel-distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] B-P-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Beveled-Polar-Cylicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D beveled (chamfered-edge) polar conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { b_p_cylicone, b_polar_cylicone, b_pole_cylicone, b_polar_point_cylicone, bevel_p_cylicone, bevel_polar_cylicone, bevel_pole_cylicone, bevel_polar_point_cylicone, beveled_p_cylicone, beveled_polar_cylicone, beveled_pole_cylicone, beveled_polar_point_cylicone, ... (+12) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 bpcylicone ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bpcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bpcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, I segments, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 bpcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the bpcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius at the top of the bpcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the bpcylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the bpcylicone (both its lower and upper circular edges) - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than the bpcylicone's lower and upper radii and less than half of the bpcylicone's length.→ [ length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] > bevel_distance
→ length > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * 8 + 2 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments * 5 )Practical Examples:return bpcylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit bpcylicone
return bpcylicone(0.05);
// returns a unit bpcylicone with a bevel-distance of 0.05 units and the default 32 segments
return bpcylicone(0.25,0.5,0.125);
// returns a unit bpcylicone with a lower-radius of 0.25 units an upper-radius of 0.5 units, the default 32 segments and a bevel-distance of 0.125 units
return bpcylicone(0.75,0.25,4.5,0.05);
// returns a bpcylicone with a lower-radius of 0.75 units, an upper-radius of 0.25 units, a length of 4.5 units and a bevel-distance of 0.05 units
return bpcylicone(4,2,10,16,1);
// returns a bpcylicone with a lower-radius of 4 units, an upper-radius of 2 units, a length of 10 units, 16 segments and a bevel-distance of 1 unit
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]
+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] R-P-CONE : Generate 3D Rounded-Polar-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded/smooth polar conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_p_cone, r_polar_cone, r_pole_cone, r_polar_point_cone, rnd_p_cone, rnd_polar_cone, rnd_pole_cone, rnd_polar_point_cone, round_p_cone, round_polar_cone, round_pole_cone, round_polar_point_cone, ... (+4) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rpcone ( I segments )prefix G3 rpcone ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rpcone ( I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rpcone ( D radius, D length, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rpcone ( D radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the rpcone (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the rpcone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the circular edge of the rpcone - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than the radius of the rpcone and less than the length of the rpcone.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the circular edge of the rpcone (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, round_radius ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ radius, length ] > round_radius
→ round_steps >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( round_steps + 2 ) * segments )Practical Examples:return rpcone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rpcone
return rpcone(8);
// returns a unit rpcone with 8 segments and default main-radius, length, round-radius and round-steps of (respectively) 0.5 units, 1 unit, 0.125 units and 8
return rpcone(0.125,1);
// returns a unit rpcone with a round-radius of 0.125 units and 1 round-step - with defaults for all other arguments - which results in mirroring the geometry of the default unit bpcone whilst preserving smooth-shading across the surface
return rpcone(16,0.25,4);
// returns a unit rpcone with 16 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.25 units and 4 rounding-steps
return rpcone(2,5,1,2);
// returns a rpcone with a main-radius of 2 units, a length of 5 units, a rounding-radius of 1 unit and 2 rounding-steps
return rpcone(1.23,4.56,78,0.123,4);
// returns a rpcone with main-radius of 1.23 units, a length of 4.56 units, 78 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.123 units and 4 rounding-steps
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] R-P-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Rounded-Polar-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded/smooth polar cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_p_cylinder, r_polar_cylinder, r_pole_cylinder, r_polar_point_cylinder, rnd_p_cylinder, rnd_polar_cylinder, rnd_pole_cylinder, rnd_polar_point_cylinder, round_p_cylinder, round_polar_cylinder, round_pole_cylinder, round_polar_point_cylinder, ... (+4) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rpcylinder ( I segments )prefix G3 rpcylinder ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rpcylinder ( I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rpcylinder ( D radius, D length, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rpcylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the rpcylinder (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the rpcylinder (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the circular edges of the rpcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than the radius of the rpcylinder and less than half the length of the rpcylinder.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the circular edges of the rpcylinder (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, round_radius ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ radius > round_radius
→ length > ( round_radius * 2 )
→ round_steps >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * 2 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( round_steps * 2 + 1 + 2 ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return rpcylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rpcylinder
return rpcylinder(8);
// returns a unit rpcylinder with 8 segments and default main-radius, length, round-radius and round-steps of (respectively) 0.5 units, 1 unit, 0.125 units and 8
return rpcylinder(0.125,1);
// returns a unit rpcylinder with a round-radius of 0.125 units and 1 round-step - with defaults for all other arguments - which results in mirroring the geometry of the default unit bpcylinder whilst preserving smooth-shading across the surface
return rpcylinder(16,0.25,4);
// returns a unit rpcylinder with 16 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.25 units and 4 rounding-steps
return rpcylinder(2,5,1,2);
// returns a rpcylinder with a main-radius of 2 units, a length of 5 units, a rounding-radius of 1 unit and 2 rounding-steps
return rpcylinder(1.23,4.56,78,0.123,4);
// returns a rpcylinder with main-radius of 1.23 units, a length of 4.56 units, 78 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.123 units and 4 rounding-steps
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] R-P-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Rounded-Polar-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D rounded/smooth polar conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { r_p_cylicone, r_polar_cylicone, r_pole_cylicone, r_polar_point_cylicone, rnd_p_cylicone, rnd_polar_cylicone, rnd_pole_cylicone, rnd_polar_point_cylicone, round_p_cylicone, round_polar_cylicone, round_pole_cylicone, round_polar_point_cylicone, ... (+4) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 rpcylicone ( I segments )prefix G3 rpcylicone ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rpcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rpcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 rpcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the rpcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius at the top of the rpcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the rpcylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the lower and upper circular edges of the rpcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than both the lower and upper radii of the rpcylicone and less than half the length of the rpcylicone.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of steps used to round the lower and upper circular edges of the rpcylicone (i.e. the discretisation resolution) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ length, round_radius ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] > round_radius
→ length > ( round_radius * 2 )
→ round_steps >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * 2 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( round_steps * 2 + 1 + 2 ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return rpcylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit rpcylicone
return rpcylicone(8);
// returns a unit rpcylicone with 8 segments and default lower-radius, upper-radius, length, round-radius and round-steps of (respectively) 0.5 units, 0.25 units, 1 unit, 0.125 units and 8
return rpcylicone(0.125,1);
// returns a unit rpcylicone with a round-radius of 0.125 units and 1 round-step - with defaults for all other arguments - which results in mirroring the geometry of the default unit bpcylicone whilst preserving smooth-shading across the surface
return rpcylicone(0.25,0.5,0.05,4);
// returns a unit rpcylicone with a lower-radius of 0.25 units, an upper-radius of 0.5 units, the default 32 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.05 units and 4 rounding-steps
return rpcylicone(4,2,64,1,2);
// returns a rpcylicone with a lower-radius of 4 units, an upper-radius of 2 units, 64 segments, a rounding-radius of 1 unit and 2 rounding-steps
return rpcylicone(1.23,4.56,78,9,0.123,4);
// returns a rpcylicone with a lower-radius of 1.23 units, an upper-radius of 4.56 units, a length of 78 units, 9 segments, a rounding-radius of 0.123 units and 4 rounding-steps
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]
+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] S-P-CONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Polar-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided polar conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_p_cone, s_polar_cone, s_pole_cone, s_polar_point_cone, sd_p_cone, sd_polar_cone, sd_pole_cone, sd_polar_point_cone, subd_p_cone, subd_polar_cone, subd_pole_cone, subd_polar_point_cone, ... (+8) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 spcone ( I segments )prefix G3 spcone ( I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 spcone ( I segments, I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 spcone ( D radius, D length, I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 spcone ( D radius, D length, I segments, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the spcone (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the spcone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the spcone along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the spcone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ xcount, ycount ] >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments ) + ( ycount * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( xcount + ycount ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return spcone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit spcone
return spcone(16);
// returns a unit spcone with 16 segments and default values for all other arguments
return spcone(2,4);
// returns a unit spcone with 2 sub-divide steps along the spcone's base and 4 sub-divide steps along the spcone's length
return spcone(8,1,2);
// returns a unit spcone with 8 segments, a single step along the base and 2 sub-divide steps along the length
return spcone(1.75,3.25,4,8);
// returns a spcone with radius 1.75 units, a length of 3.25 units, the default 32 segments, 4 sub-divide steps along the base and 8 sub-divide steps along the length
return spcone(1.23,4.56,78,9,10);
// returns a spcone with radius 1.23 units, a length of 4.56 units, 78 segments, 9 sub-divide steps along the base and 10 sub-divide steps along the length
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] S-P-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Polar-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided polar cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_p_cylinder, s_polar_cylinder, s_pole_cylinder, s_polar_point_cylinder, sd_p_cylinder, sd_polar_cylinder, sd_pole_cylinder, sd_polar_point_cylinder, subd_p_cylinder, subd_polar_cylinder, subd_pole_cylinder, subd_polar_point_cylinder, ... (+8) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 spcylinder ( I segments )prefix G3 spcylinder ( I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 spcylinder ( I segments, I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 spcylinder ( D radius, D length, I xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 spcylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the spcylinder (diameter = radius * 2) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the spcylinder (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the spcylinder along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base and top) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the spcylinder along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ xcount, ycount ] >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments * 2 ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( xcount * 2 + ycount ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return spcylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit spcylinder
return spcylinder(16);
// returns a unit spcylinder with 16 segments and default values for all other arguments
return spcylinder(2,4);
// returns a unit spcylinder with 2 sub-divide steps along the x-axis and 4 sub-divide steps along the y-axis
return spcylinder(8,1,2);
// returns a unit spcylinder with 8 segments, a single step along the x-axis and 2 sub-divide steps along the y-axis
return spcylinder(1.75,3.25,4,8);
// returns a spcylinder with radius 1.75 units, a length of 3.25 units, the default 32 segments, 4 sub-divide steps along the x-axis and 8 sub-divide steps along the y-axis
return spcylinder(1.23,4.56,78,9,10);
// returns a spcylinder with radius 1.23 units, a length of 4.56 units, 78 segments, 9 sub-divide steps along the x-axis and 10 sub-divide steps along the y-axis
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] S-P-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Polar-Cylicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided polar conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_p_cylicone, s_polar_cylicone, s_pole_cylicone, s_polar_point_cylicone, sd_p_cylicone, sd_polar_cylicone, sd_pole_cylicone, sd_polar_point_cylicone, subd_p_cylicone, subd_polar_cylicone, subd_pole_cylicone, subd_polar_point_cylicone, ... (+8) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 spcylicone ( I segments )prefix G3 spcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius )prefix G3 spcylicone ( I lower_xcount, I upper_xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 spcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, I lower_xcount, I upper_xcount, I ycount )prefix G3 spcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments, I lower_xcount, I upper_xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the spcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius at the top of the spcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the spcylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretistion resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I lower_xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the spcylicone along the x-axis at its lower circular edge - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I upper_xcount :
default = 2 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the spcylicone along the x-axis at its upper circular edge - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the spcylicone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] >= 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ lower_xcount, upper_xcount, ycount ] >= 1
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments * 2 ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( lower_xcount + upper_xcount + ycount ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return spcylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit spcylicone
return spcylicone(4);
// returns a unit spcylicone with 4 segments and defaults for all other arguments
return spcylicone(0.25,0.375);
// returns a spcylicone with a lower-radius of 0.25 units and an upper-radius of 0.375 units and default values for all other arguments
return spcylicone(4,2,8);
// returns a unit spcylicone sub-divided 4 times along the x-axis at its base, twice at its top and 8 times along the y-axis (along its length)
return spcylicone(2,1,4,2,4);
// returns a spcylicone with a lower-radius of 2 units, an upper-radius of 1 unit, and sub-divided 4 times and twice along the x-axis (at base and top) and 4 times along the y-axis
return spcylicone(5,2,10,64,10,4,20);
// returns a spcylicone with a lower-radius of 5 units, an upper-radius of 2 units, a length of 10 units, 64 segments and sub-divided 10 times along the x-axis at its base, 4 times at its top, and 20 times along the y-axis
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] S-C-CAPSULE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Capped-Capsule
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided flat-topped (capped) capsule solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_c_capsule, s_c_cap_3D, s_c_capsule_3D, s_cap_capsule, s_cap_cap_3D, s_cap_capsule_3D, s_capped_capsule, s_capped_cap_3D, s_capped_capsule_3D, sd_c_capsule, sd_c_cap_3D, sd_c_capsule_3D, ... (+33) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 sccapsule ( I sub_divide_count )prefix G3 sccapsule ( D radius, D length, I sub_divide_count )prefix G3 sccapsule ( D radius, D length, I segments, I steps, I sub_divide_count )prefix G3 sccapsule ( D radius, D x1, D y1, D z1, D x2, D y2, D z2, I sub_divide_count )prefix G3 sccapsule ( D radius, D x1, D y1, D z1, D x2, D y2, D z2, I segments, I steps, I sub_divide_count )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.25 : the radius of the sccapsule's hemispheres - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
D length :
default = 0.5 : the length of the sccapsule's straight-edge section (i.e. its cylindrical portion's height along the y-axis between its north and south hemispheres) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal slices (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps about the y-axis) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 3.•
I steps :
default = 16 : the number of latitudinal stacks (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of quarter-circle steps from each of the sccapsule's hemisphere's poles, to their equators) - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 2.•
I sub_divide_count :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sccapsule's straight-edge section along the y-axis - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 2.•
D x1 :
default = 0 : the x-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the sccapsule's central spine.•
D y1 :
default = -0.25 : the y-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the sccapsule's central spine.•
D z1 :
default = 0 : the z-axis component of the first vertex in the line defining the sccapsule's central spine.•
D x2 :
default = 0 : the x-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the sccapsule's central spine.•
D y2 :
default = 0.25 : the y-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the sccapsule's central spine.•
D z2 :
default = 0 : the z-axis component of the second vertex in the line defining the sccapsule's central spine.→ [ radius, length ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ steps >= 2
→ sub_divide_count >= 2
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = slices ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( segments * steps * 2 ) + 2 + ( ( sub_divide_count - 1 ) * segments )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( segments * steps * 2 ) + ( sub_divide_count * segments )Practical Examples:return sccapsule();
// returns the default zero-argument unit sccapsule
return sccapsule(2);
// returns a sccapsule sub-divided twice along y-axis - with defaults for all other arguments
return sccapsule(1,8,8);
// returns a sccapsule with a radius of 1 unit, a length of 8 units and 8 sub-divide steps along its length
return sccapsule(1,8,16,8,4);
// returns a sccapsule with radius equal to 2 unit, a length of 8 units, 16 segments, 8 semi-spherical-steps and 4 sub-divide steps along its length
return sccapsule(0.25,-5,-5,-5,5,5,5,24);
// returns a sccapsule with a radius of 0.25 units and start and end positions of respectively [-5,-5,-5] and [5,5,5] - corresponding to a dialogonal line with length sqrt(300) (approximately: 17.35 units) - using the default 32 slices and 16 stacks - with 24 sub-divide steps along its length
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ capsule | cap_3D | capsule_3D ]•
If the sub_divide_count argument is less than 2 (i.e. 1) then the s-c-capsule is equivalent to a c-capsule. S-B-CUBE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Beveled-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided beveled (chamfered-edge) cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_b_cube, s_b_box_3D, s_b_cuboid, s_bevel_cube, s_bevel_box_3D, s_bevel_cuboid, s_beveled_cube, s_beveled_box_3D, s_beveled_cuboid, s_bevelled_cube, s_bevelled_box_3D, s_bevelled_cuboid, ... (+78) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 sbcube ( D bevel_distance )prefix G3 sbcube ( D size, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 sbcube ( D size, D bevel_distance, I ncount )prefix G3 sbcube ( D width, D height, D depth, D bevel_distance )prefix G3 sbcube ( D width, D height, D depth, D bevel_distance, I bcount, I xcount, I ycount, I zcount )prefix G3 sbcube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth, D bevel_distance, I bcount, I xcount, I ycount, I zcount )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the sbcube - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum x-coordinate position of the sbcube - a decimal number.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum y-coordinate position of the sbcube - a decimal number.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the axis-aligned bounding-box minimum z-coordinate position of the sbcube - a decimal number.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the sbcube - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the sbcube - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the sbcube - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the corners and edges of the sbcube - a non-zero positive decimal number which must be less than half of the minimum of the sbcube's width, height, depth or uniform size.•
I bcount :
default = 1 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcube's beveled region - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ncount :
default = 4 : the uniform number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcube along the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcube along the x-axis (i.e. along the sbcube's width) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcube along the y-axis (i.e. along the sbcube's height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I zcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcube along the z-axis (i.e. along the sbcube's depth) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ width, height, depth, size, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ [ bcount, ncount, xcount, ycount, zcount ] >= 1
→ [ width, height, depth, size ] > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( xcount + 1 ) * ( ycount + 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( xcount + 1 ) * ( zcount + 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * ( zcount + 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( bcount + 1 ) * ( xcount + 1 + ycount + 1 + zcount + 1 ) * 4 ) + ( ( bcount * 3 + 1 ) * 8 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( xcount * ycount * 2 ) + ( xcount * zcount * 2 ) + ( ycount * zcount * 2 ) + ( bcount * ( xcount + ycount + zcount ) * 4 ) + ( bcount * 3 * 8 )Practical Examples:return sbcube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit sbcube
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]+
[ cube | box_3D | cuboid ] S-B-CONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Beveled-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided beveled (chamfered-edge) conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_b_cone, s_bevel_cone, s_beveled_cone, s_bevelled_cone, s_chamfer_cone, s_chamfered_cone, sd_b_cone, sd_bevel_cone, sd_beveled_cone, sd_bevelled_cone, sd_chamfer_cone, sd_chamfered_cone, ... (+18) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 sbcone ( D radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance, I bcount, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the sbcone - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the sbcone (i.e. its height along the y-axis - or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or number of circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the sbcone - a non-zero positive decimal which must be less than the sbcone's radius and less than the sbcone's length.•
I bcount :
default = 1 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcone's beveled region - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcone along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions apploed to the sbcone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ bcount, xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ [ radius, length ] > bevel_distance
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments ) + ( ycount * segments ) + ( ( bcount + 1 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( ( xcount - 1 ) + ycount + bcount ) * segments ) + 1Practical Examples:return sbcone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit sbcone
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ] S-B-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Beveled-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided beveled (chamfered-edge) cylinderical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_b_cylinder, s_bevel_cylinder, s_beveled_cylinder, s_bevelled_cylinder, s_chamfer_cylinder, s_chamfered_cylinder, sd_b_cylinder, sd_bevel_cylinder, sd_beveled_cylinder, sd_bevelled_cylinder, sd_chamfer_cylinder, sd_chamfered_cylinder, ... (+18) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 sbcylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance, I bcount, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the sbcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the sbcylinder (i.e. its height along the y-axis - or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or number of circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perdandicular chamfer of bevel length) applied to the sbcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal which must be less than the sbcylinder's radius and less than half of the sbcylinder's length.•
I bcount :
default = 1 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcylinder's beveled regions - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcylinder along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base and top) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbyclinder along the y-axis (i.e. along its length pr vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ bcount, xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ radius > bevel_distance
→ length > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments * 2 ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + ( ( bcount + 1 ) * segments * 2 ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( ( xcount - 1 ) * 2 ) + ycount + ( bcount * 2 ) ) * segments + 2Practical Examples:return sbcylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit sbcylinder
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ] S-B-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Beveled-Cylicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided beveled (chamfered-edge) conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_b_cylicone, s_bevel_cylicone, s_beveled_cylicone, s_bevelled_cylicone, s_chamfer_cylicone, s_chamfered_cylicone, sd_b_cylicone, sd_bevel_cylicone, sd_beveled_cylicone, sd_bevelled_cylicone, sd_chamfer_cylicone, sd_chamfered_cylicone, ... (+18) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 sbcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance, I bcount, I lower_xcount, I upper_xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the sbcylicone - a positive decimal greater than zero and greater than the beveling distance.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the top of the sbcylicone - a positive decimal greater than zero and greater than the beveling distance.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the sbcylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the sbcylicone (both its lower and upper circular edges) - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than the sbcylicone's lower and upper radii and less than half of the sbcylicone's length.•
I bcount :
default = 1 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcylicone's beveled regions - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I lower_xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcylicone along the x-axis at its lower circular edge - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I upper_xcount :
default = 2 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcylicone along the x-axis at its upper circular edge - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbcylicone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] >= 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ bcount, lower_xcount, upper_xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] > bevel_distance
→ length > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( lower_xcount * segments ) + ( upper_xcount * segments ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + ( ( bcount + 1 ) * segments * 2 ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( lower_xcount - 1 ) + ( upper_xcount - 1 ) + ycount + ( bcount * 2 ) ) * segments + 2Practical Examples:return sbcylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit sbcylicone
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ] S-R-CUBE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Rounded-Cuboid
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided rounded (smooth-edged) cuboidal solid'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_r_cube, s_r_box_3D, s_r_cuboid, s_rnd_cube, s_rnd_box_3D, s_rnd_cuboid, s_round_cube, s_round_box_3D, s_round_cuboid, s_rounded_cube, s_rounded_box_3D, s_rounded_cuboid, ... (+48) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 srcube ( D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 srcube ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 srcube ( D size, D round_radius, I round_steps, I ncount )prefix G3 srcube ( D width, D height, D depth, D round_radius, I round_steps )prefix G3 srcube ( D width, D height, D depth, D round_radius, I round_steps, I xcount, I ycount, I zcount )prefix G3 srcube ( D x, D y, D z, D width, D height, D depth, D round_radius, I round_steps, I xcount, I ycount, I zcount )Input Arguments:•
D size :
default = 1 : the uniform scale factor applied to the srcube - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D x :
default = -0.5 * width : the bounding-box minimum x-coordinate position of the srcube.•
D y :
default = -0.5 * height : the bounding-box minimum y-coordinate position of the srcube.•
D z :
default = -0.5 * depth : the bounding-box minimum z-coordinate position of the srcube.•
D width :
default = 1 : the x-axis extent of the srcube - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D height :
default = 1 : the y-axis extent of the srcube - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D depth :
default = 1 : the z-axis extent of the srcube - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the corners and edges of the srcube - a non-zero positive decimal which should be less than half of the minimum of the srcube's width, height, depth or uniform size factor.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of discretisation steps used to round the corners and edges of the srcube - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I ncount :
default = 4 : the uniform number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcube along the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcube along the x-axis (i.e. along the srcube's width) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcube along the y-axis (i.e. along the srcube's height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I zcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcube along the z-axis (i.e. along the srcube's depth) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ width, height, depth, size, round_radius ] > 0
→ [ round_steps, ncount, xcount, ycount, zcount ] >= 1
→ [ width, height, depth, size ] > ( round_radius * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( ( xcount + 1 ) * ( ycount + 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( xcount + 1 ) * ( zcount + 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * ( zcount + 1 ) * 2 ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * ( xcount + 1 + ycount + 1 + zcount + 1 ) * 4 ) + ( ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * round_steps + 1 ) * 8 )Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( xcount * ycount * 2 ) + ( xcount * zcount * 2 ) + ( ycount * zcount * 2 ) + ( round_steps * ( xcount + ycount + zcount ) * 4 ) + ( round_steps * round_steps * 8 )Practical Examples:return srcube();
// returns the default zero-argument unit srcube
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]+
[ cube | box_3D | cuboid ] S-R-CONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Rounded-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided rounded (smooth-edged) conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_r_cone, s_rnd_cone, s_round_cone, s_rounded_cone, sd_r_cone, sd_rnd_cone, sd_round_cone, sd_rounded_cone, subd_r_cone, subd_rnd_cone, subd_round_cone, subd_rounded_cone, ... (+8) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 srcone ( D radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the srcone - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the srcone - (i.e. its height along the y-axis - or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or number of circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the circular edge of the srcone - a non-zero positive decimal which should be less than both the srcone's radius and length.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of discretisation steps used to round the circle edge of the srcone - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcone along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, round_radius ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ round_steps, xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ [ radius, length ] > round_radius
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments ) + ( ycount * segments ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( ( xcount - 1 ) + ycount + round_steps ) * segments ) + 1Practical Examples:return srcone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit srcone
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ r | rnd | round | rounded ] S-R-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Rounded-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided rounded (smooth-edged) cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_r_cylinder, s_rnd_cylinder, s_round_cylinder, s_rounded_cylinder, sd_r_cylinder, sd_rnd_cylinder, sd_round_cylinder, sd_rounded_cylinder, subd_r_cylinder, subd_rnd_cylinder, subd_round_cylinder, subd_rounded_cylinder, ... (+8) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 srcylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the srcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the srcylinder - (i.e. its height along the y-axis - or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or number of circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the circular edges of the srcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal which should be less than the srcylinder's radius and less than half of the srcylinder's length.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of discretisation steps used to round the circular edges of the srcylinder - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcylinder along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base and top) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcylinder along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, round_radius ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ round_steps, xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ radius > round_radius
→ length > ( round_radius * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments * 2 ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * segments * 2 ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( ( xcount - 1 ) * 2 ) + ycount + ( round_steps * 2 ) ) * segments + 2Practical Examples:return srcylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit srcylinder
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ r | rnd | round | rounded ] S-R-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Rounded-Cylicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided rounded (smooth-edged) conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_r_cylicone, s_rnd_cylicone, s_round_cylicone, s_rounded_cylicone, sd_r_cylicone, sd_rnd_cylicone, sd_round_cylicone, sd_rounded_cylicone, subd_r_cylicone, subd_rnd_cylicone, subd_round_cylicone, subd_rounded_cylicone, ... (+8) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 srcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps, I lower_xcount, I upper_xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the srcylicone - a positive decimal greater than zero and greater than the rounding radius.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the top of the srcylicone - a positive decimal greater than zero and greater than the rounding radius.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the srcylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the circular edges of the srcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal which should be less than the srcylicone's lower and upper radii and less than half of the srcylicone's length.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of discretisation steps used to round the circular edges of the srcylicone - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I lower_xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcylicone along the x-axis at its lower circular edge - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I upper_xcount :
default = 2 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcylicone along the x-axis at its upper circular edge - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srcylicone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ length, round_radius ] > 0
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] >= 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ round_steps, lower_xcount, upper_xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] > round_radius
→ length > ( round_radius * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals, N-gons: where N = segments ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( lower_xcount * segments ) + ( upper_xcount * segments ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * segments * 2 ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( lower_xcount - 1 ) + ( upper_xcount - 1 ) + ycount + ( round_steps * 2 ) ) * segments + 2Practical Examples:return srcylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit srcylicone
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ r | rnd | round | rounded ] S-B-P-CONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Beveled-Polar-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided beveled (chamfered-edge) polar conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_b_p_cone, s_b_polar_cone, s_b_pole_cone, s_b_polar_point_cone, s_bevel_p_cone, s_bevel_polar_cone, s_bevel_pole_cone, s_bevel_polar_point_cone, s_beveled_p_cone, s_beveled_polar_cone, s_beveled_pole_cone, s_beveled_polar_point_cone, ... (+108) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 sbpcone ( D radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance, I bcount, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the sbpcone - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the sbpcone (i.e. its height along the y-axis - or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or number of circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the sbpcone - a non-zero positive decimal which must be less than the sbpcone's radius and less than the sbpcone's length.•
I bcount :
default = 1 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbpcone's beveled region - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbpcone along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions apploed to the sbpcone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ bcount, xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ [ radius, length ] > bevel_distance
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments ) + ( ycount * segments ) + ( ( bcount + 1 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( xcount + ycount + bcount ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return sbpcone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit sbpcone
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] S-B-P-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Beveled-Polar-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided beveled (chamfered-edge) polar cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_b_p_cylinder, s_b_polar_cylinder, s_b_pole_cylinder, s_b_polar_point_cylinder, s_bevel_p_cylinder, s_bevel_polar_cylinder, s_bevel_pole_cylinder, s_bevel_polar_point_cylinder, s_beveled_p_cylinder, s_beveled_polar_cylinder, s_beveled_pole_cylinder, s_beveled_polar_point_cylinder, ... (+108) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 sbpcylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance, I bcount, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the sbpcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the sbpcylinder (i.e. its height along the y-axis - or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or number of circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perdandicular chamfer of bevel length) applied to the sbpcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal which must be less than the sbpcylinder's radius and less than half of the sbpcylinder's length.•
I bcount :
default = 1 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbpcylinder's beveled regions - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbpcylinder along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base and top) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbyclinder along the y-axis (i.e. along its length pr vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ bcount, xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ radius > bevel_distance
→ length > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments * 2 ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + ( ( bcount + 1 ) * segments * 2 ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( xcount * 2 ) + ycount + ( bcount * 2 ) ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return sbpcylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit sbpcylinder
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] S-B-P-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Beveled-Polar-Cylicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided beveled (chamfered-edge) polar conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_b_p_cylicone, s_b_polar_cylicone, s_b_pole_cylicone, s_b_polar_point_cylicone, s_bevel_p_cylicone, s_bevel_polar_cylicone, s_bevel_pole_cylicone, s_bevel_polar_point_cylicone, s_beveled_p_cylicone, s_beveled_polar_cylicone, s_beveled_pole_cylicone, s_beveled_polar_point_cylicone, ... (+108) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 sbpcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments, D bevel_distance, I bcount, I lower_xcount, I upper_xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the sbpcylicone - a positive decimal greater than zero and greater than the beveling distance.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the top of the sbpcylicone - a positive decimal greater than zero and greater than the beveling distance.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the sbpcylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D bevel_distance :
default = 0.125 : the projective-inset distance (i.e. the perpandicular chamfer or bevel length) applied to the sbpcylicone (both its lower and upper circular edges) - a non-zero positive decimal number - which must be less than the sbpcylicone's lower and upper radii and less than half of the sbpcylicone's length.•
I bcount :
default = 1 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbpcylicone's beveled regions - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I lower_xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbpcylicone along the x-axis at its lower circular edge - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I upper_xcount :
default = 2 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbpcylicone along the x-axis at its upper circular edge - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the sbpcylicone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ length, bevel_distance ] > 0
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] >= 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ bcount, lower_xcount, upper_xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] > bevel_distance
→ length > ( bevel_distance * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( lower_xcount * segments ) + ( upper_xcount * segments ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + ( ( bcount + 1 ) * segments * 2 ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( lower_xcount + upper_xcount + ycount + ( bcount * 2 ) ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return sbpcylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit sbpcylicone
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ b | bevel | beveled | bevelled | chamfer | chamfered ]+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] S-R-P-CONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Rounded-Polar-Cone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided rounded (smooth-edged) polar conic solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_r_p_cone, s_r_polar_cone, s_r_pole_cone, s_r_polar_point_cone, s_rnd_p_cone, s_rnd_polar_cone, s_rnd_pole_cone, s_rnd_polar_point_cone, s_round_p_cone, s_round_polar_cone, s_round_pole_cone, s_round_polar_point_cone, ... (+68) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 srpcone ( D radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the srpcone - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the srpcone - (i.e. its height along the y-axis - or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or number of circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the circular edge of the srpcone - a non-zero positive decimal which should be less than both the srpcone's radius and length.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of discretisation steps used to round the circle edge of the srpcone - a positive whole number greater than or equal to 1.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srpcone along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srpcone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, round_radius ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ round_steps, xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ [ radius, length ] > round_radius
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments ) + ( ycount * segments ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * segments ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( xcount + ycount + round_steps ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return srpcone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit srpcone
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] S-R-P-CYLINDER : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Rounded-Polar-Cylinder
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided rounded (smooth-edge) polar cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_r_p_cylinder, s_r_polar_cylinder, s_r_pole_cylinder, s_r_polar_point_cylinder, s_rnd_p_cylinder, s_rnd_polar_cylinder, s_rnd_pole_cylinder, s_rnd_polar_point_cylinder, s_round_p_cylinder, s_round_polar_cylinder, s_round_pole_cylinder, s_round_polar_point_cylinder, ... (+68) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 srpcylinder ( D radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps, I xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius of the srpcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the srpcylinder - (i.e. its height along the y-axis - or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or number of circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the circular edges of the srpcylinder - a non-zero positive decimal which should be less than the srpcylinder's radius and less than half of the srpcylinder's length.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of discretisation steps used to round the circular edges of the srpcylinder - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srpcylinder along the x-axis (i.e. along the radius at its circular base and top) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srpcylinder along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ radius, length, round_radius ] > 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ round_steps, xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ radius > round_radius
→ length > ( round_radius * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( xcount * segments * 2 ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * segments * 2 ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( ( xcount * 2 ) + ycount + ( round_steps * 2 ) ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return srpcylinder();
// returns the default zero-argument unit srpcylinder
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] S-R-P-CYLICONE : Generate 3D Sub-Divided-Rounded-Polar-Cylicone
→ 'instantiates a 3D bi-linearly sub-divided rounded (smooth-edge) polar conic-cylindrical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { s_r_p_cylicone, s_r_polar_cylicone, s_r_pole_cylicone, s_r_polar_point_cylicone, s_rnd_p_cylicone, s_rnd_polar_cylicone, s_rnd_pole_cylicone, s_rnd_polar_point_cylicone, s_round_p_cylicone, s_round_polar_cylicone, s_round_pole_cylicone, s_round_polar_point_cylicone, ... (+68) };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 srpcylicone ( D lower_radius, D upper_radius, D length, I segments, D round_radius, I round_steps, I lower_xcount, I upper_xcount, I ycount )Input Arguments:•
D lower_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the base of the srpcylicone - a positive decimal greater than zero and greater than the rounding radius.•
D upper_radius :
default = 0.5 : the radius at the top of the srpcylicone - a positive decimal greater than zero and greater than the rounding radius.•
D length :
default = 1 : the length of the srpcylicone (i.e. its height along the y-axis or its vertical extent) - a non-zero positive decimal number.•
I segments :
default = 32 : the number of longitudinal segments (i.e. the discretisation resolution or the number of circular steps) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 3.•
D round_radius :
default = 0.125 : the radius applied to round the circular edges of the srpcylicone - a non-zero positive decimal which should be less than the srpcylicone's lower and upper radii and less than half of the srpcylicone's length.•
I round_steps :
default = 8 : the number of discretisation steps used to round the circular edges of the srpcylicone - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I lower_xcount :
default = 4 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srpcylicone along the x-axis at its lower circular edge - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I upper_xcount :
default = 2 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srpcylicone along the x-axis at its upper circular edge - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.•
I ycount :
default = 8 : the number of sub-division partitions applied to the srpcylicone along the y-axis (i.e. along its length or vertical height) - a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.→ [ length, round_radius ] > 0
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] >= 0
→ segments >= 3
→ [ round_steps, lower_xcount, upper_xcount, ycount ] >= 1
→ [ lower_radius, upper_radius ] > round_radius
→ length > ( round_radius * 2 )
Topology Types:→ [ triangles, quadrilaterals ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ( lower_xcount * segments ) + ( upper_xcount * segments ) + ( ( ycount + 1 ) * segments ) + ( ( round_steps + 1 ) * segments * 2 ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = ( lower_xcount + upper_xcount + ycount + ( bcount * 2 ) ) * segmentsPractical Examples:return srpcylicone();
// returns the default zero-argument unit srpcylicone
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ s | sd | subd | sub_divide | sub_divided ]
+
[ r | rnd | round | rounded ]+
[ p | polar | pole | polar_point ] ICOSPHERE : Generate 3D Icosahedral-Sphere
→ 'instantiates a 3D icosahedron-derived sub-divided spherical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { icosphere, icosahedral_sphere };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 icosphere ( D diameter, I sub_division_iterations )prefix G3 icosphere ( D diameter, I sub_division_iterations, I geodesic )Input Arguments:•
D diameter :
default = 1.0 : the diameter of the icosphere - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I sub_division_iterations :
default = 1 : the number of sub-division-iterations applied to the base icosahedron in order to form the icosphere.•
I geodesic :
default = 1 : the geodesic/geodetic configuration applied to the icosphere - an integer flag of either 0 or 1 - where 1 is used to signal standard/true geodesic behaviour and 0 denotes non-standard/pseudo geodesic behaviour.→ diameter > 0
→ sub_division_iterations > 0
→ geodesic == [ 0 | 1 ]
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 10 * ( 4 ^ sub_division_iterations ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = 20 * ( 4 ^ sub_division_iterations )Practical Examples:return icosphere();
// returns the default zero-argument unit icosphere
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ ico | icosahedral ]
Additional Notes:•
The icosphere supports disabling true geodesic spherical-projection behaviour (for example - for aesthetic reasons such as to reduce the variance between minimum and maximum polyhedral element-size) - by setting the geodesic configuration argument to zero (0). OCTASPHERE : Generate 3D Octahedral-Sphere
→ 'instantiates a 3D octahedron-derived sub-divided spherical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { octasphere, octahedral_sphere };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 octasphere ( D diameter, I sub_division_iterations )prefix G3 octasphere ( D diameter, I sub_division_iterations, I geodesic )Input Arguments:•
D diameter :
default = 1.0 : the diameter of the octasphere - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I sub_division_iterations :
default = 1 : the number of sub-division-iterations applied to the base octahedron in order to form the octasphere.•
I geodesic :
default = 1 : the geodesic/geodetic configuration applied to the octasphere - an integer flag of either 0 or 1 - where 1 is used to signal standard/true geodesic behaviour and 0 denotes non-standard/pseudo geodesic behaviour.→ diameter > 0
→ sub_division_iterations > 0
→ geodesic == [ 0 | 1 ]
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 4 * ( 4 ^ sub_division_iterations ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = 8 * ( 4 ^ sub_division_iterations )Practical Examples:return octasphere();
// returns the default zero-argument unit octasphere
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ octa | octahedral ]
Additional Notes:•
The octasphere supports disabling true geodesic spherical-projection behaviour (for example - for aesthetic reasons such as to reduce the variance between minimum and maximum polyhedral element-size) - by setting the geodesic configuration argument to zero (0). TETRASPHERE : Generate 3D Tetrahedral-Sphere
→ 'instantiates a 3D tetrahedron-derived sub-divided spherical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { tetrasphere, tetrahedral_sphere };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 tetrasphere ( D diameter, I sub_division_iterations )prefix G3 tetrasphere ( D diameter, I sub_division_iterations, I geodesic )Input Arguments:•
D diameter :
default = 1.0 : the diameter of the tetrasphere - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I sub_division_iterations :
default = 1 : the number of sub-division-iterations applied to the base tetrahedron in order to form the tetrasphere.•
I geodesic :
default = 1 : the geodesic/geodetic configuration applied to the tetrasphere - an integer flag of either 0 or 1 - where 1 is used to signal standard/true geodesic behaviour and 0 denotes non-standard/pseudo geodesic behaviour.→ diameter > 0
→ sub_division_iterations > 0
→ geodesic == [ 0 | 1 ]
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = 2 * ( 4 ^ sub_division_iterations ) + 2Polygon Count:→ |P| = 4 * ( 4 ^ sub_division_iterations )Practical Examples:return tetrasphere();
// returns the default zero-argument unit tetrasphere
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ tetra | tetrahedral ]
Additional Notes:•
The tetrasphere supports disabling true geodesic spherical-projection behaviour (for example - for aesthetic reasons such as to reduce the variance between minimum and maximum polyhedral element-size) - by setting the geodesic configuration argument to zero (0). GEOSPHERE : Generate 3D Geodesic-Sphere
→ 'instantiates a 3D generalised platonic-primitive-derived frequency-based (i.e. an incrementally refined regular-polyhedron) geodesic (or geodetic) spherical solid centered at the origin (0,0,0)'
Classification:→ { instantiative, convex };
Alias & Synonyms:→ { geosphere, geodesic_sphere, geodetic_sphere };
Invocation Options:prefix G3 geosphere ( C type_key, D diameter, I frequency )prefix G3 geosphere ( C type_key, D diameter, I frequency, I project, I manifold )Input Arguments:•
C type_key :
default = 'I' : the class of regular platonic primitive used as the basis for geo-sphere construction - represented as a symbolic type-key which corresponds to the initial character of each platonics' formal name - such that the characters 'I','O','T','H', and 'D' denote (respectively): icosahedra, octahedra, tetrahedra, hexahedra and dodecahedra.•
D diameter :
default = 1.0 : the diameter of the geodesic-sphere - a non-zero positive decimal.•
I frequency :
default = 3 : the number of incremental refinement steps applied to the edges of each equilateral triangle (prior to spherical projection) in the base platonic primitive that is used to form the geo-sphere (i.e the refinement frequency for class-1 regular geodesics) - a positive integer greater than zero.•
I project :
default = 1 : the spherical-projection configuration applied to the geodesic-sphere post incremental refinement - an integer flag of either 0 (to indicate no-projection) or 1 (to indicate apply-projection).•
I manifold :
default = 1 : the polyhedral-manifold configuration applied to the geodesic-sphere post incremental refinement - an integer flag of either 0 (to indicate removal of the manifold-mandate) or 1 (to indicate enforcement of the manifold-mandate).→ type_key == [ 'I' | 'O' | 'T' | 'H' | 'D' ]
→ diameter > 0
→ frequency > 0
→ project == [ 0 | 1 ]
→ manifold == [ 0 | 1 ]
Topology Types:→ [ triangles ]Vertex Count:→ |V| = ? [ type_key dependent ] ?Polygon Count:→ |P| = ? [ type_key dependent ] ?Practical Examples:return geosphere();
// returns the default zero-argument unit geosphere
Alias Formation Rule-Sets:[ geo | geodesic | geodetic ]
Additional Notes:•
The geosphere offers a greater level of control over the number and type of polyhedral-elements that are emitted relative to the named counterparts: icosphere, octasphere and tetrasphere. In-particular the geosphere supports construction of hexahedral and dodecahedral geodesics using the type-keys 'H' and 'D' and the construction of odd-parity/odd-frequency partitions alongside even-parity/even-frequency partitions - by virtue of applying the frequency-based division to each platonic in a single pass rather than in an iterative or recursive manner. When coupled with the ability to alter the underlying platonic-primitive dynamically - this renders the geosphere a far more expressive and versatile function when compared to the icosphere, octasphere and tetrasphere. However bear in mind that the geosphere does not expose support for disabling true geodesic spherical-projection behaviour which the aforementioned counterparts each do support.•
The geosphere can also be used to construct manifold and faceted incrementally refined (but not spherically-projected) platonic-primitives by setting the optional 'project' argument to zero (0) and the optional 'manifold' argument to zero (0) or one (1) based on one's desire for (respectively) either a faceted or 2-manifold/smooth-shaded yield. This facility can also be used to coordinate the creation of platonics featuring higher quality triangle elements in a manner that affords granular control over the cardinality of the result.•
For platonics composed of elements other than triangles (i.e. the hexahedron and dodecahedron) the geosphere function applies a preliminary mid-point insertion step followed by a ring triangulation for each regular polygon to facilitate subsequent refinement.